Identify the internal surface features and structures associated with the laryngeal pharynx and larynx.
- Identify the
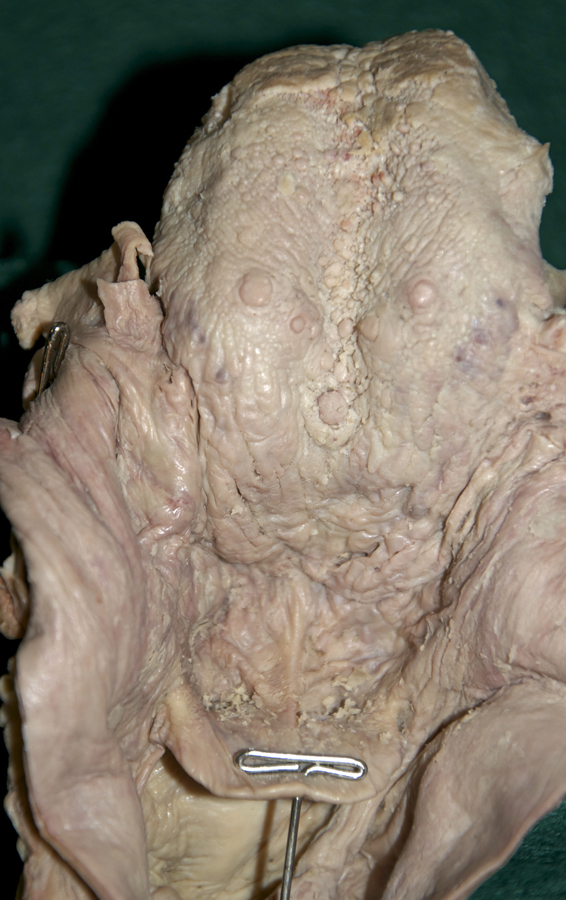
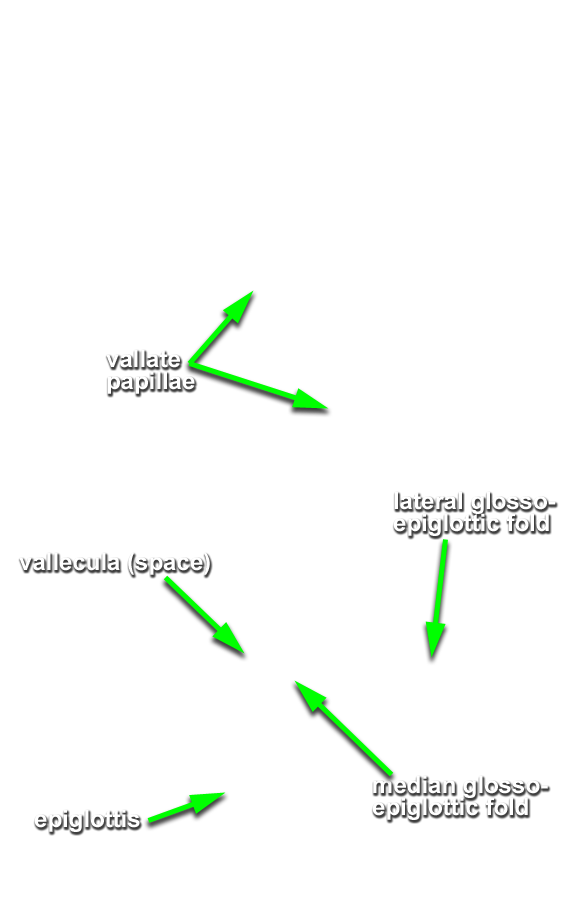
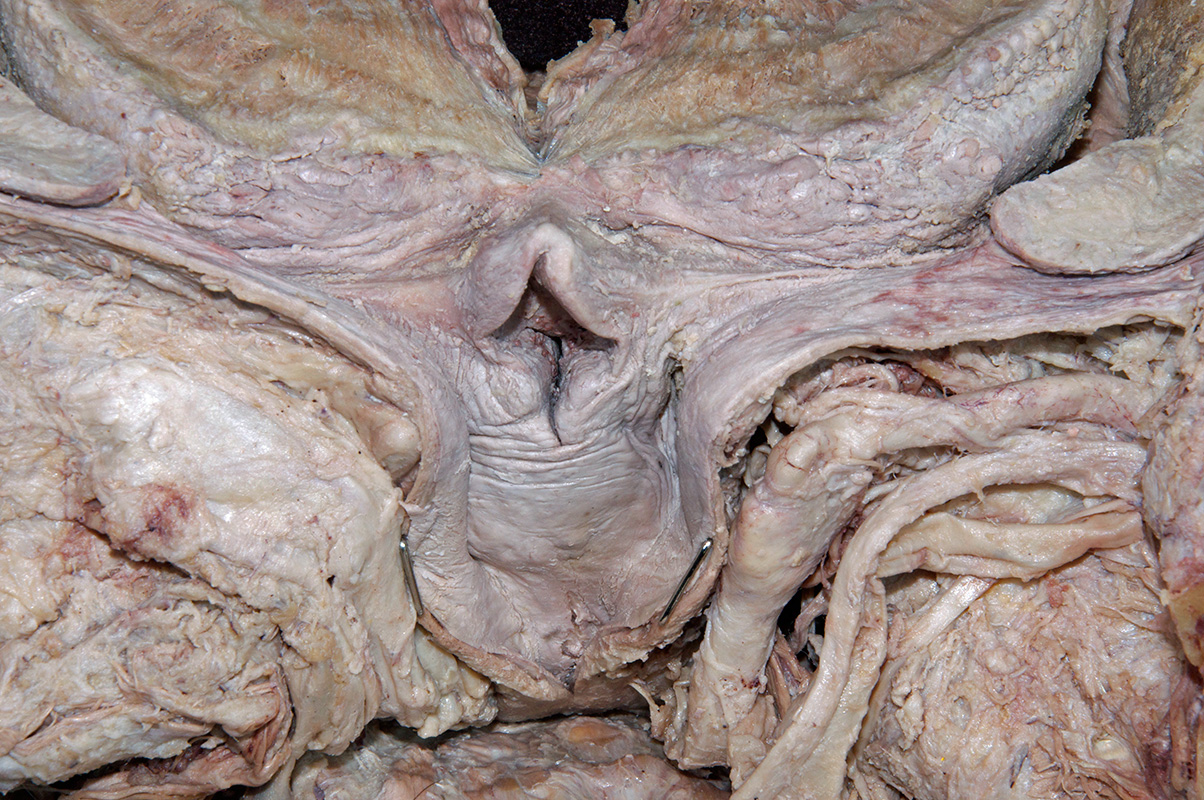
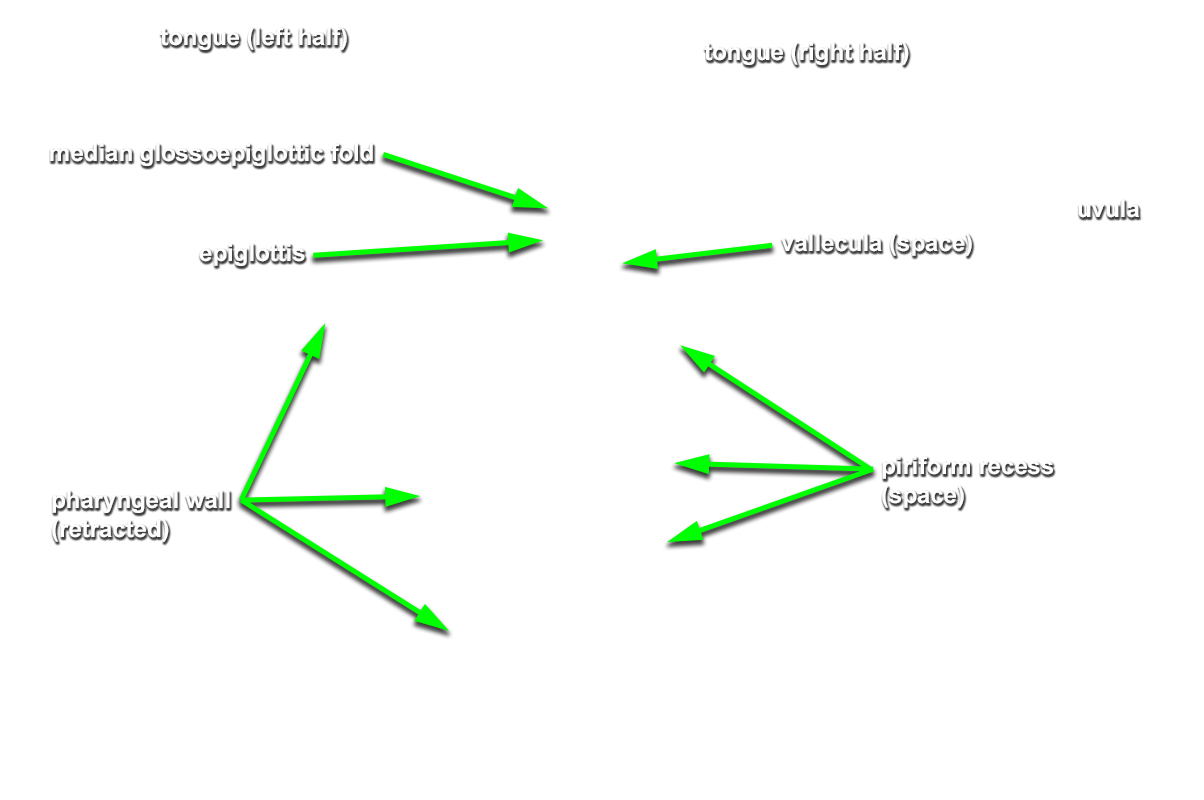
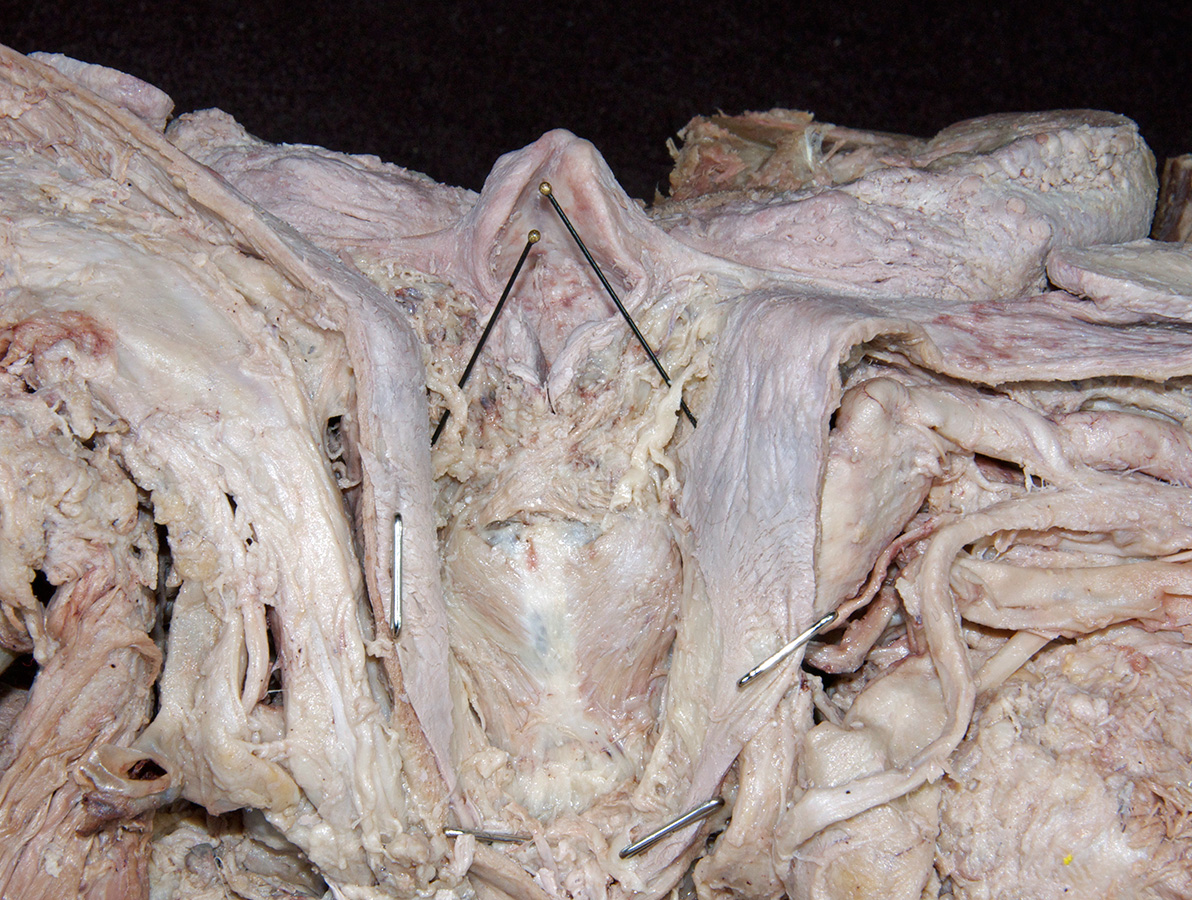
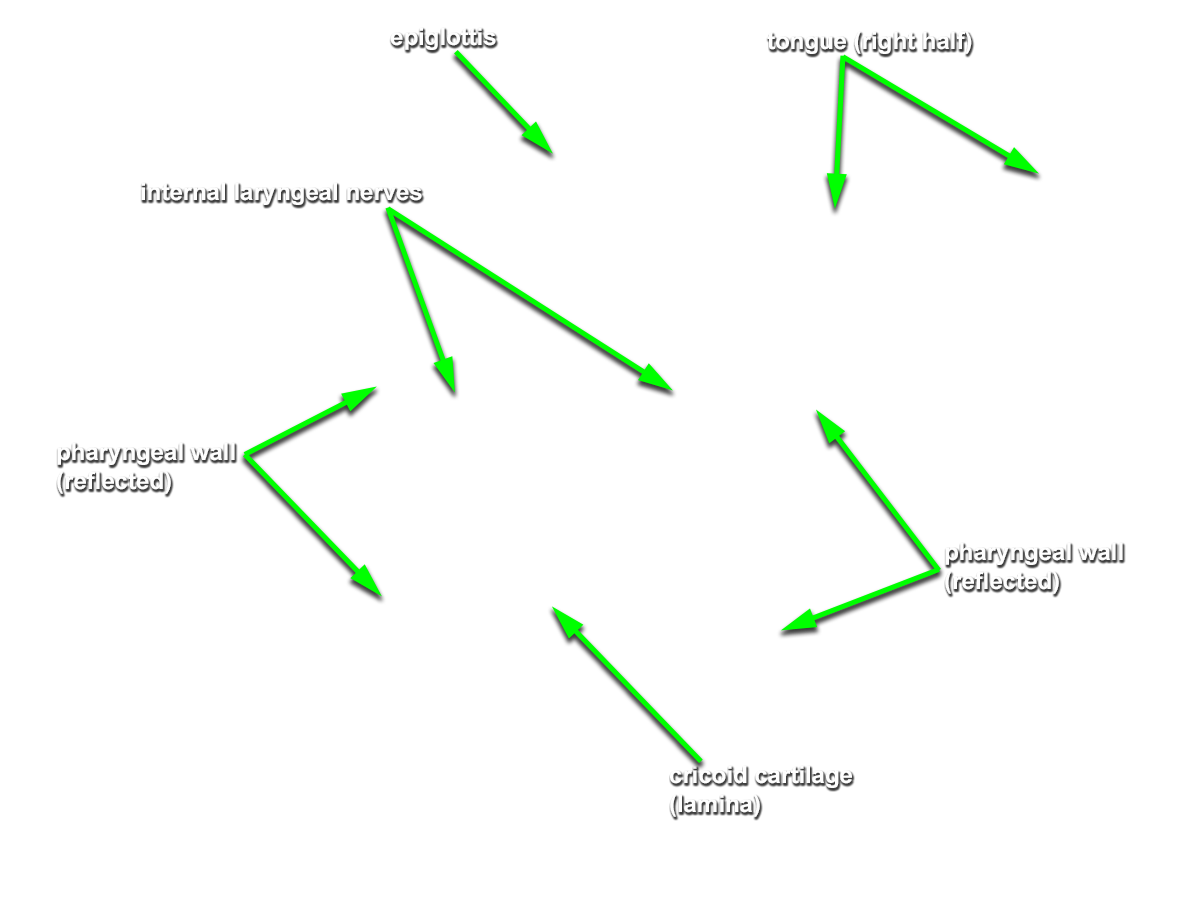
median and
lateral glossoepiglottic folds,
vallecula,
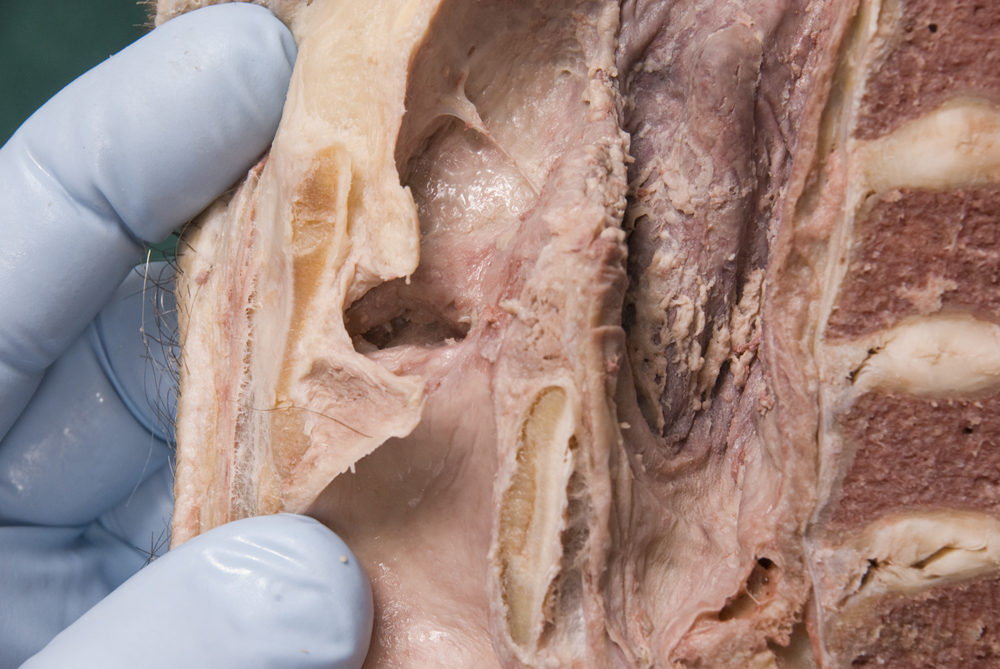
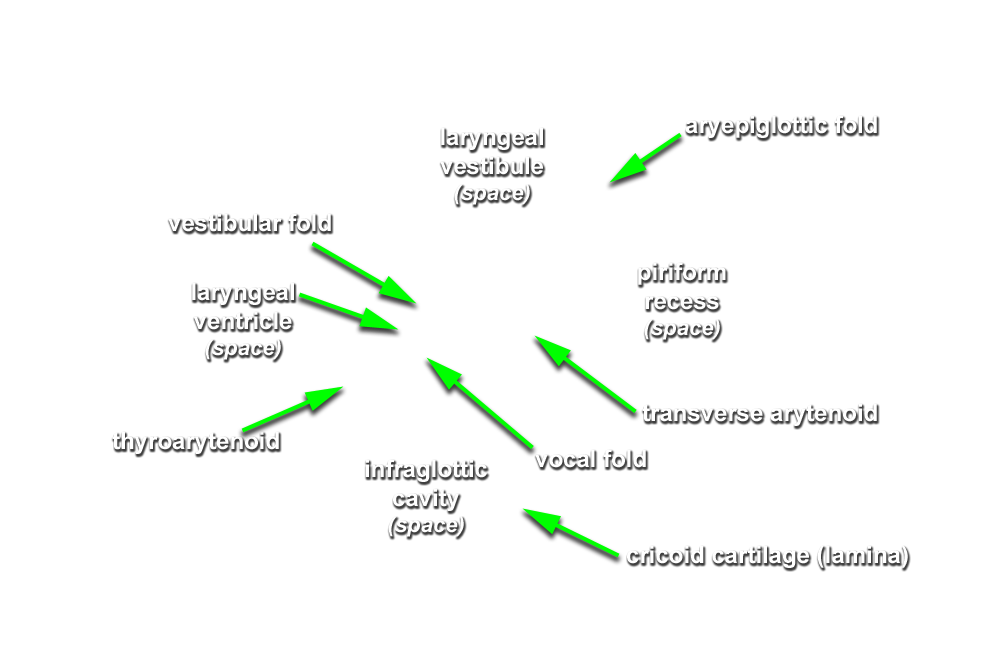
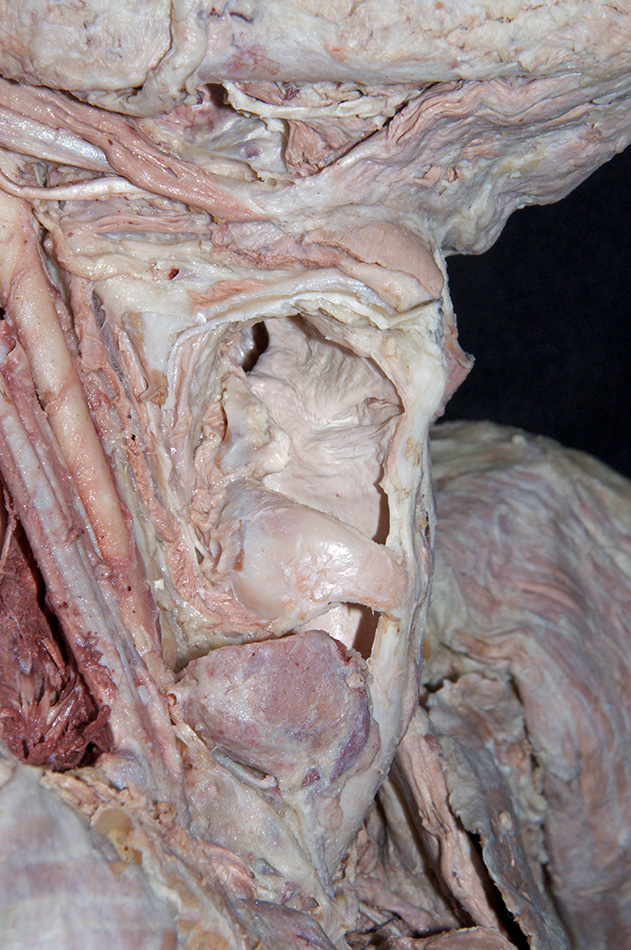
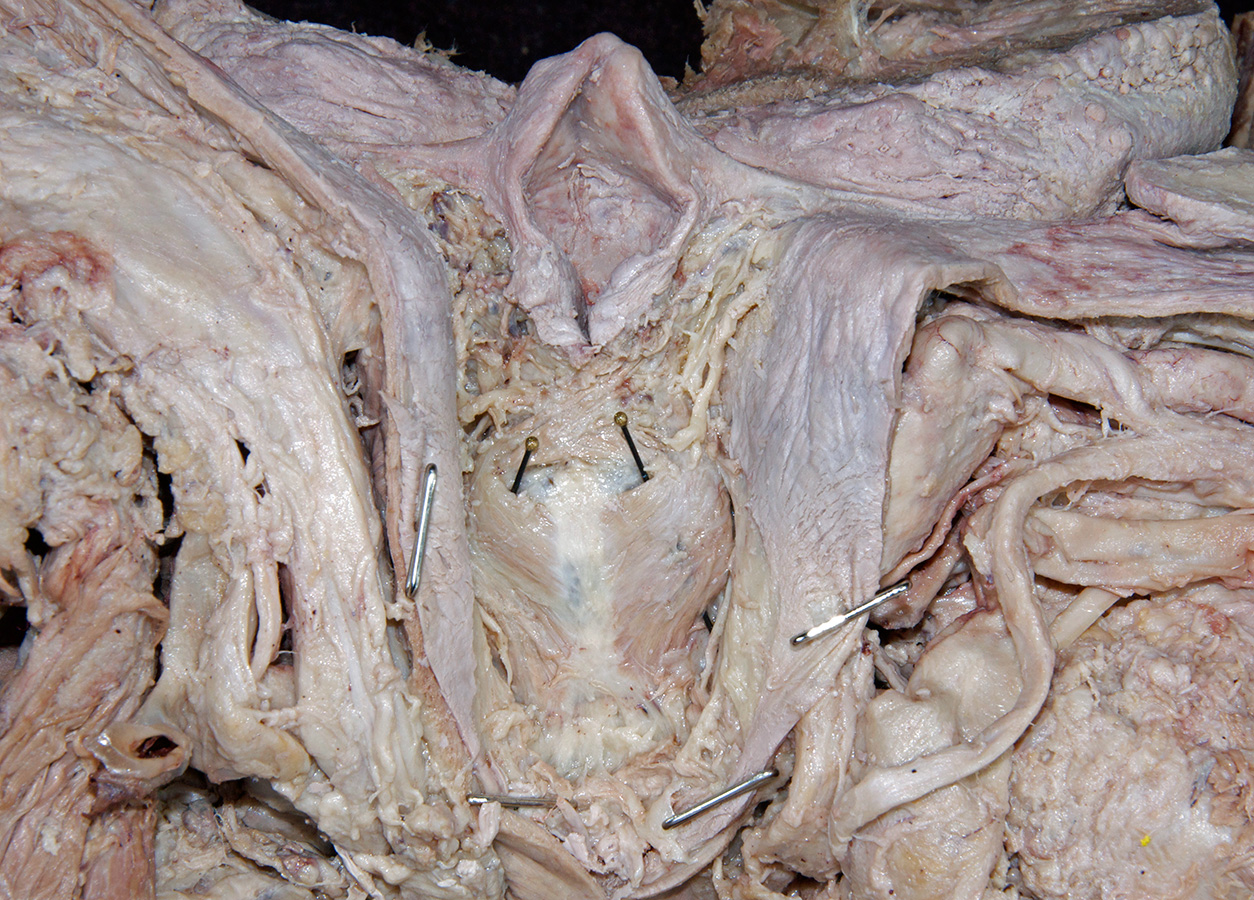
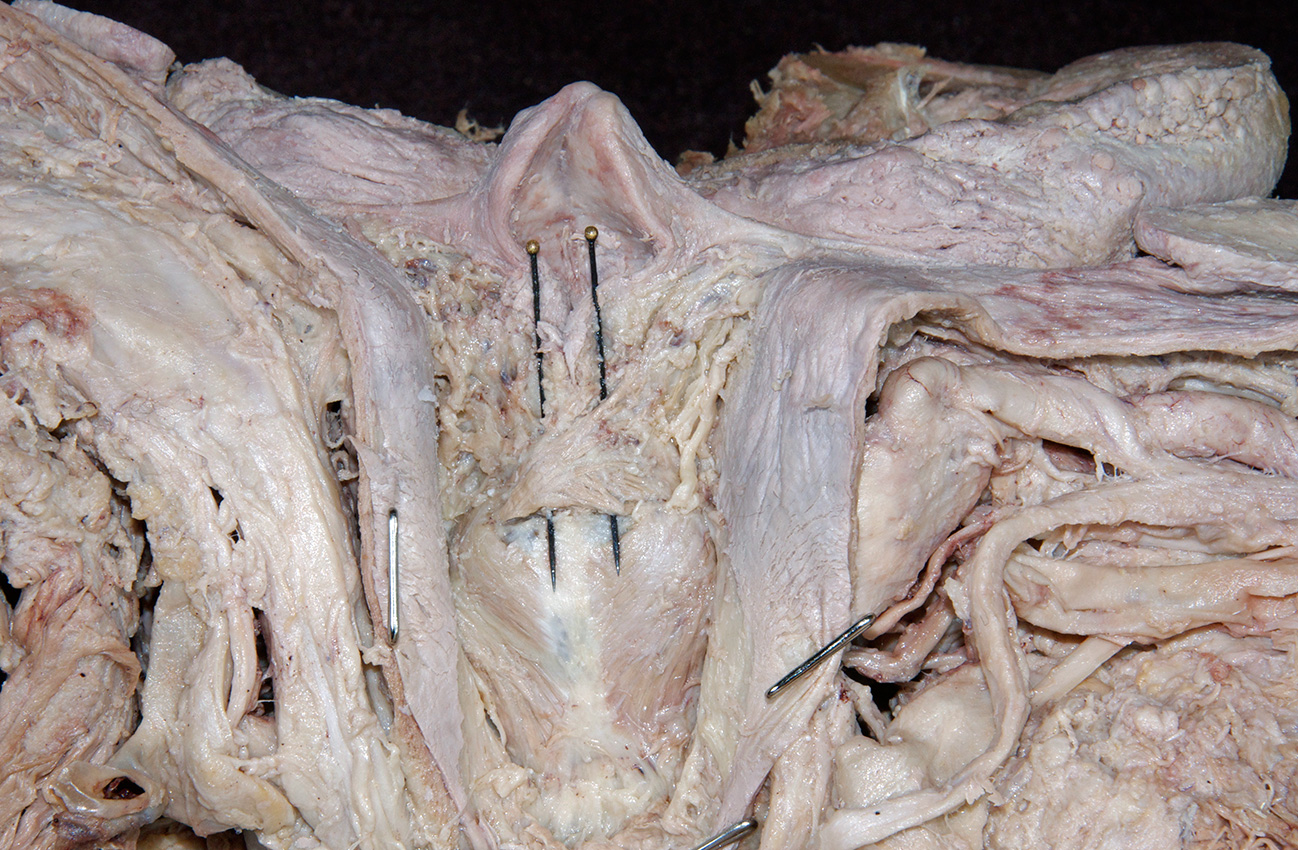
epiglottis, aryepiglottic fold, piriform recess,
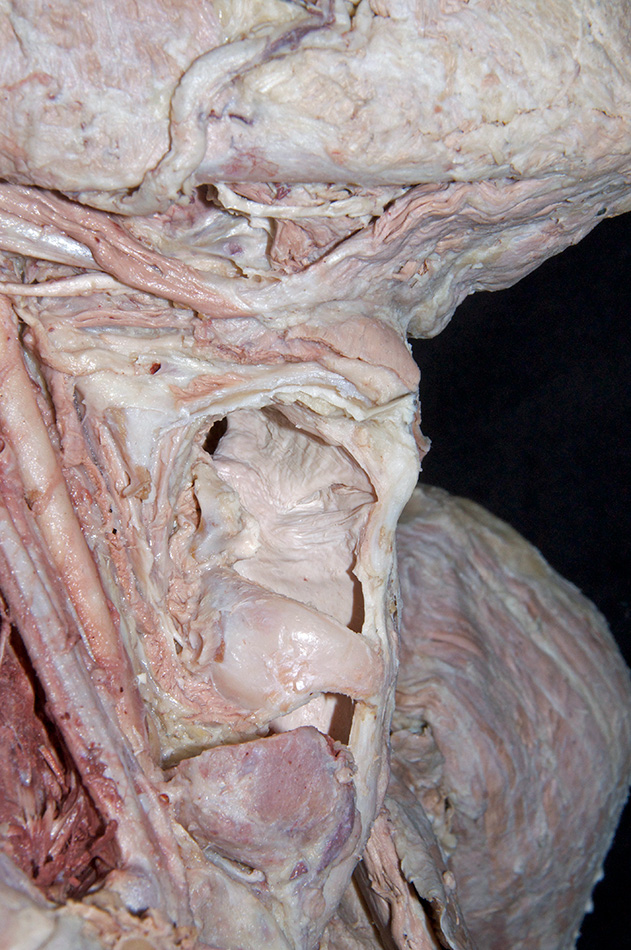
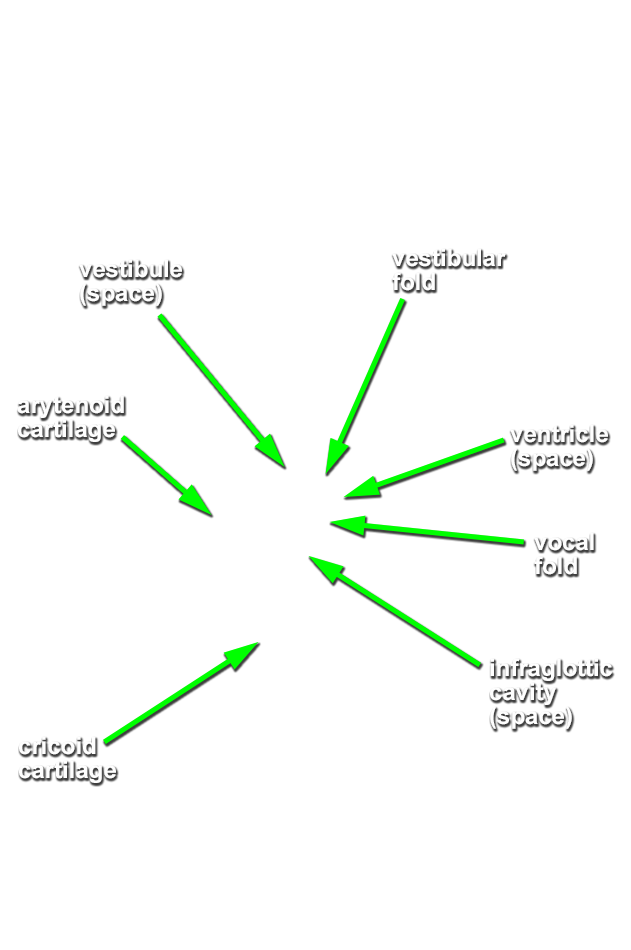
laryngeal vestibule, vestibular fold,
laryngeal ventricle,
vocal fold and
infraglottic cavity. (G 7.61A;N 60;Gl 44.27)
Important Relationship
- The vallecula is positioned directly anterior to the epiglottis and posterior to the tongue (root).
- The epiglottis is positioned posterior to the tongue (root).
- The piriform recess is positioned lateral to the laryngeal inlet.
- The vocal ligament is positioned anterior to the arytenoid cartilage.
- The vocal fold is positioned inferior to the vestibular fold.
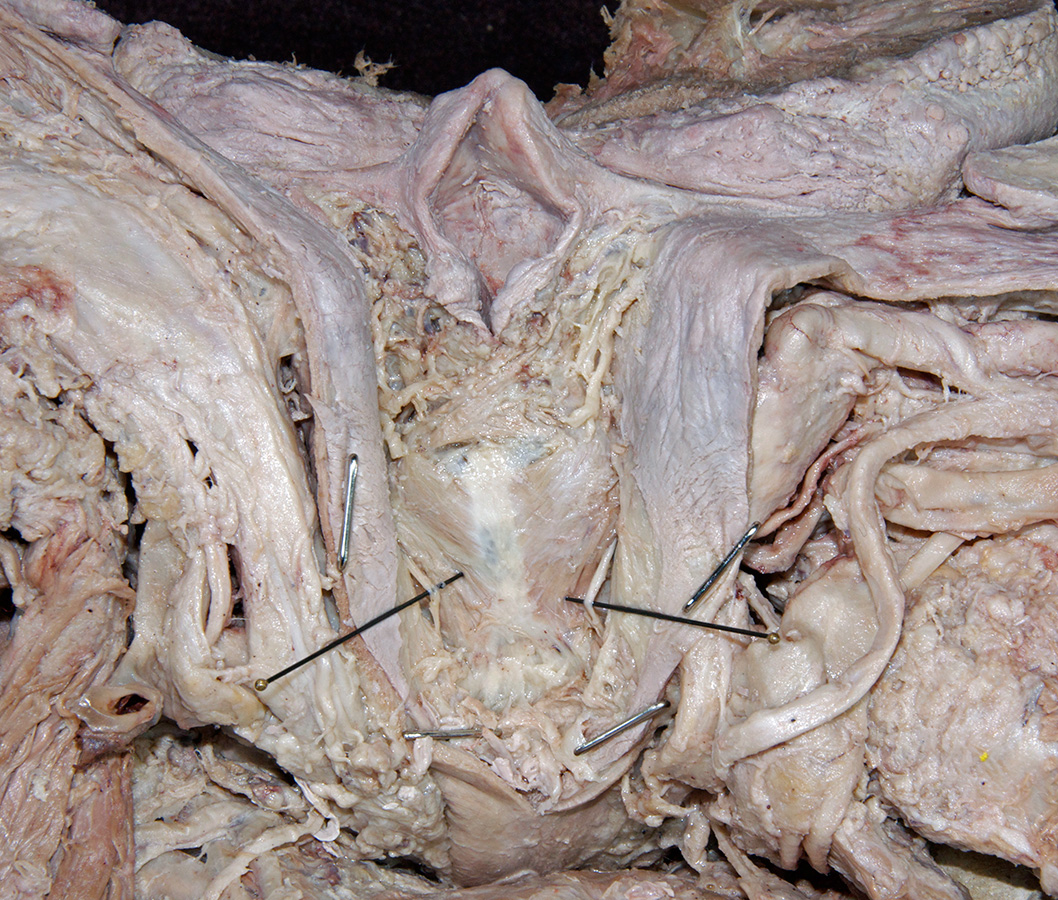
- Identify the internal laryngeal nerve in the piriform recess. (G 8.36G;N 67;Gl 45.28B)
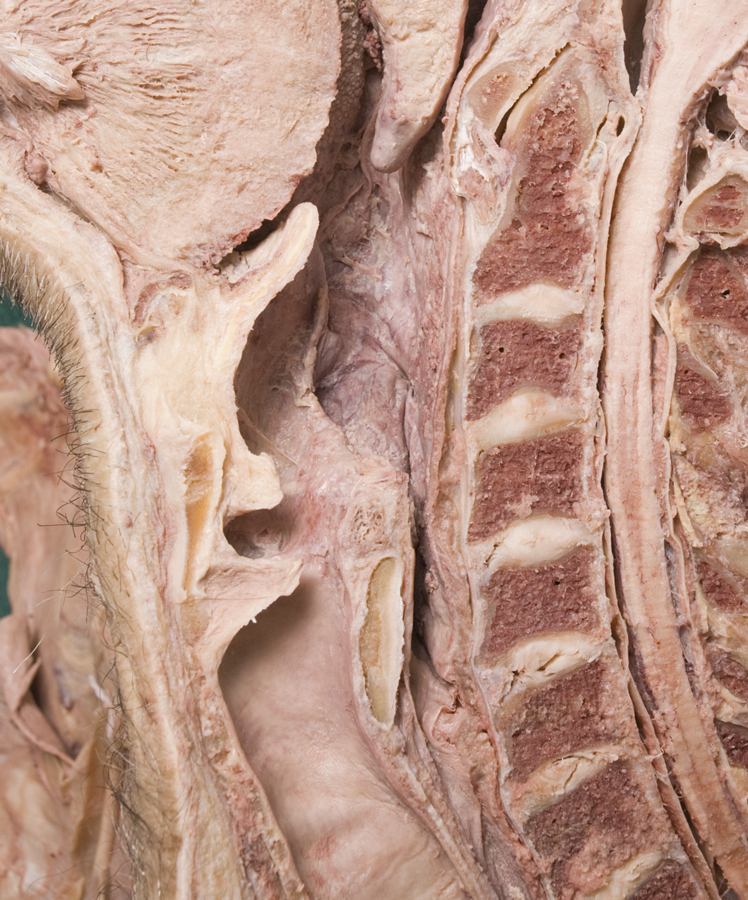
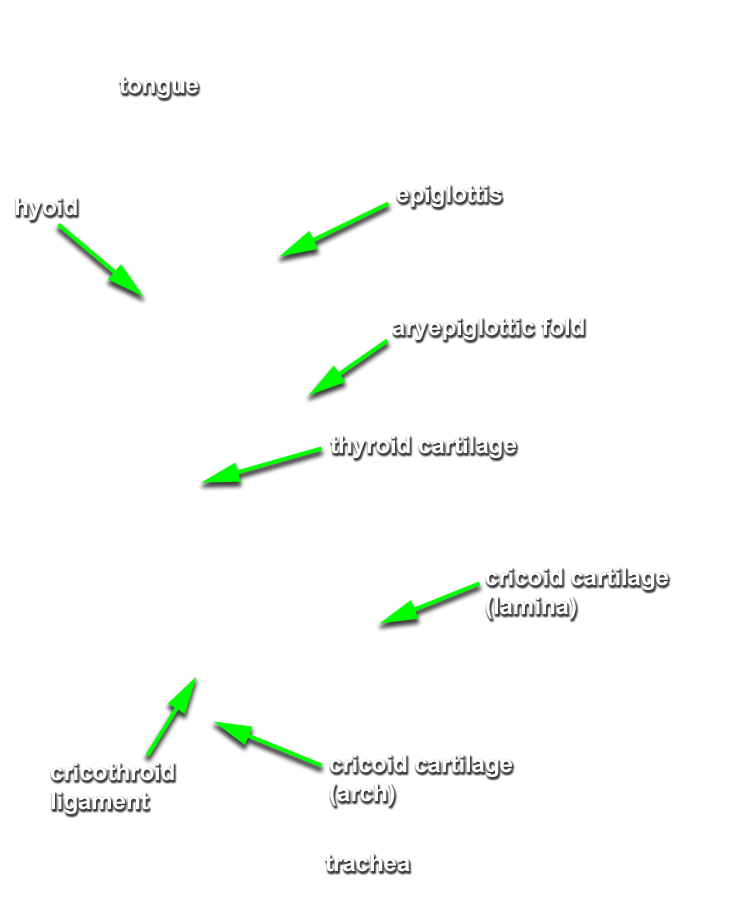
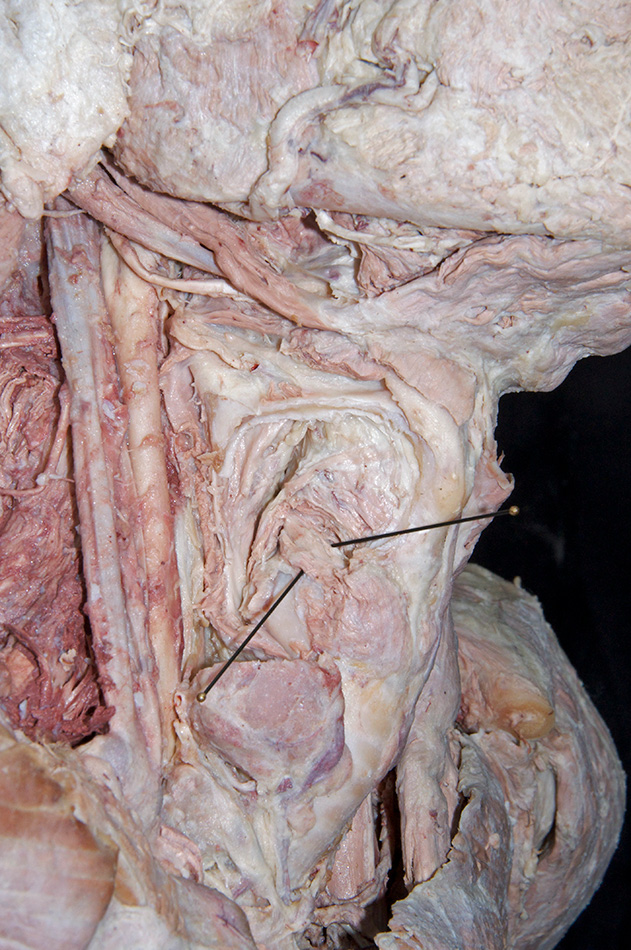
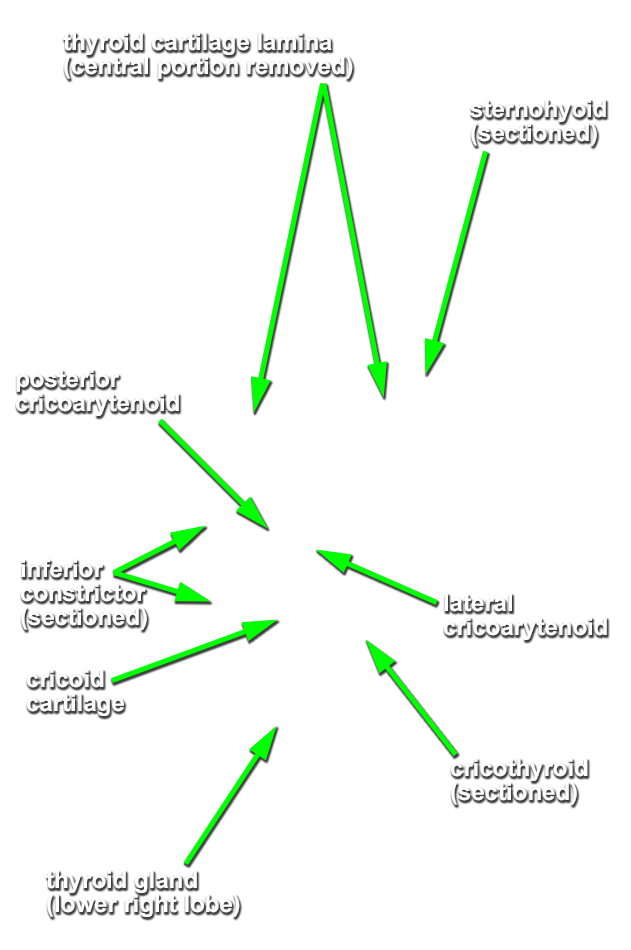
- Identify the
lamina of the cricoid cartilage (G 8.33E;N 79;Gl 45.19) and
recurrent laryngeal nerve. (G 8.36G;N 82;Gl 45.28B)
Important Relationship
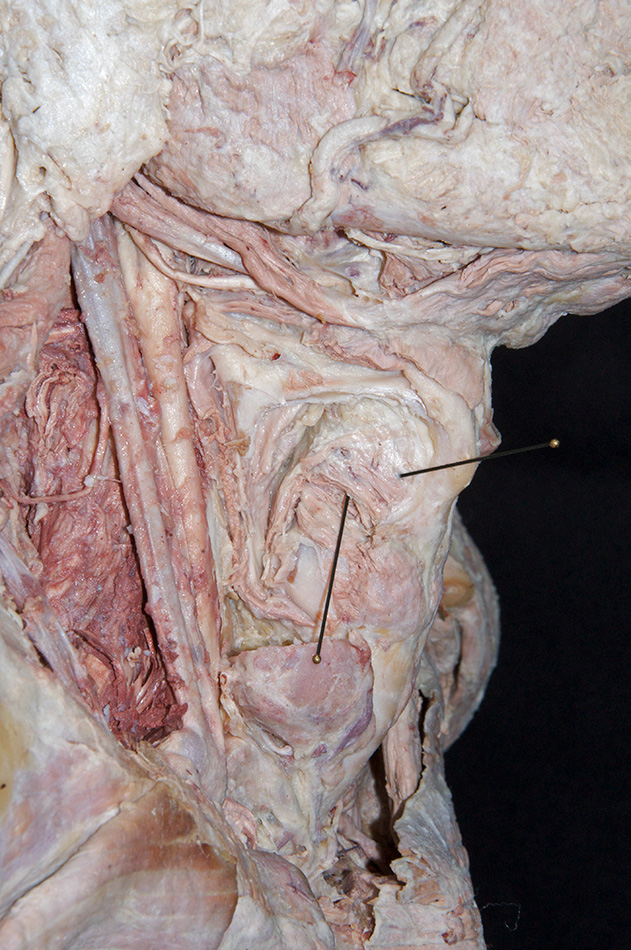
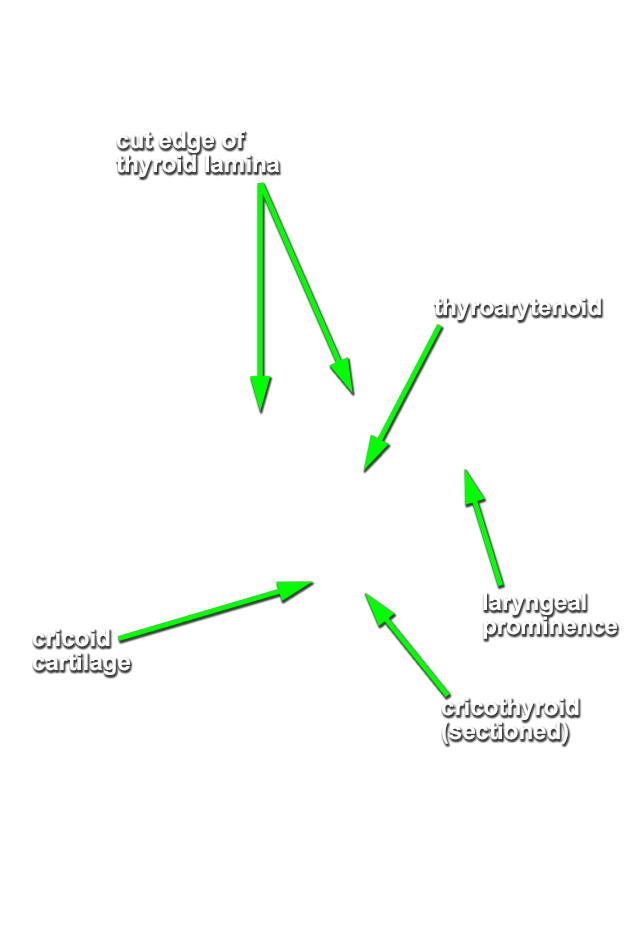
- The thyroid cartilage (laminae) are positioned superior to the cricoid cartilage.
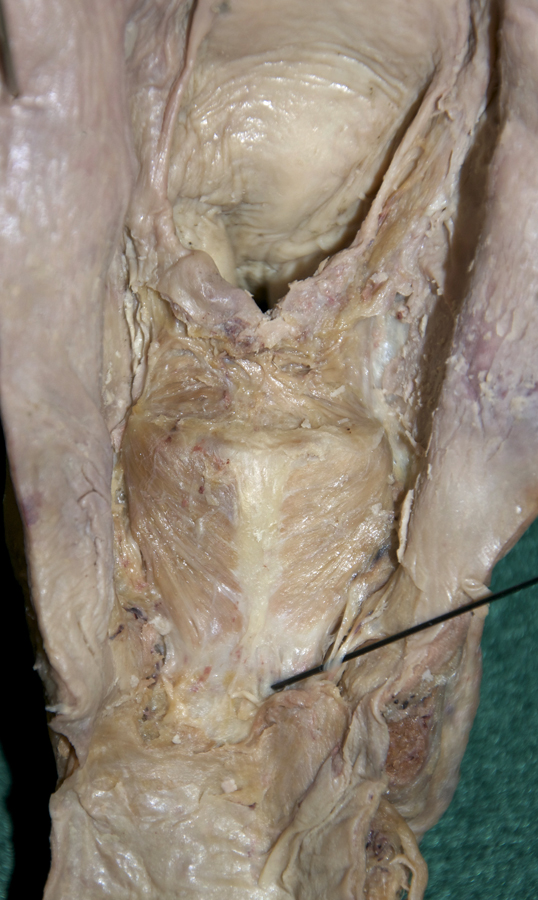
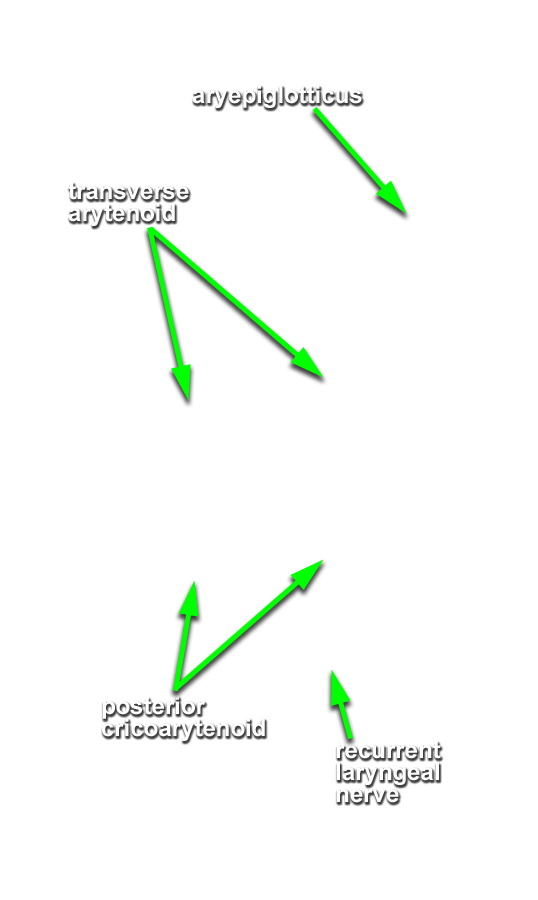
- Palpate and identify the
arytenoid cartilage. (G 8.33E;N 79;Gl 45.22C) Identify the
posterior cricoarytenoid and transverse arytenoid muscles. (G 8.36C;N 80;Gl 45.22B) Attempt to identify the aryepiglotticus muscle.
Important Relationship
- The arytenoid cartilage is positioned superior to the cricoid (lamina) cartilage.
- (OPTIONAL, ON ONE SIDE ONLY - the side where the infrahyoid muscles were cut) Attempt to identify the cricothyroid, lateral cricoarytenoid and thyroarytenoid muscles. (G 8.36C;N 80;Gl 45.22B)