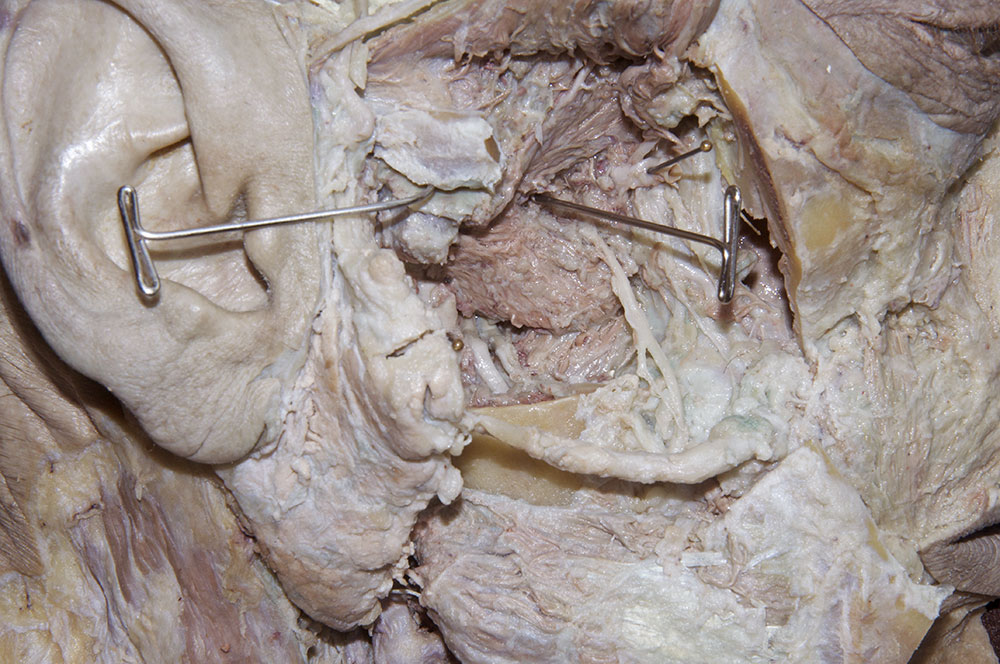
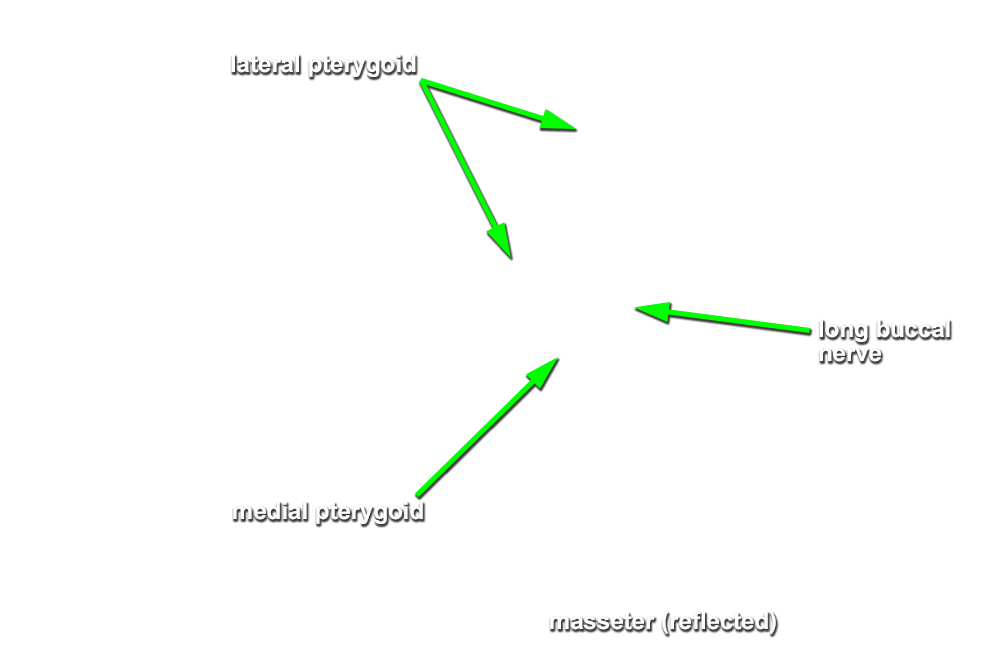
Identify the medial pterygoid muscle and the nerves, arteries and veins of the infratemporal fossa.
- Identify the medial pterygoid muscle. (G 7.42B;N 55;Gl 34.25)
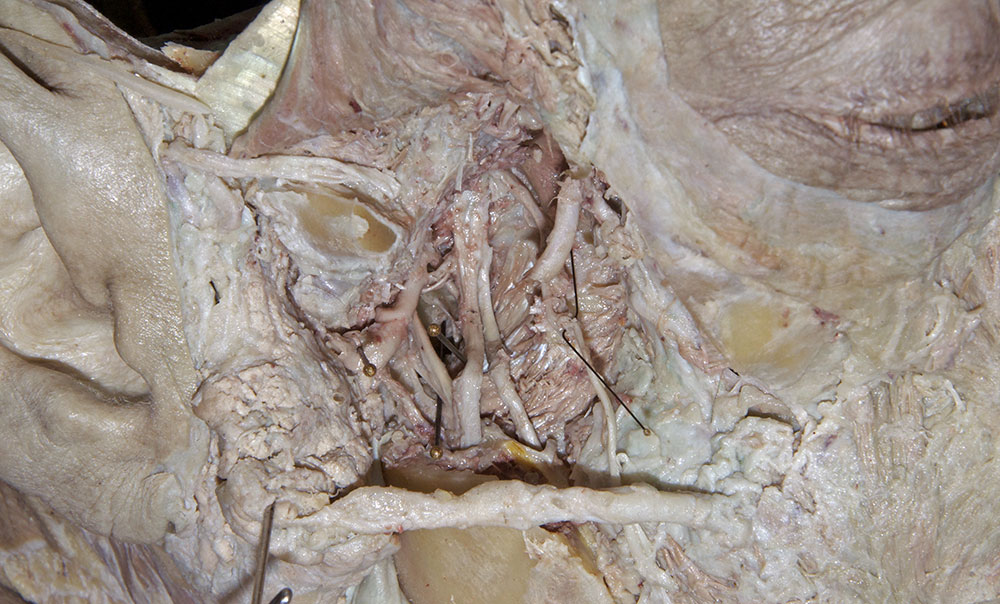
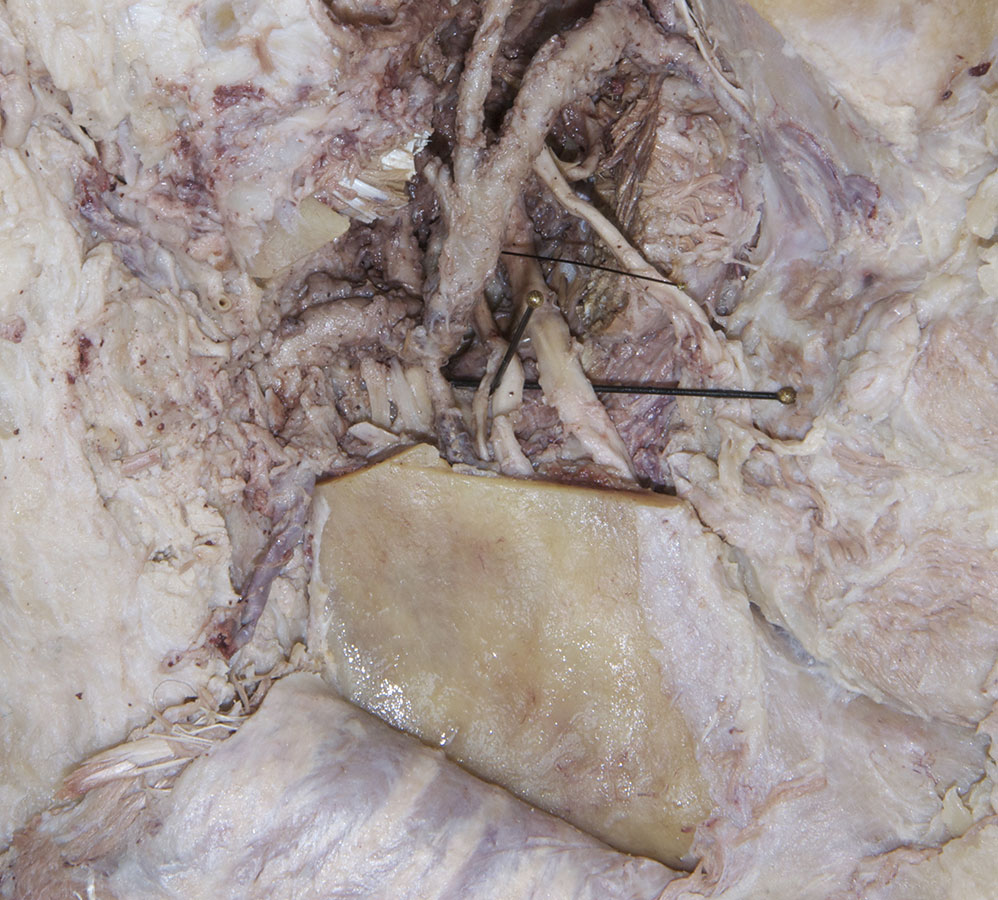
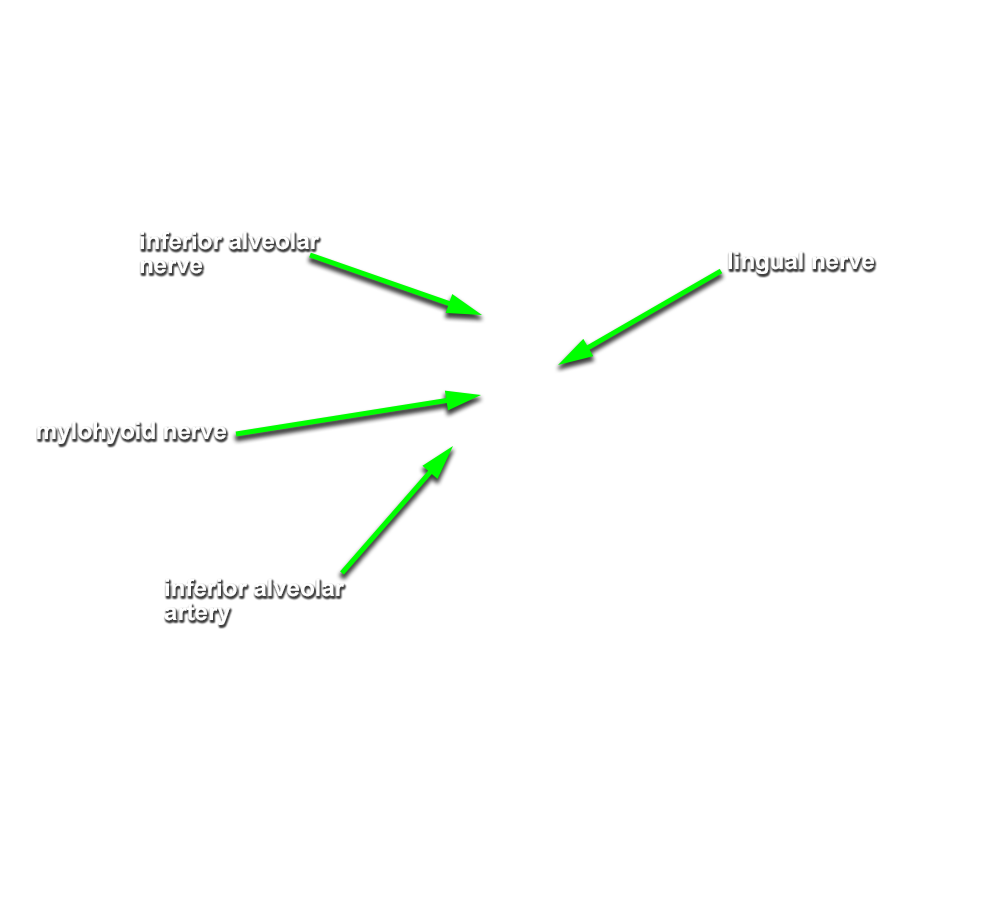
- Identify the
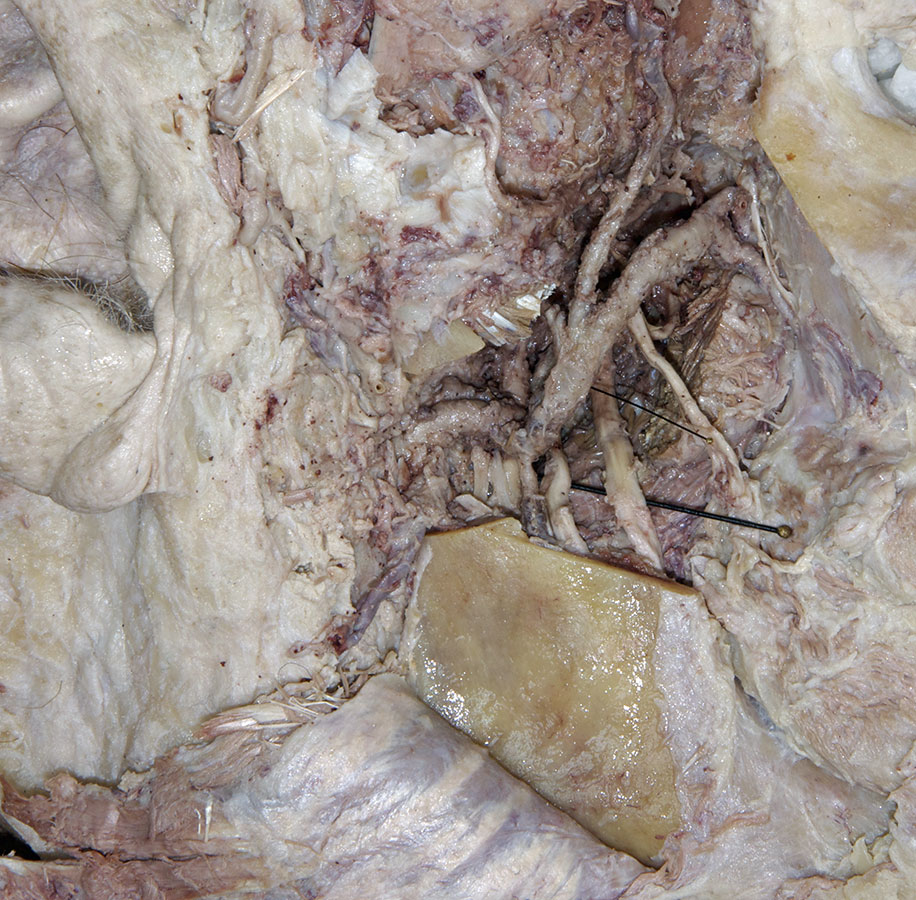
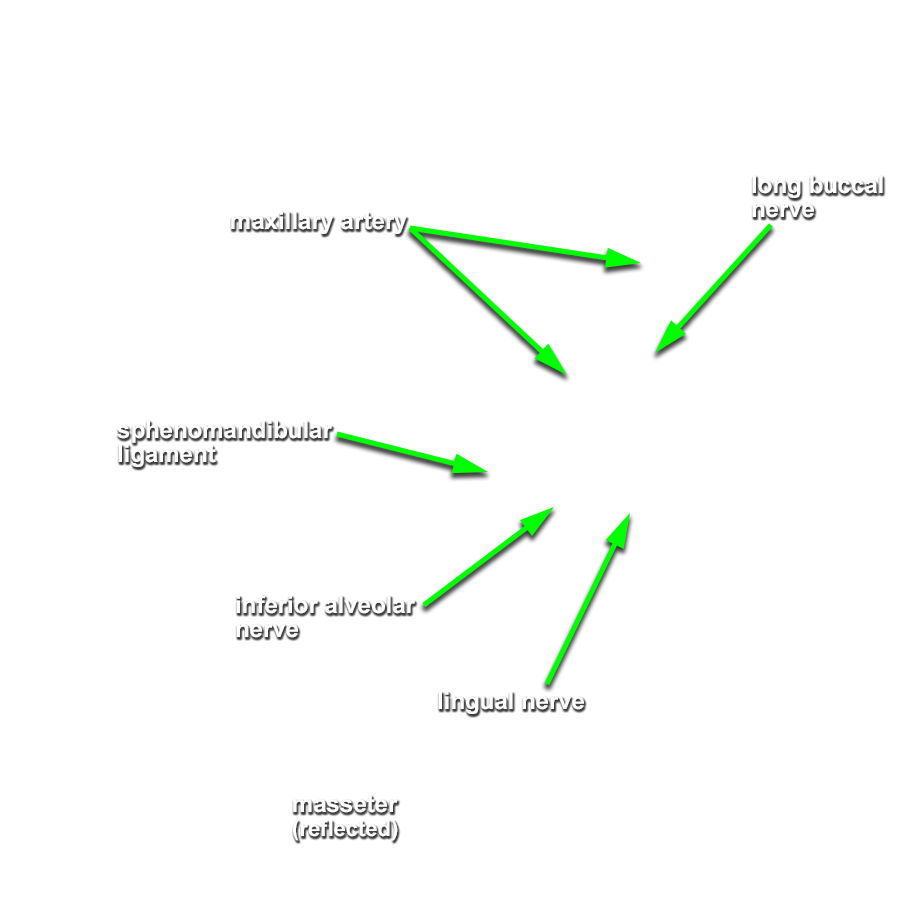
inferior alveolar and
lingual nerves and the
sphenomandibular ligament. (G 7.42B;N 39;Gl 32.17 & 38.7B) Attempt to identify the
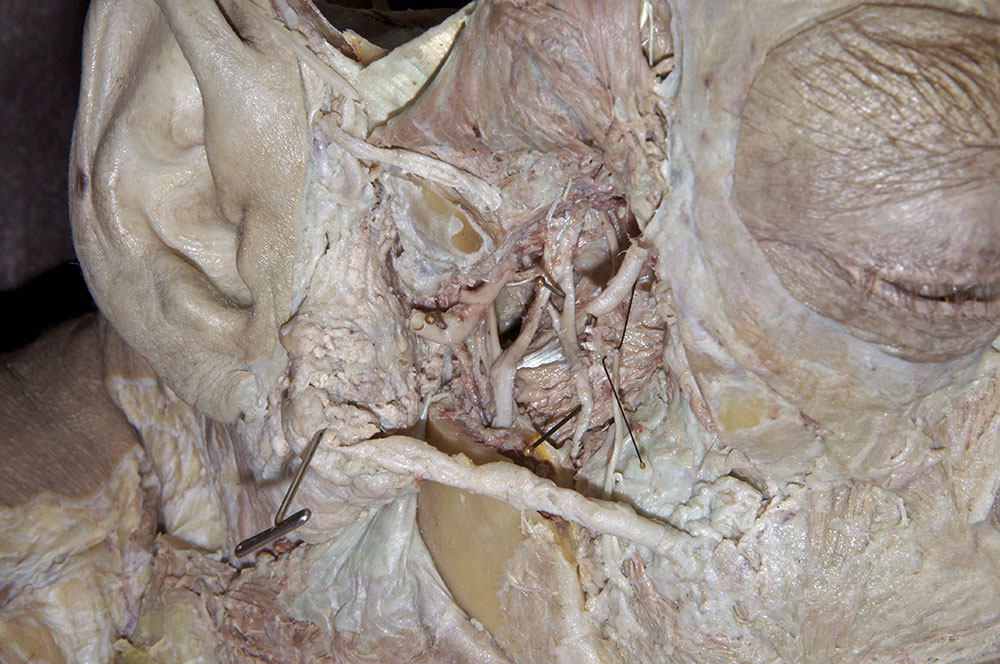
chorda tympani nerve
and the
nerve to the mylohyoid muscle
.
Important Relationships
- The lingual nerve passes medial to the mandible and lateral to the medial pterygoid muscle and is positioned anterior to the inferior alveolar nerve.
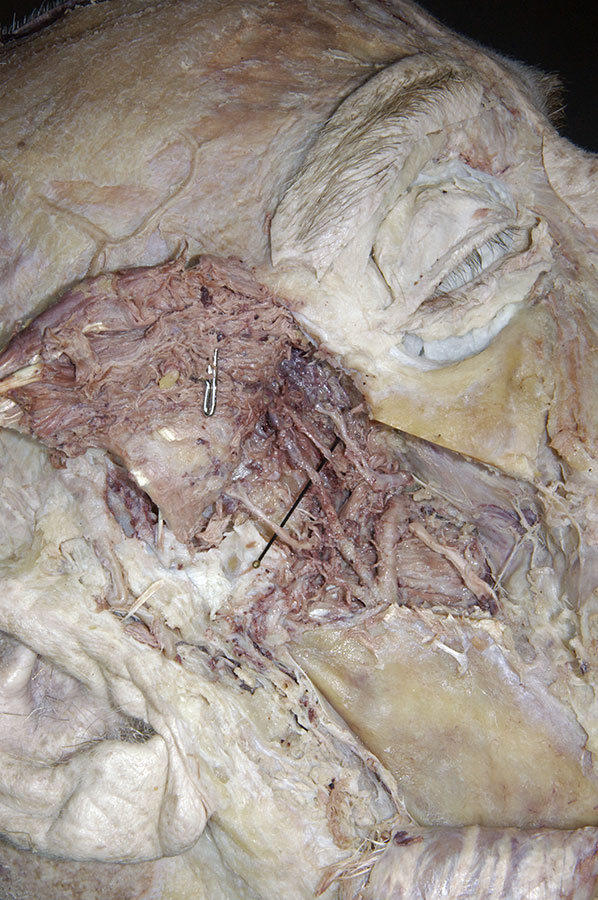
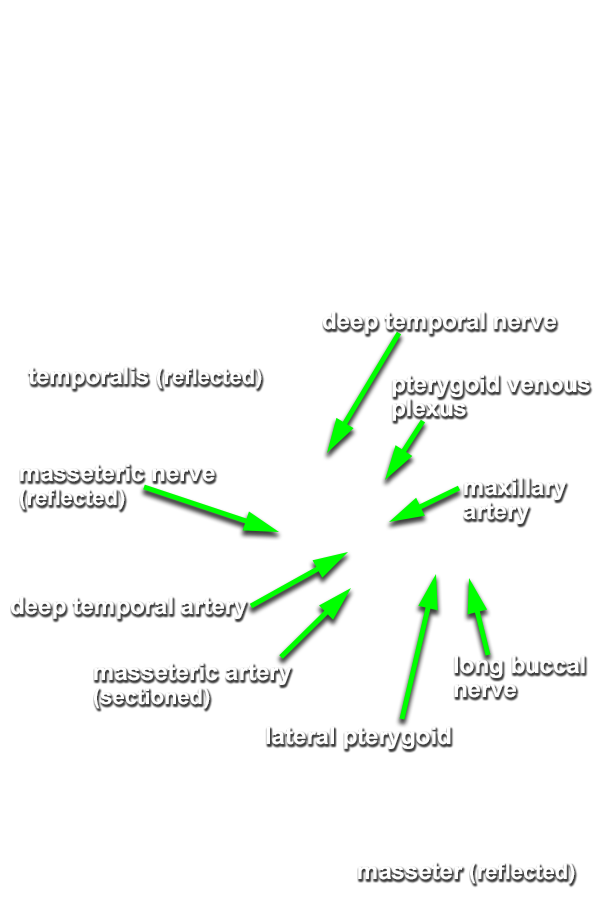
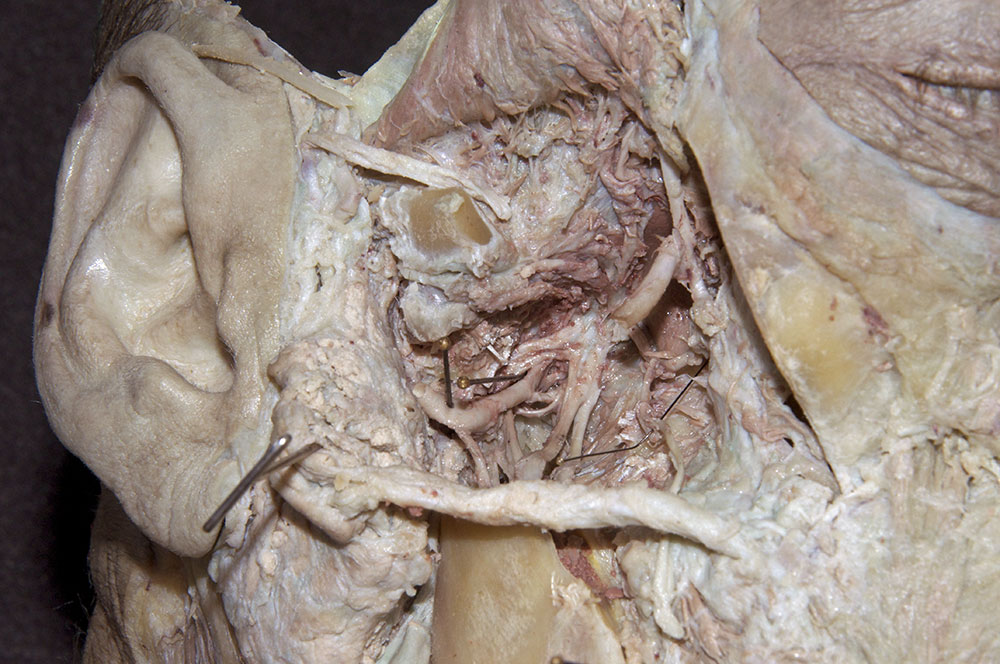
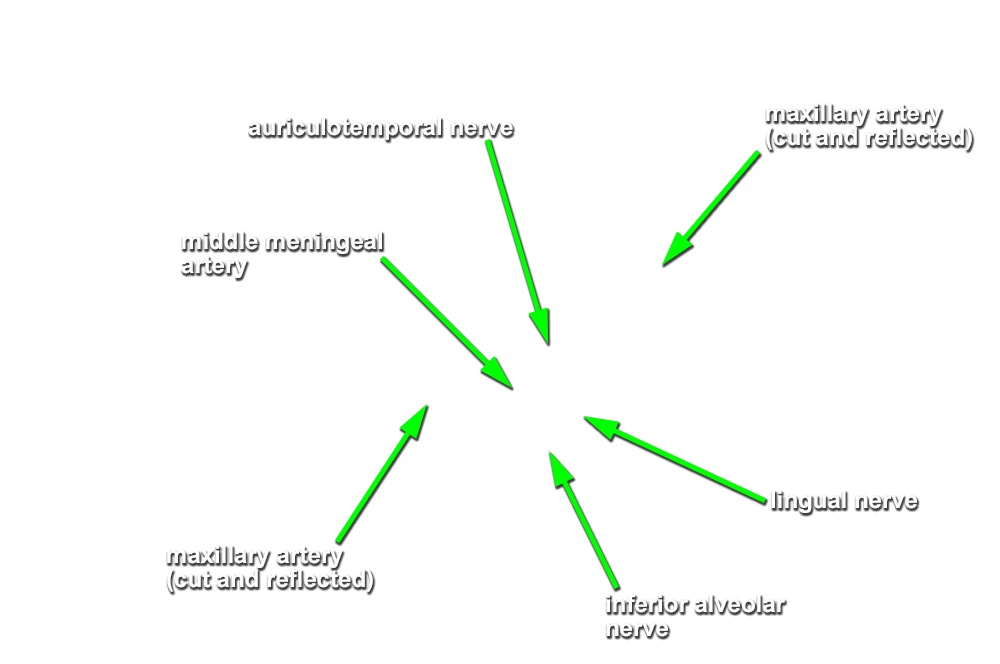
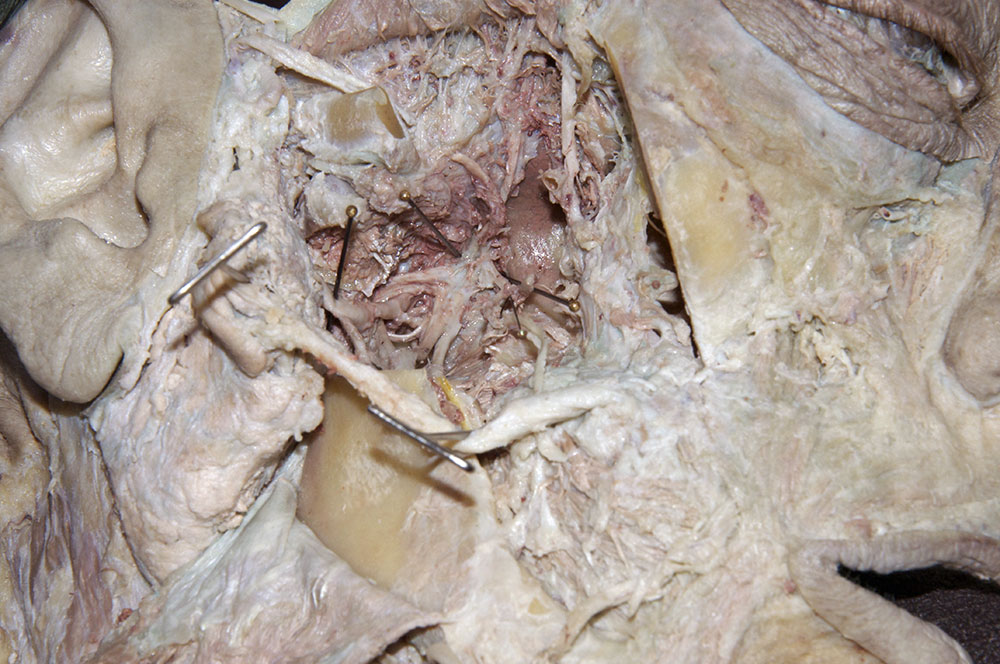
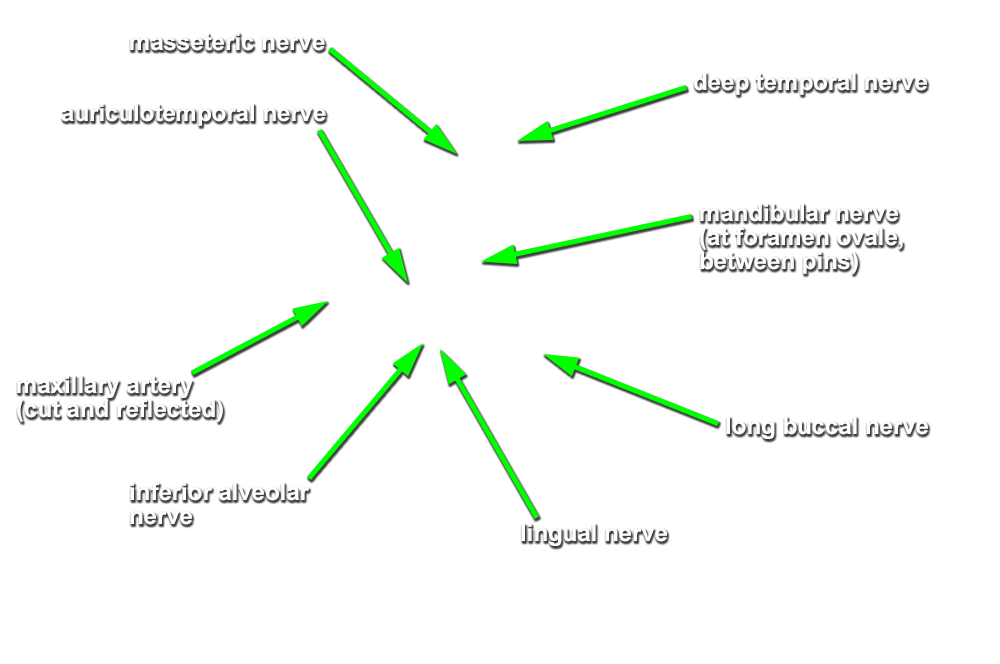
- Identify the
inferior alveolar artery. (G 7.43A;N 39;Gl 34.25) This artery should be with the inferior alveolar nerve. Trace the inferior alveolar artery in the superior direction and identify its origin from the
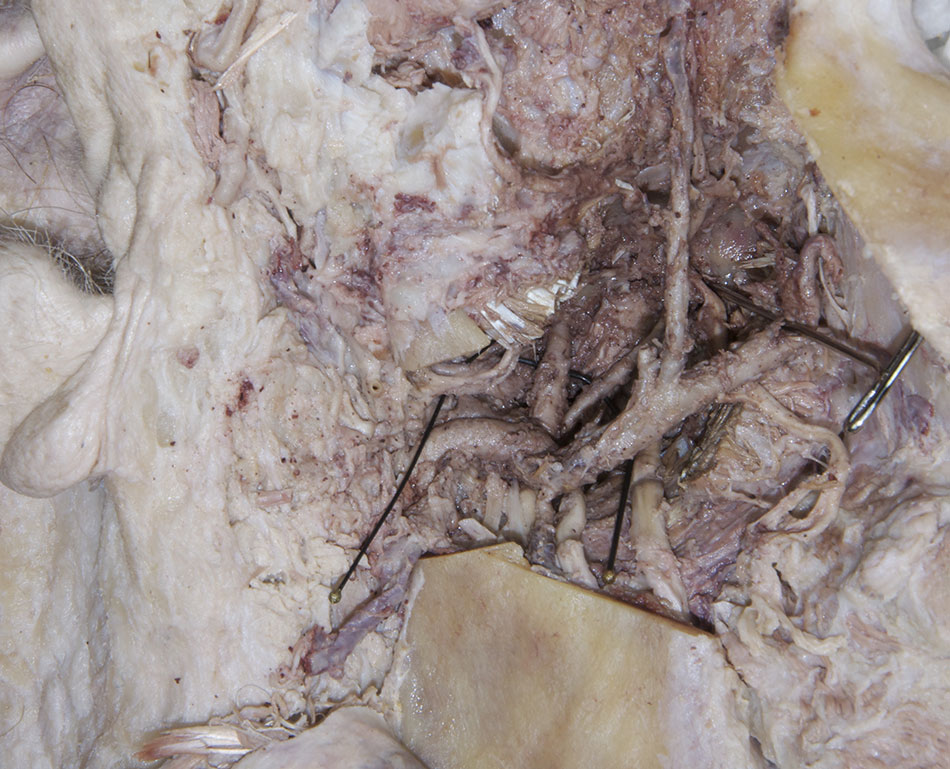
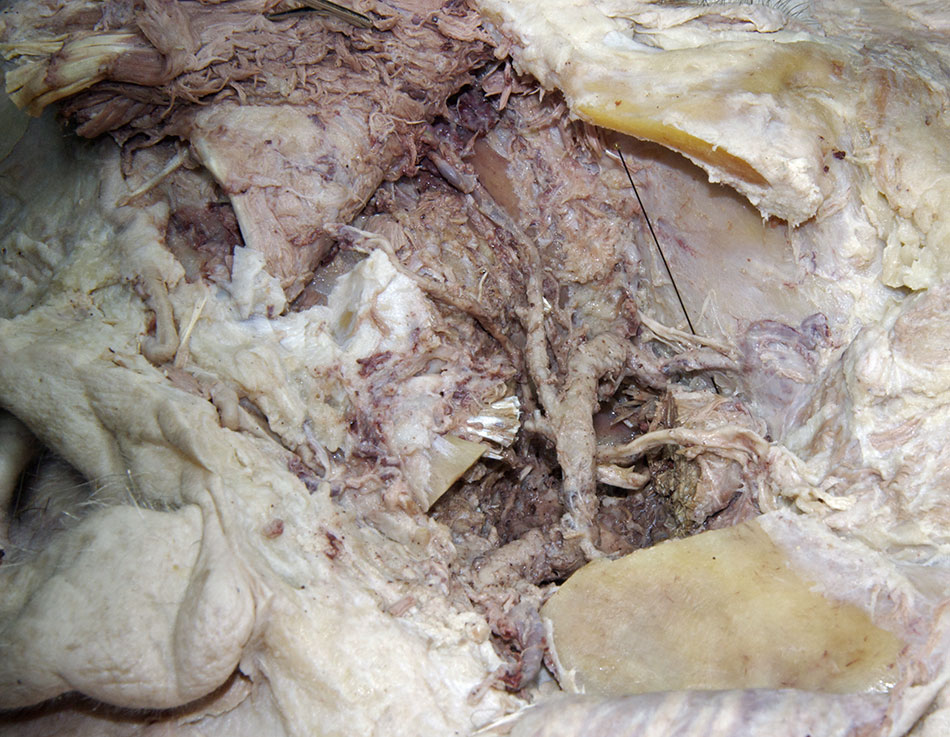
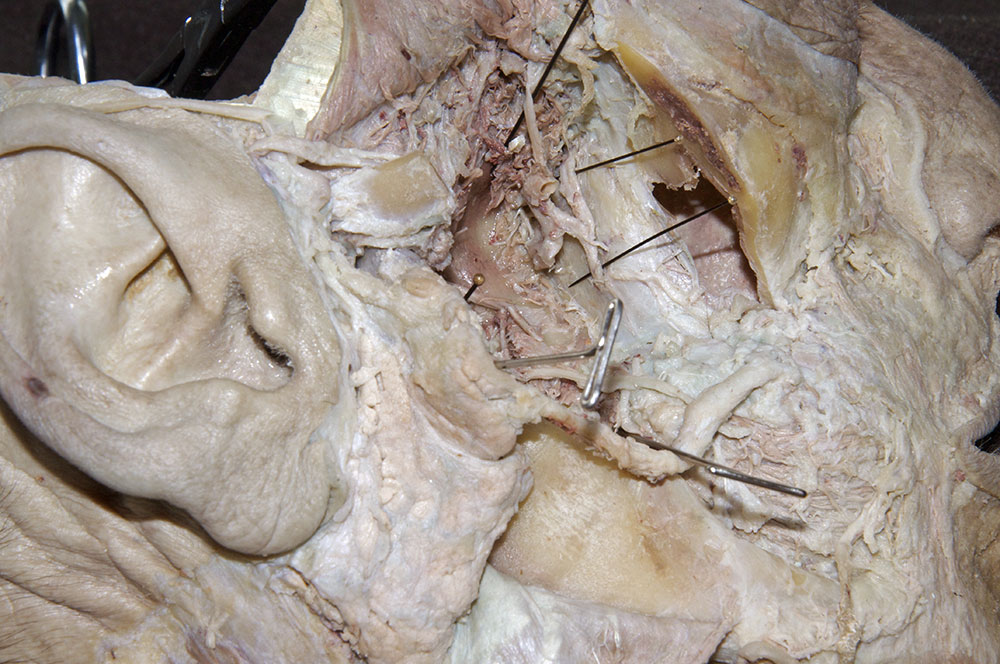
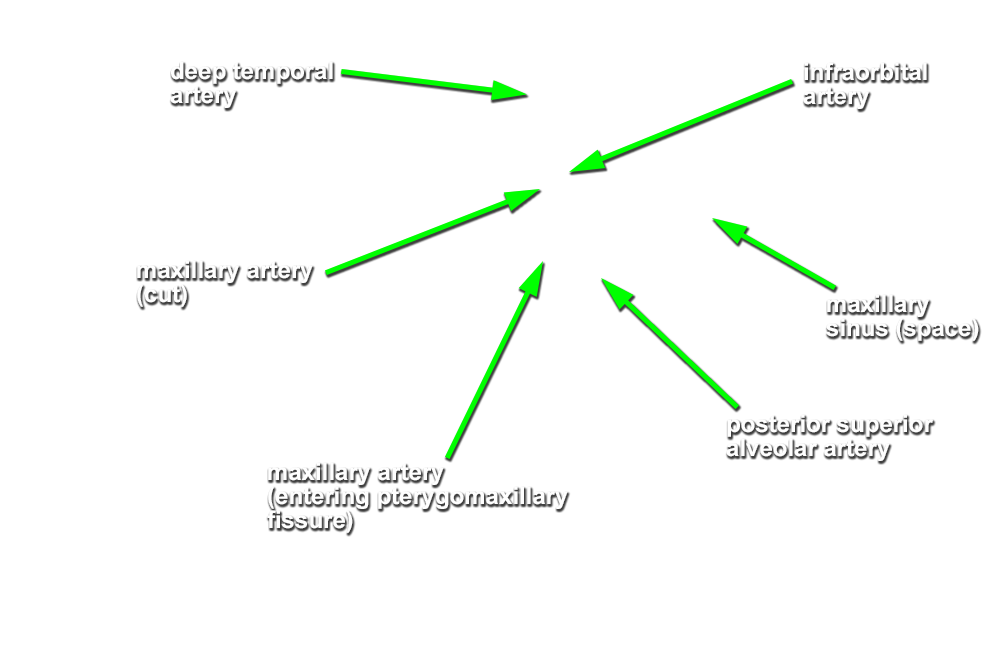
maxillary artery. Trace the maxillary artery until it disappears into the pterygomaxillary fissure. Identify the
middle meningeal,
deep temporal, and
posterior superior alveolar arteries. Attempt to trace the maxillary artery to the
pterygomaxillary fissure. Identify the
auriculotemporal nerve splitting around the
middle meningeal artery. Identify the
(long) buccal nerve (originally emerging between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle and passing adjacent to the anterior border of the coronoid process). Attempt to trace the long buccal, auriculotemporal, lingual, and inferior alveolar nerves
back to the foramen ovale.
Important Relationships
- The medial pterygoid muscle is positioned medial (deep) to the mandible (ramus).
- The maxillary artery passes medial to the mandible (neck) and lateral to the sphenomandiblar ligament. It typically passes lateral to the lateral pterygoid muscle.
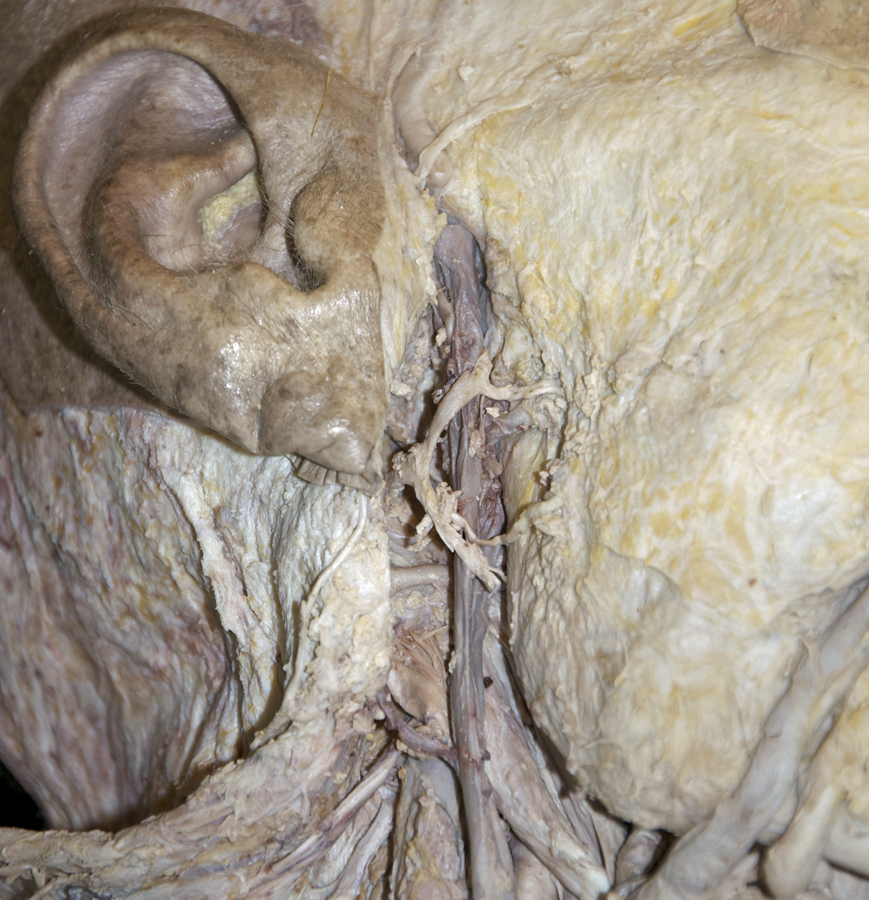
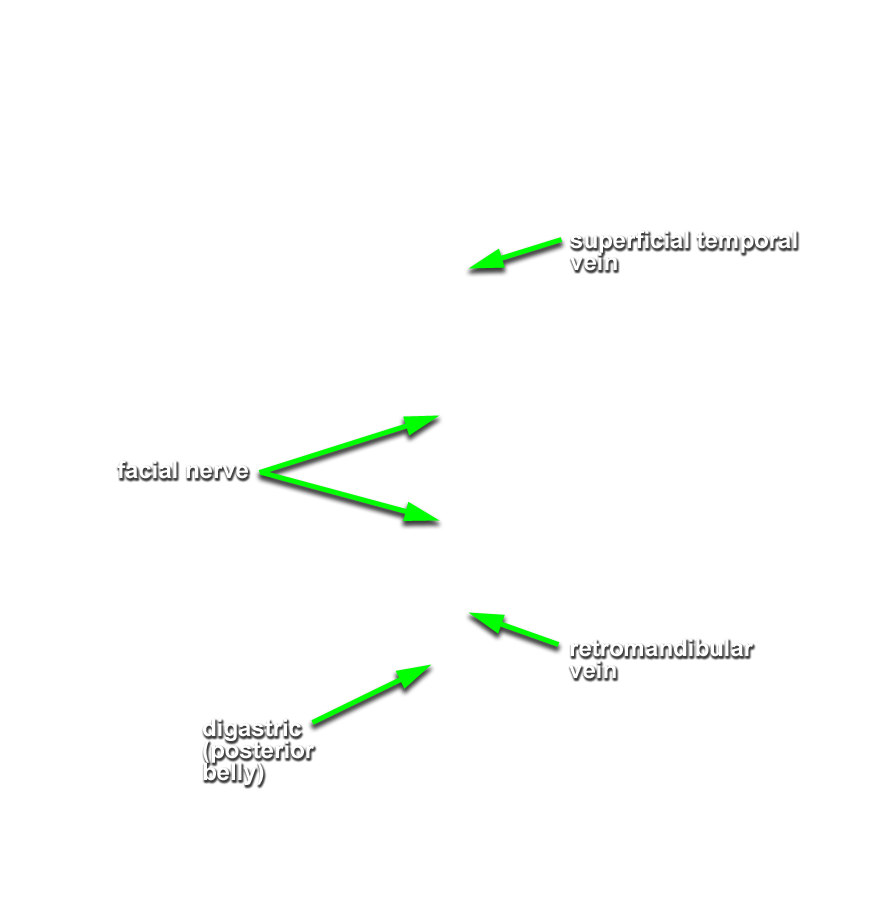
- Identify the
retromandibular vein. (G 7.39B;N 70;Gl 34.10) Trace the retromandibular vein in the inferior direction until it drains into the common facial vein (or external jugular vein).
Important Relationship
- The retromandibular vein is positioned posterior-medial to the mandible (ramus).