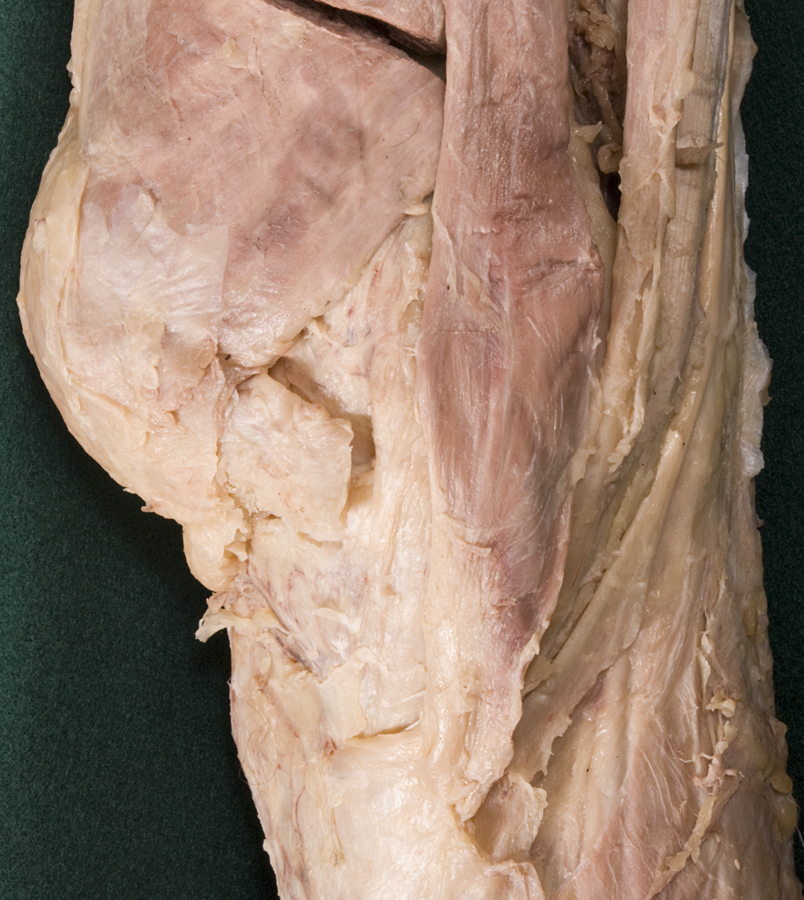
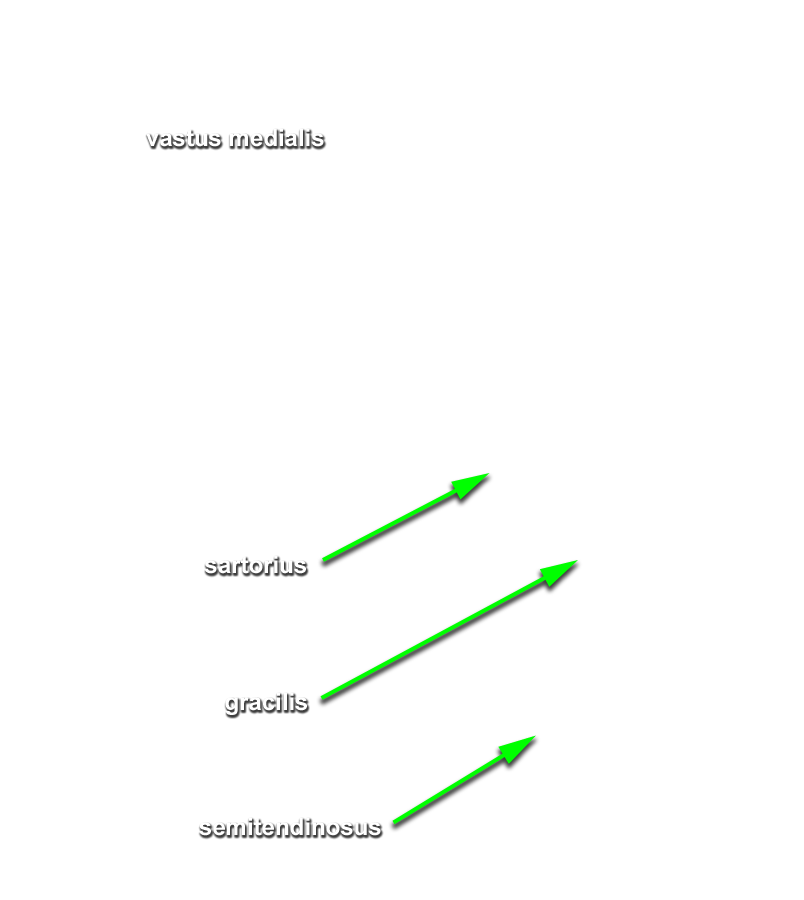
- Identify and clean the distal portions of the sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus muscles to their attachments to the proximal tibia. (G 6.50A;N 493;Gl 31.13) Transect the muscles approximately 6 cm proximal to the knee.
- Identify the distal third of the iliotibial tract. (G 6.51A;N 493;Gl 31.16) Remove the fascia lata and crural fascia leaving the iliotibial tract attached to the tibia.
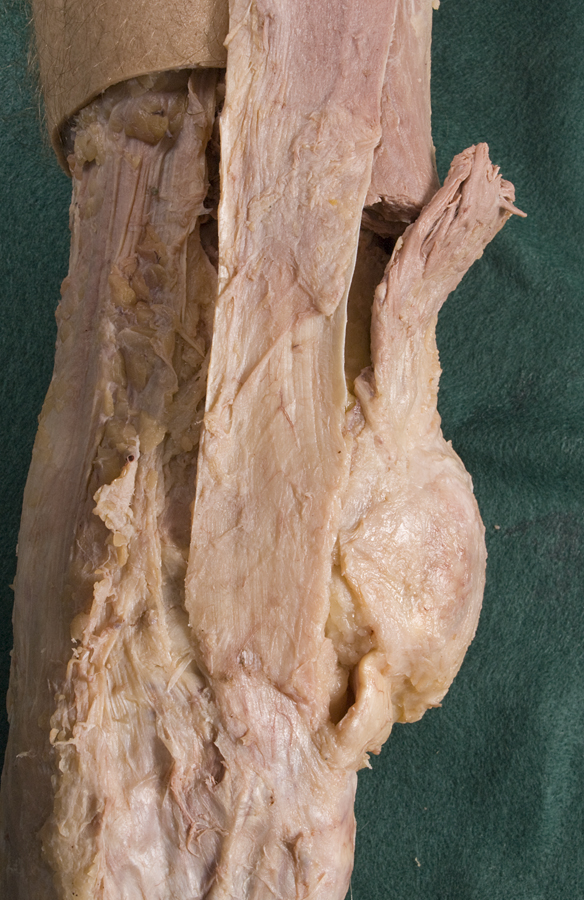
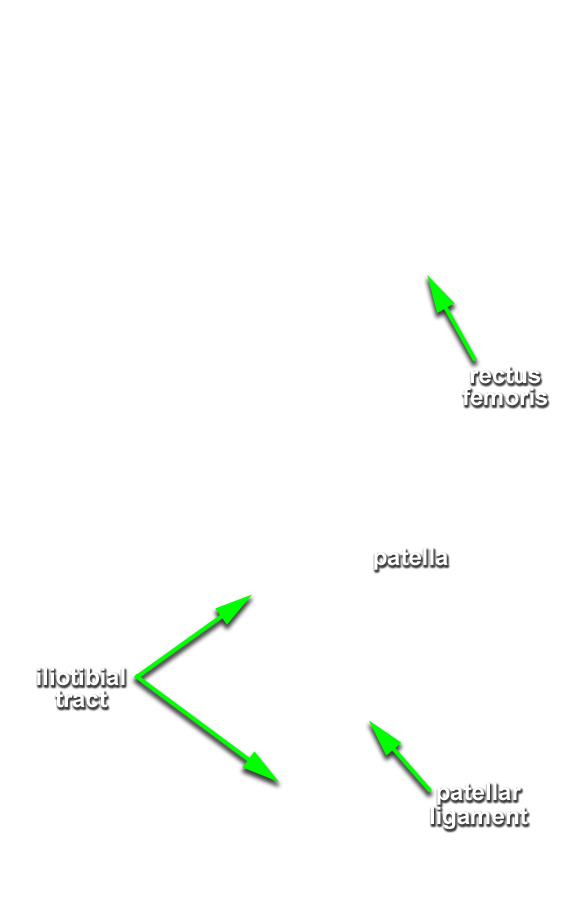
- Identify and clean the quadriceps femoris muscles near their attachment to the patella. (G 6.45A;N 494;Gl 31.11)
- Identify and clean the patellar ligament. (G 6.45A;N 494;Gl 32.5) Leave the patellar ligament intact and cut the joint capsule on both sides of the patella and ligament. Continue the cuts (approximately 10 cm) along the medial and lateral margins of the vastus medialis and vastus lateralis muscles. Blunt dissect under the patella and quadriceps muscles. Transect the quadriceps muscles approximately 6 cm superior to the patella, and reflect the muscle, patella and ligament in the inferior direction. (G 6.46A;N 494;Gl 32.5)
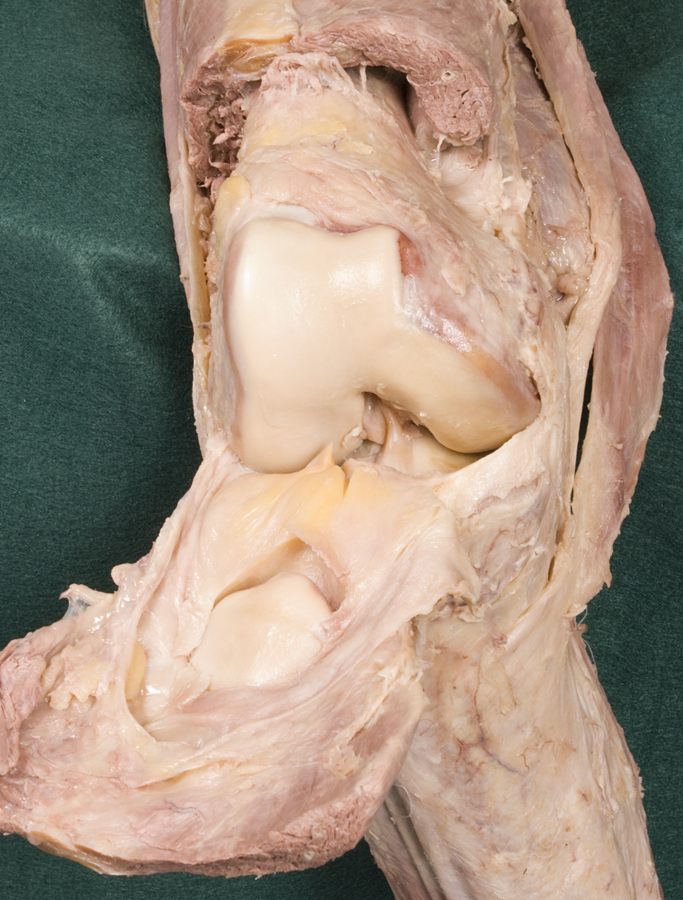
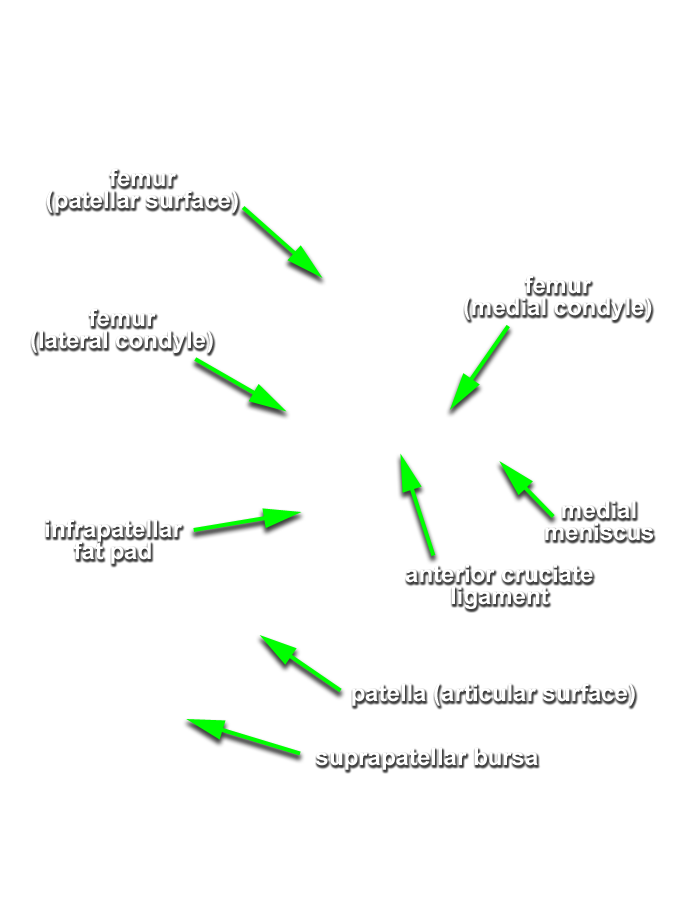
- Flex the knee joint and identify the anterior cruciate ligament, medial and lateral femoral condyles, and medial and lateral menisci. (G 6.47A;N 496;Gl 32.10A) You may need to remove a portion of the infrapatellar fat pad and synovial fold to identify the anterior cruciate ligament.
Important Relationships
- At the level of the knee, the gracilis muscle (tendon) is positioned posterior to the sartorius muscle (tendon).
- At the level of the knee, the gracilis muscle (tendon) is positioned anterior to the semitendinosus muscle (tendon).
- The iliotibial tract passes lateral to the knee joint.
- The anterior cruciate ligament passes lateral to the posterior cruciate ligament.