Identify the internal surface features and structures associated with the oral cavity.
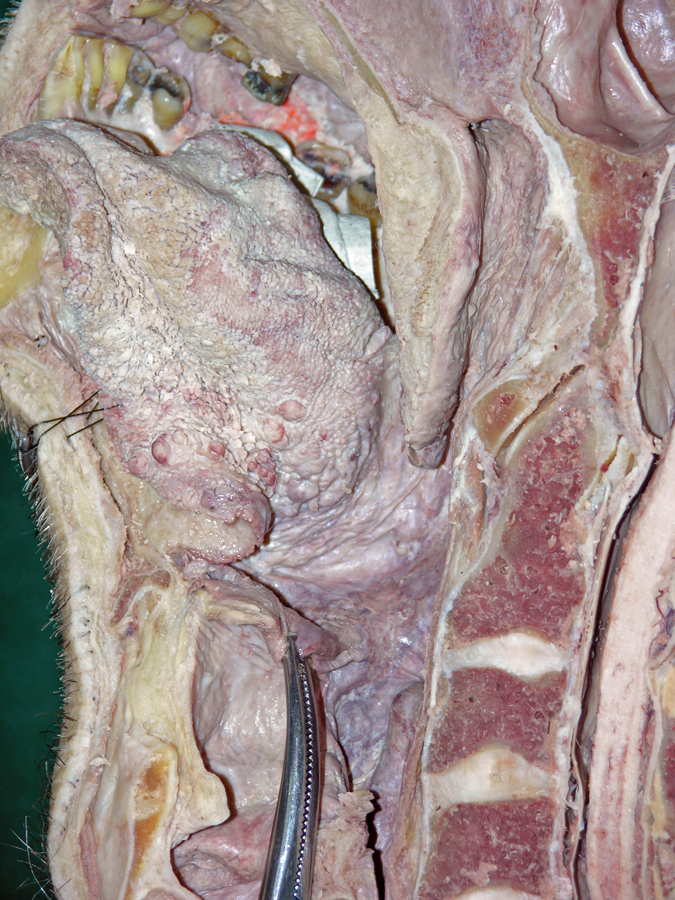
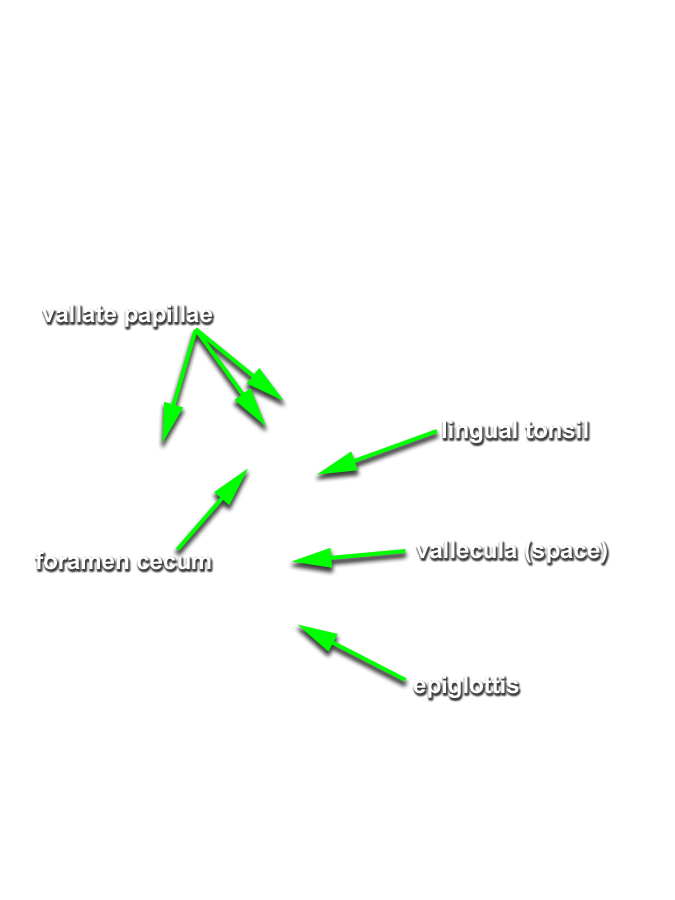
- (ON BOTH SIDES) Identify the tongue, terminal sulcus, foramen cecum, vallate papillae (the white circle at the posterior border of the tongue (not labeled)), and sublingual fold and caruncle. (G 8.29;N 60;Gl 44.18)
-
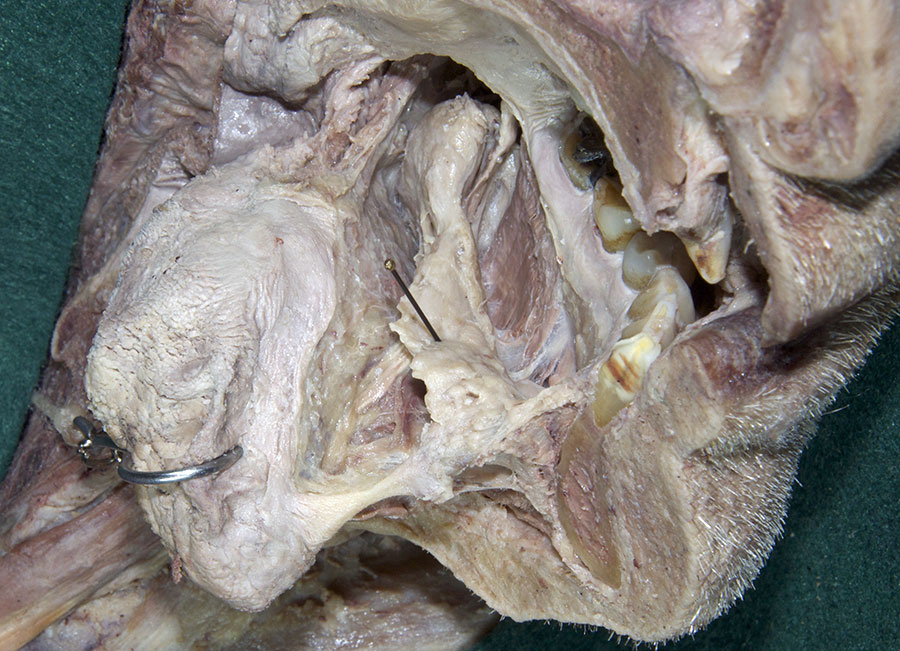
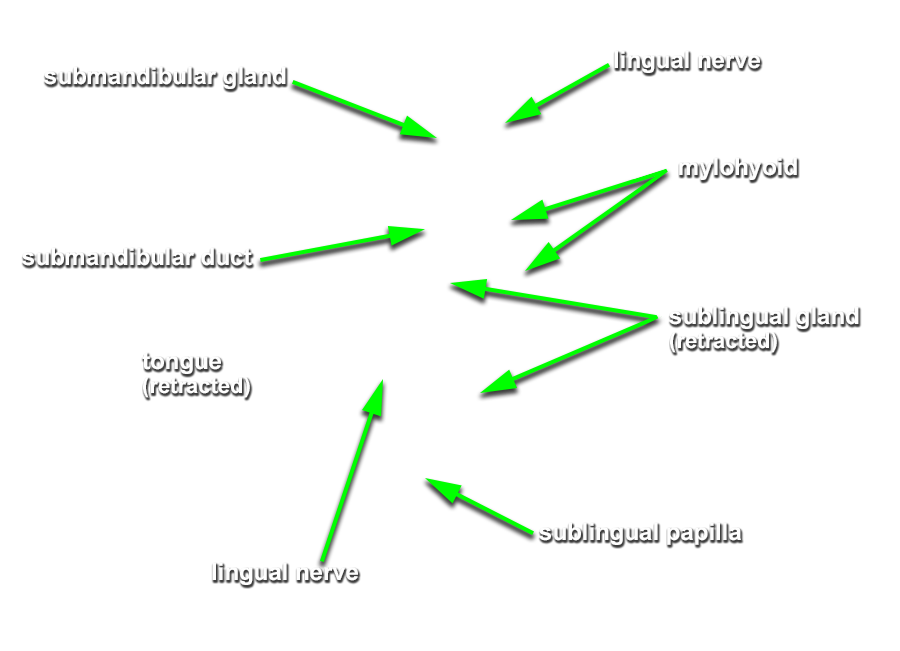
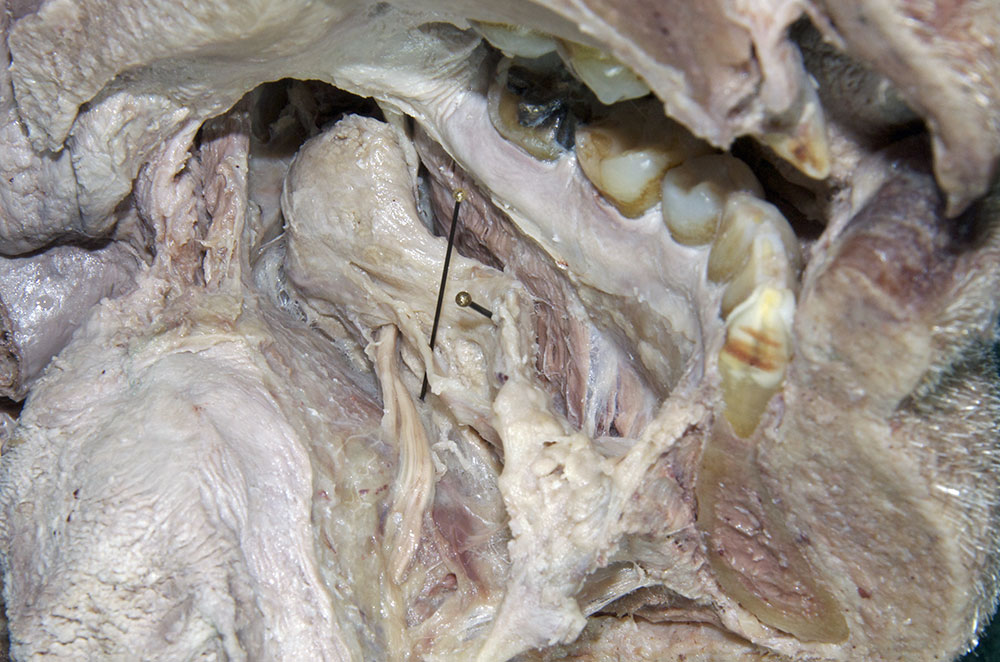
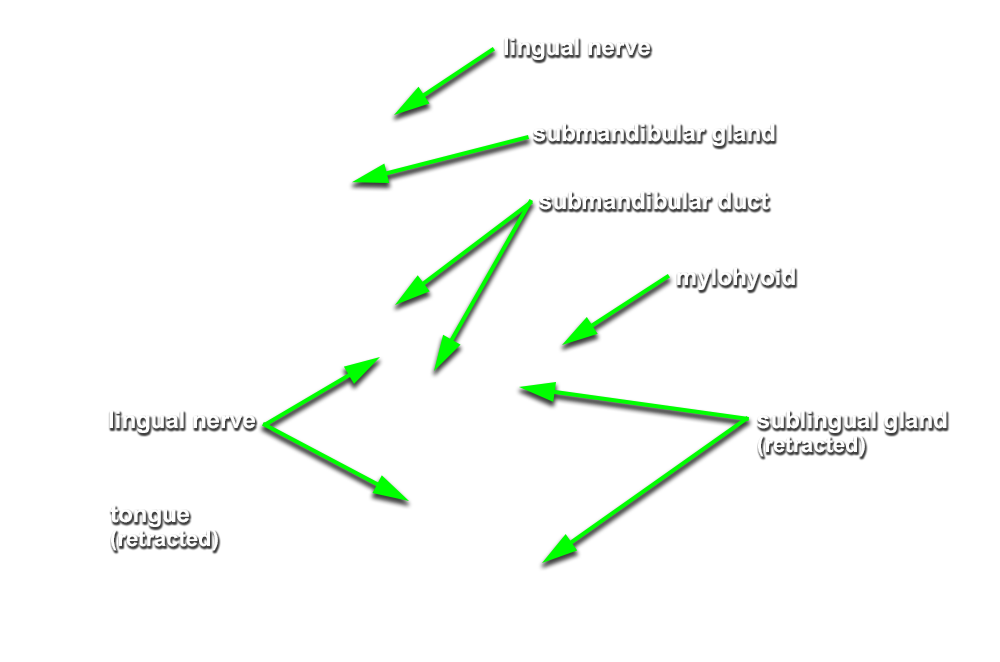
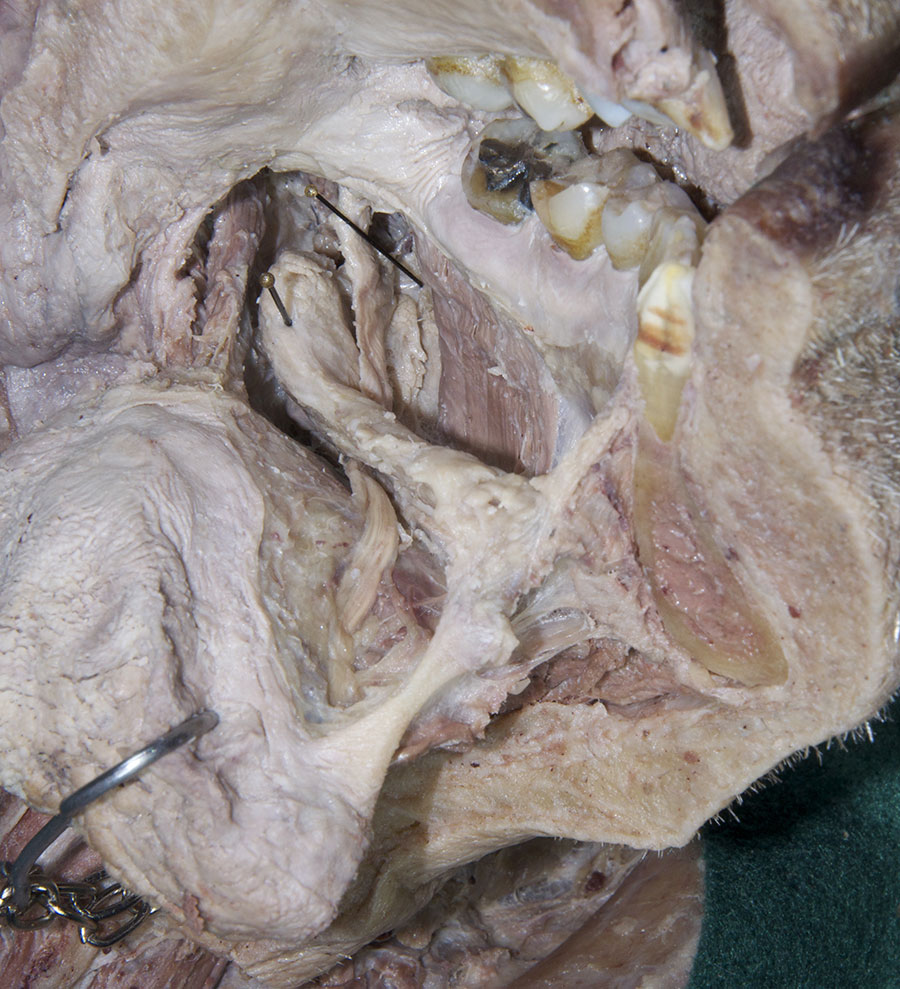
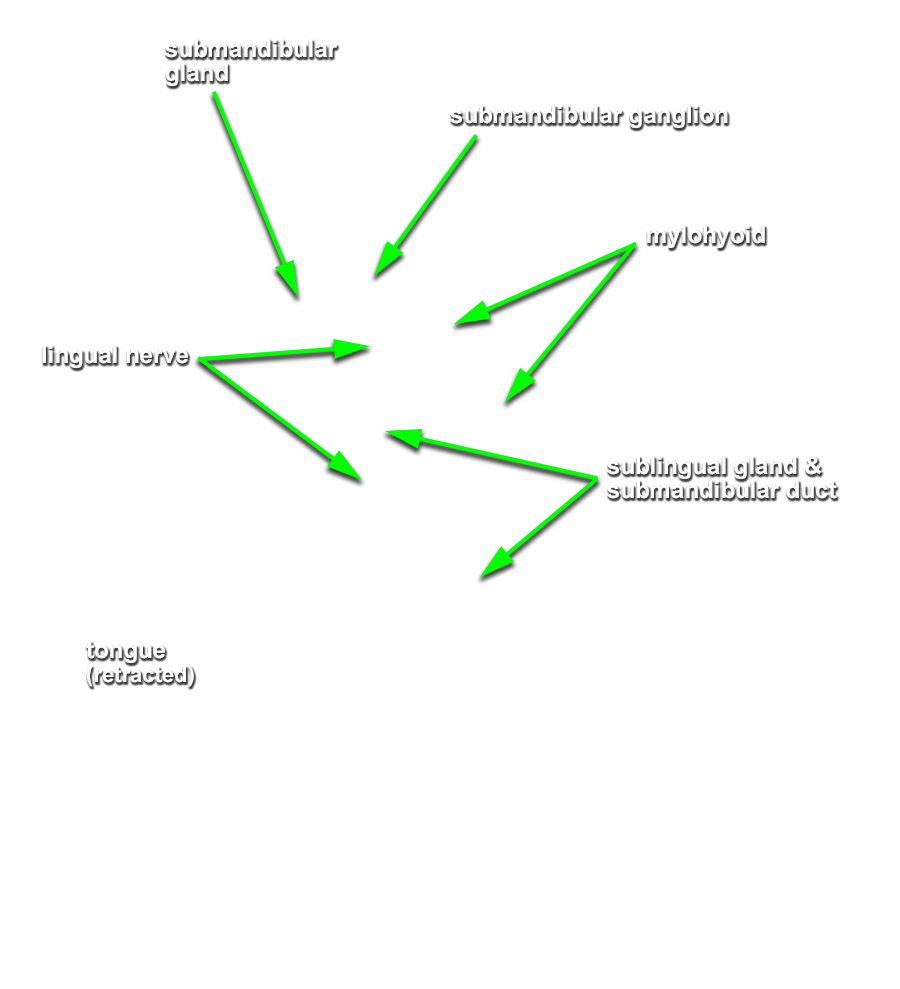
(ON THE LEFT SIDE ONLY) Carefully strip the mucosa from the sublingual fold and posterior-lateral aspect of the oral cavity. Identify and clean the sublingual gland,
submandibular duct and
lingual nerve. (G 8.26B;N 58;Gl 44.25C)
Important Relationship
- The sublingual artery is positioned inferior to the submandibular duct.
- The sublingual gland is positioned superior to the mylohyoid muscle and lateral to the genioglossus muscle.
- The lingual nerve passes medial to the mandible and lateral to the medial pterygoid and styloglossus muscles.
- The lingual nerve passes inferior to the superior constrictor and pterygomandibular raphe.
- The lingual nerve passes lateral, inferior and medial to the submandibular duct.