Identify the structures associated with the prevertebral fascia.
- Identify the
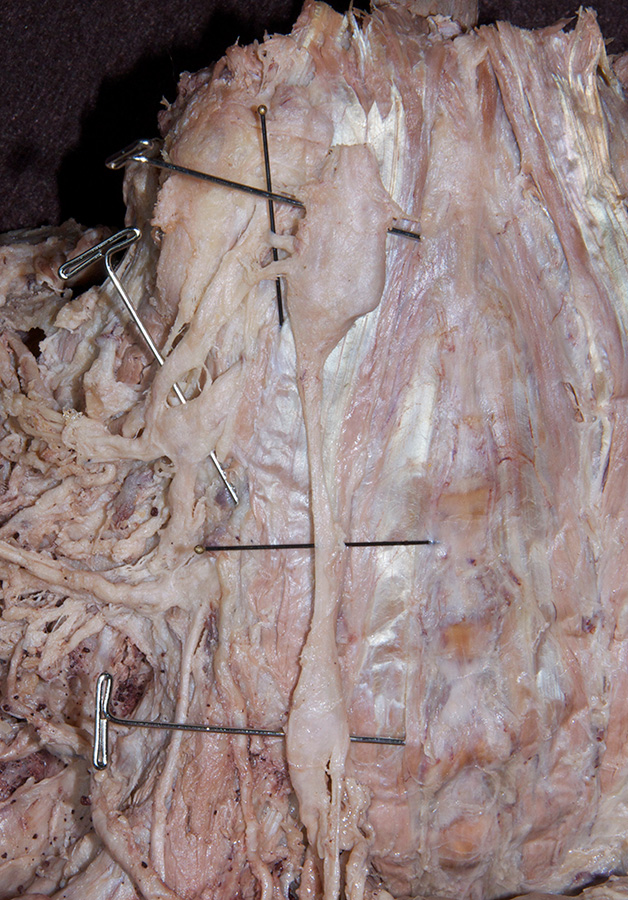
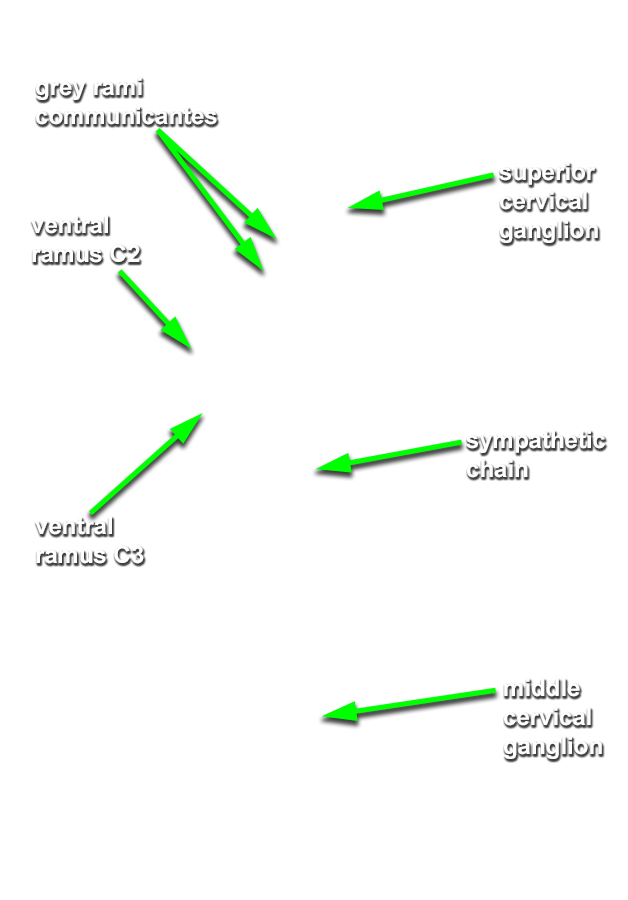
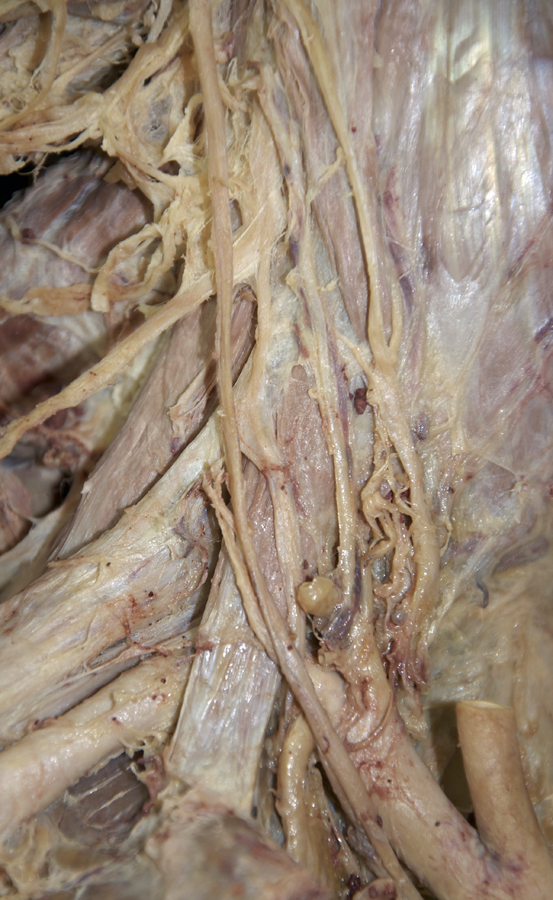
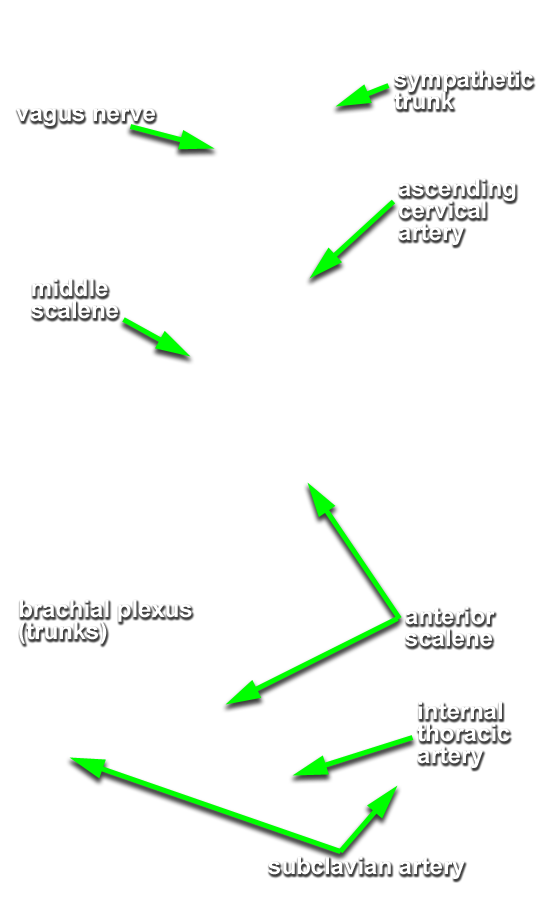
sympathetic trunk posterior to the carotid artery. (G 8.23B;N 131;Gl 44.32) Trace the sympathetic trunk in the superior direction and identify the
superior cervical ganglion. (G 8.23B;N 131;Gl 44.32) Trace the sympathetic trunk in the inferior direction and identify the
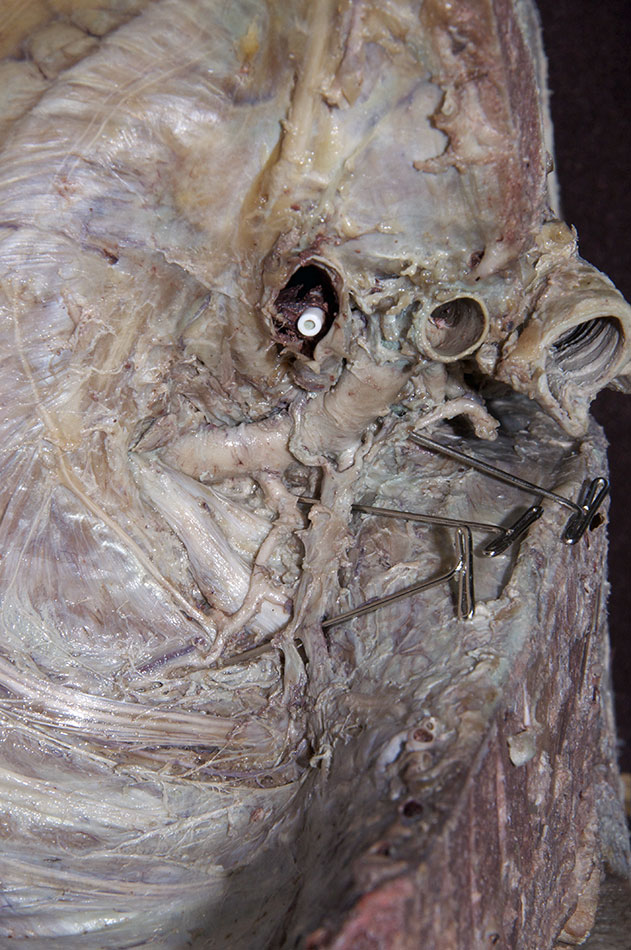
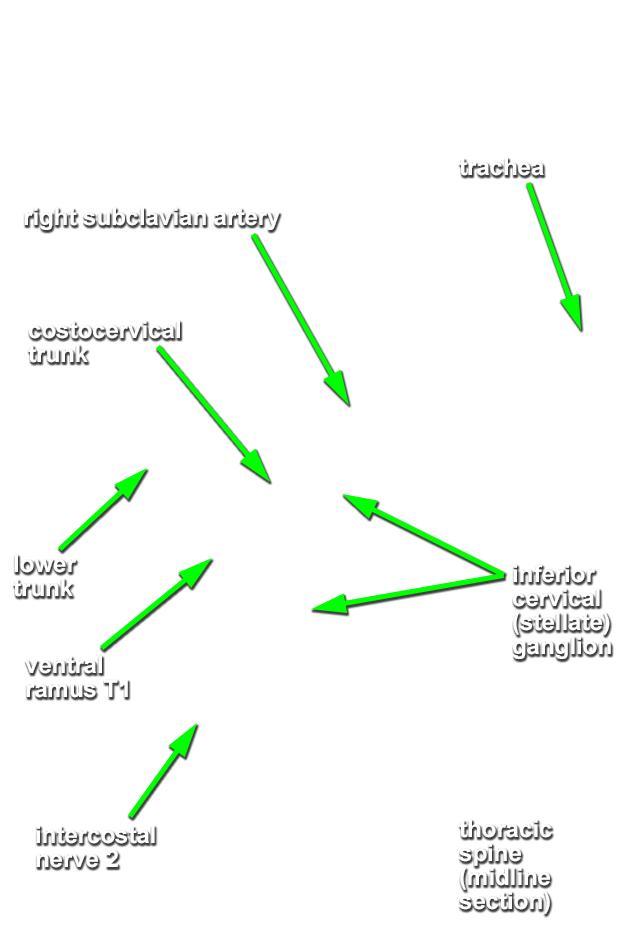
inferior cervical (stellate) ganglion (near the subclavian artery). In some cadavers it is easier to view the inferior cervical ganglion from the inferior (thoracic) direction, especially when it fuses with the T1 sympathetic ganglion forming a stellate ganglion. (G 8.24;N 131;Gl 44.32)
Important Relationships
- The sympathetic trunk is positioned directly anterior to the prevertebral muscles and directly posterior to the carotid sheath.
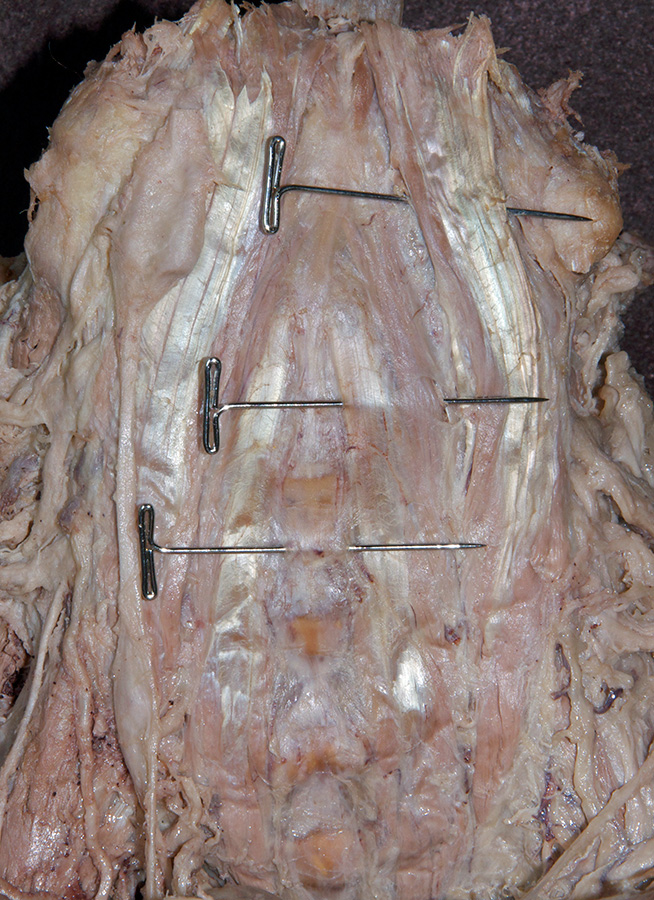
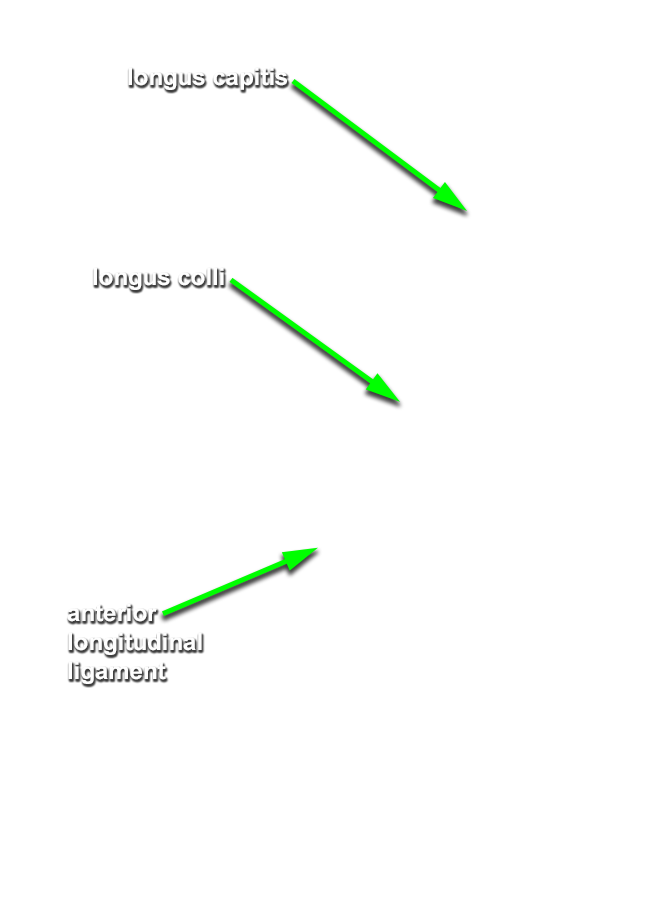
- Identify the anterior longitudinal ligament, longus colli muscle and longus capitis muscle. (G 8.23A;N 30 and 22;Gl 2.28 and 45.7B)
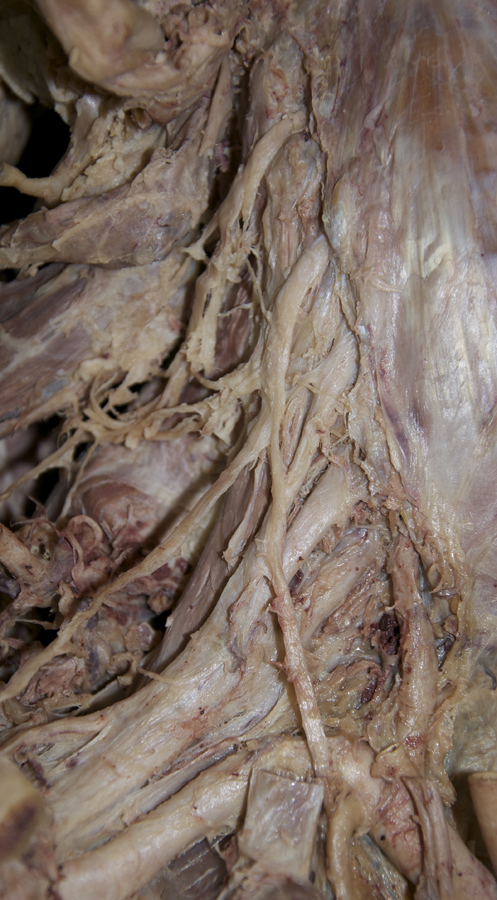
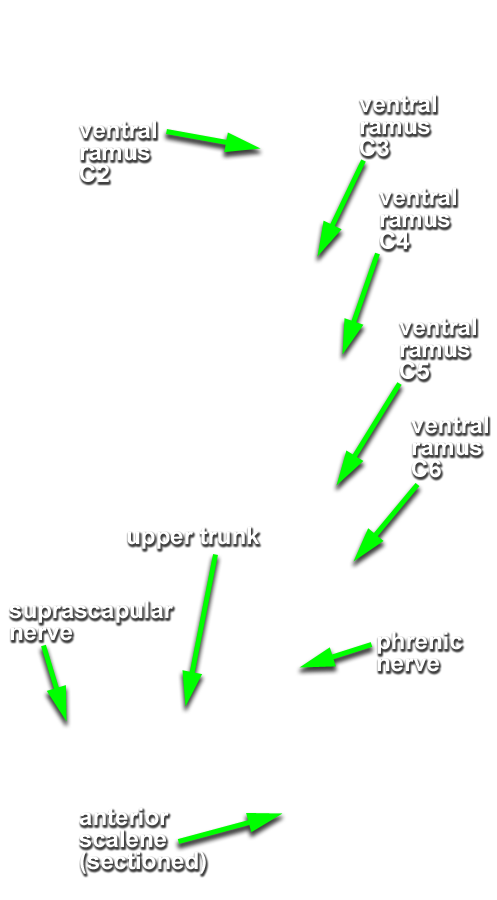
- Identify anterior (ventral) rami C3-C6 between the anterior and middle scalene muscles. (G 8.23B;N 71;Gl 45.15) Trace the suprascapular nerve back to the upper trunk to identify ventral ramus C5. Likewise, trace the great auricular nerve back to ventral ramus (C2 &) C3. Attempt to identify gray rami passing from the sympathetic trunk to the anterior rami. (G 8.24;N 131)
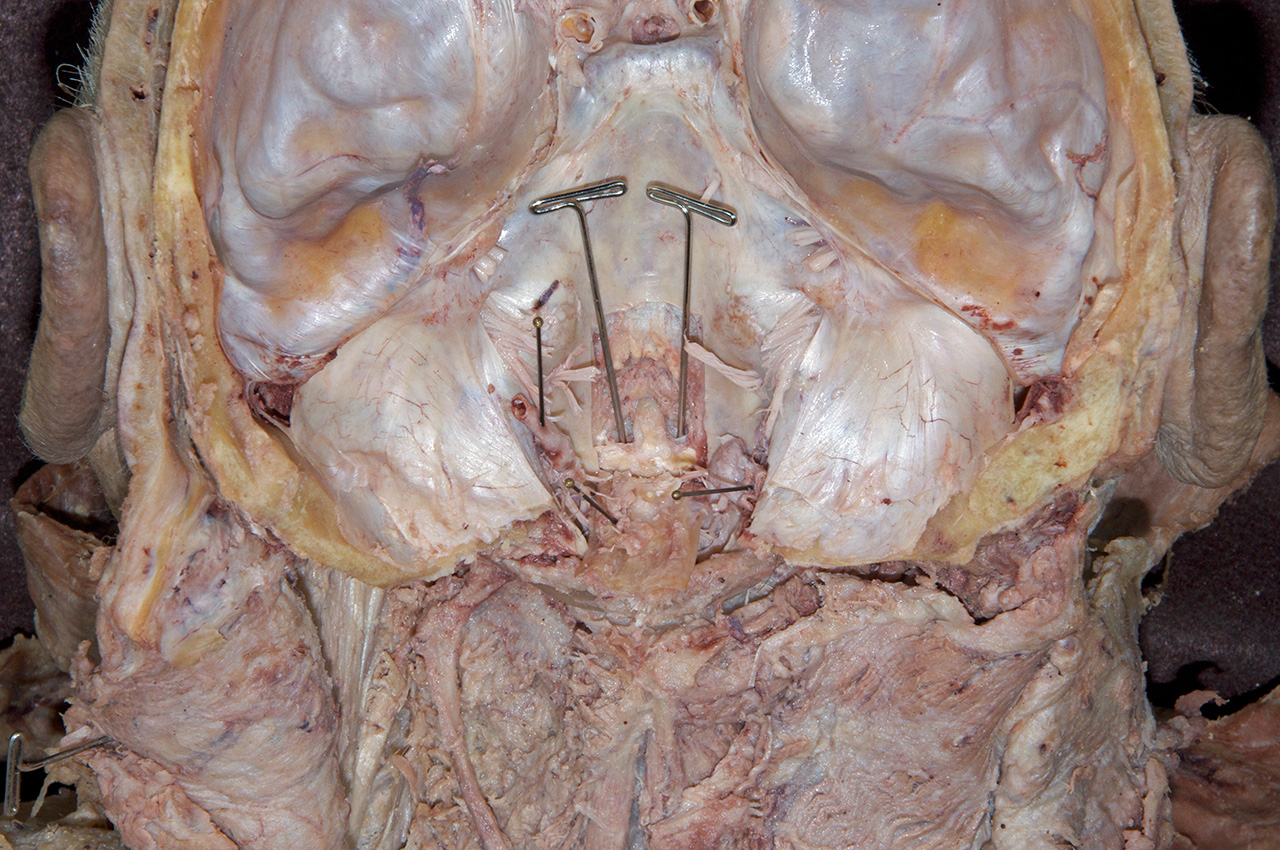
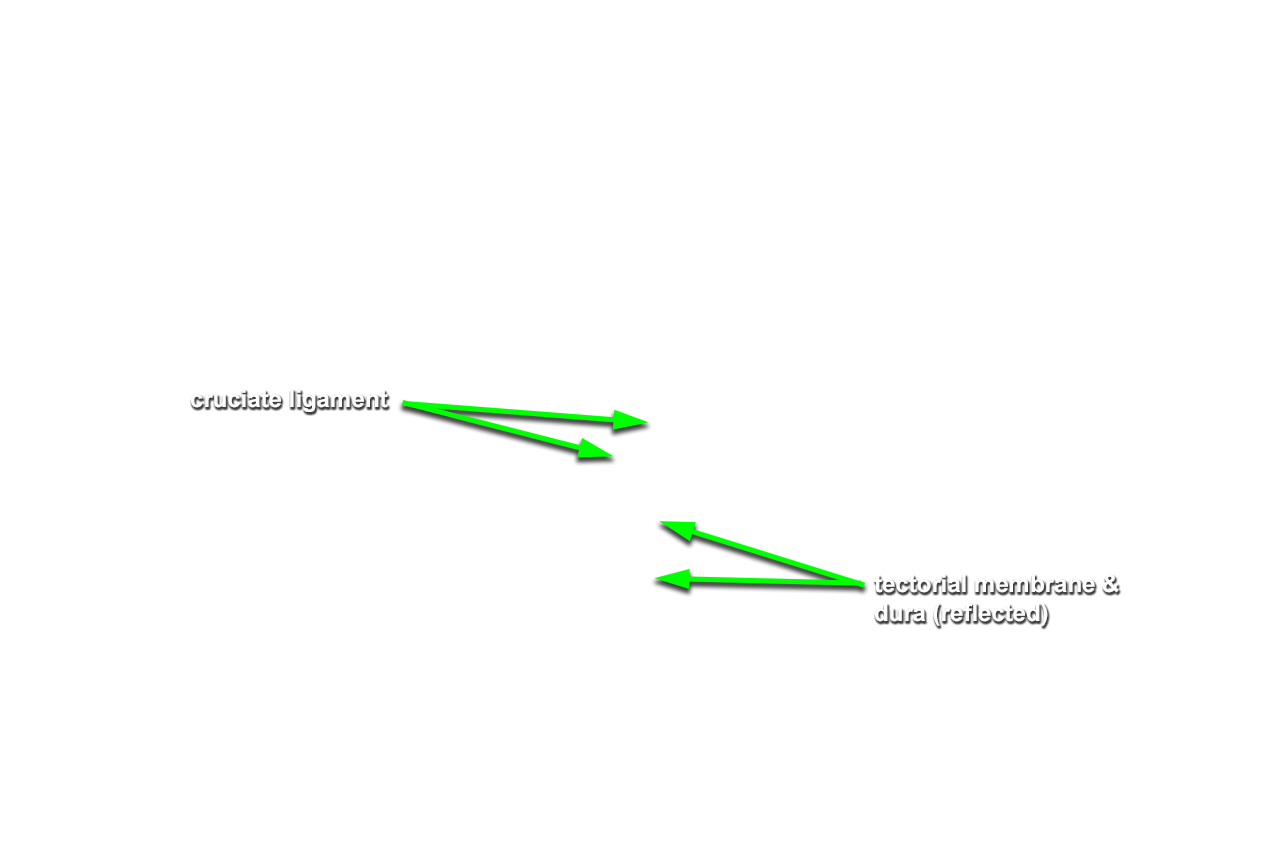
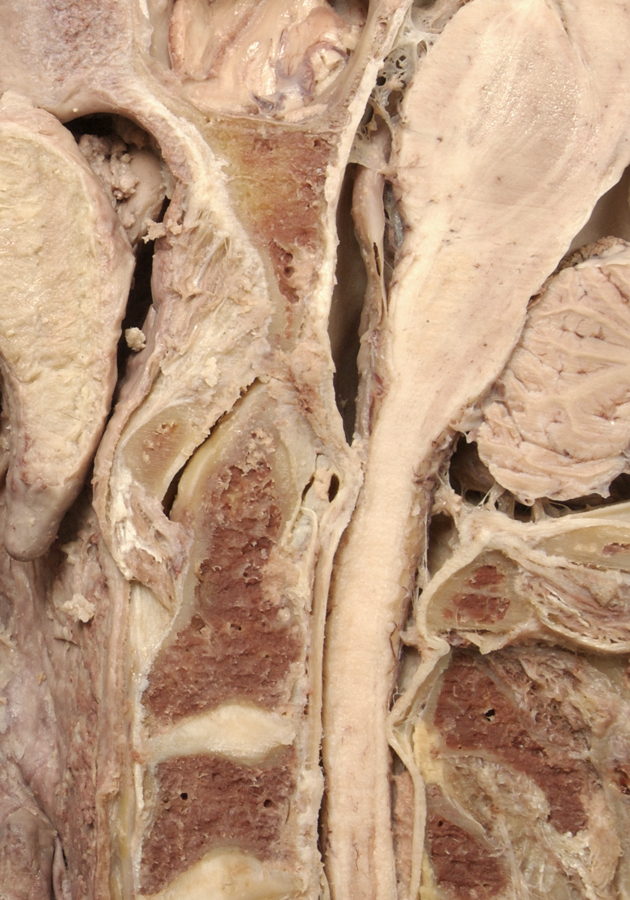
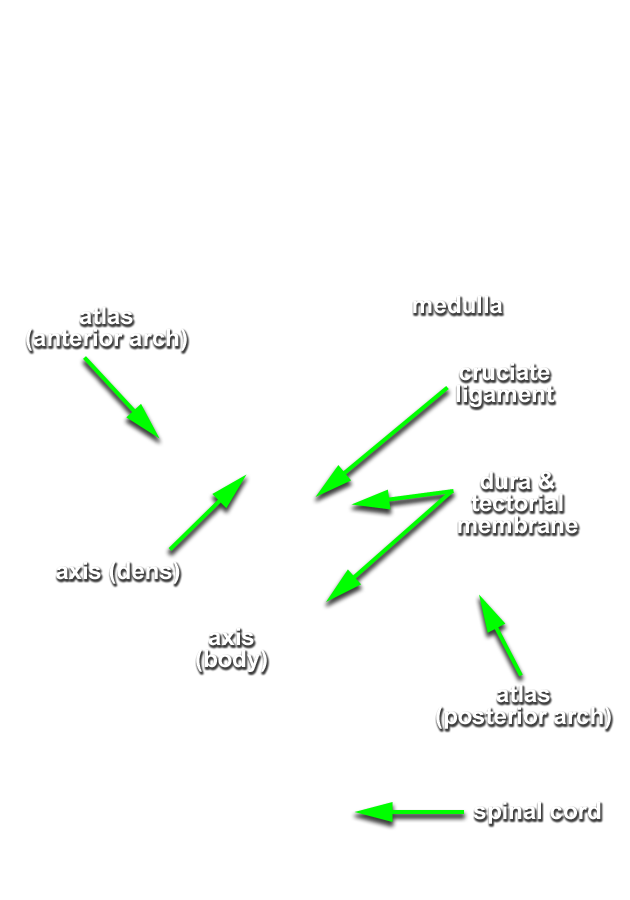
- Reflect the dura and identify the anterior arch of the atlas, the dens of the axis, the transverse (cruciate) ligament, and the tectorial membrane. (G 1.11; N 23; Gl 2.23 ) If possible, displace the dens and attempt to identify the alar ligament.