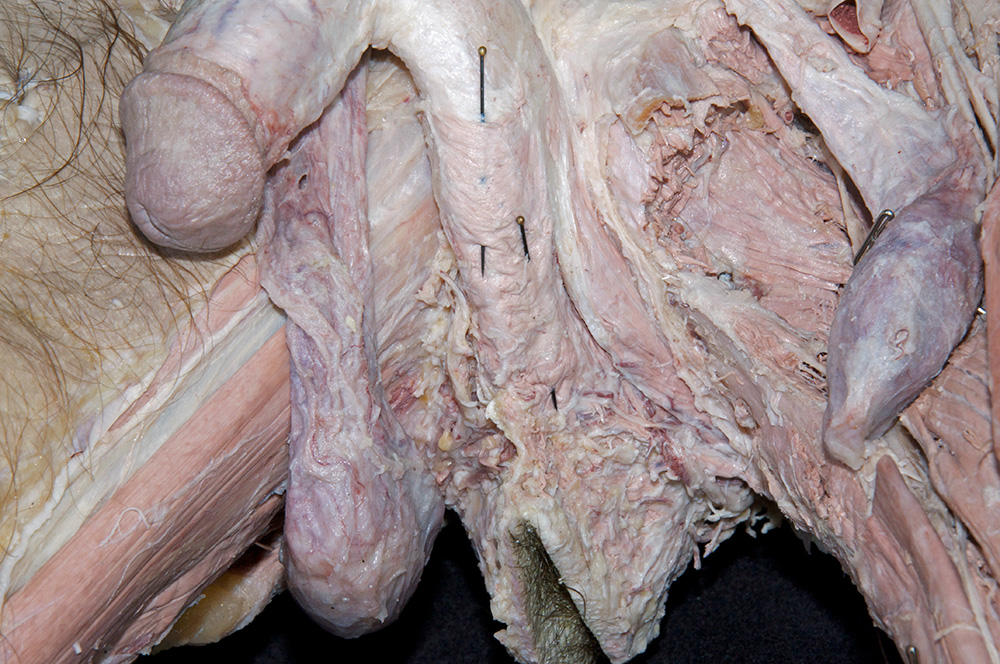
Identify and clean the muscles and erectile tissues of the perineum.
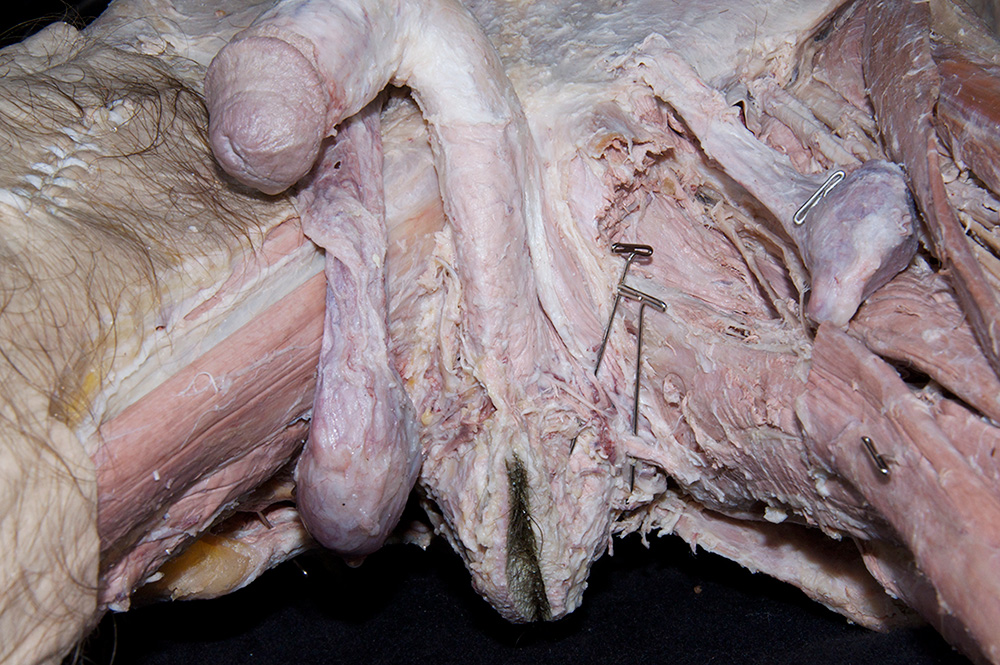
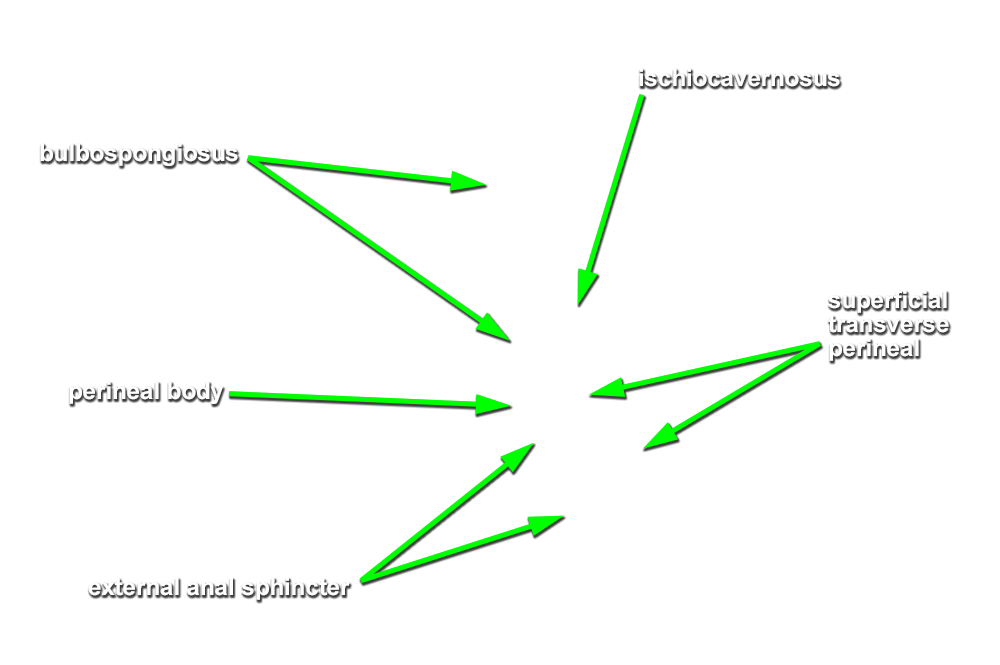
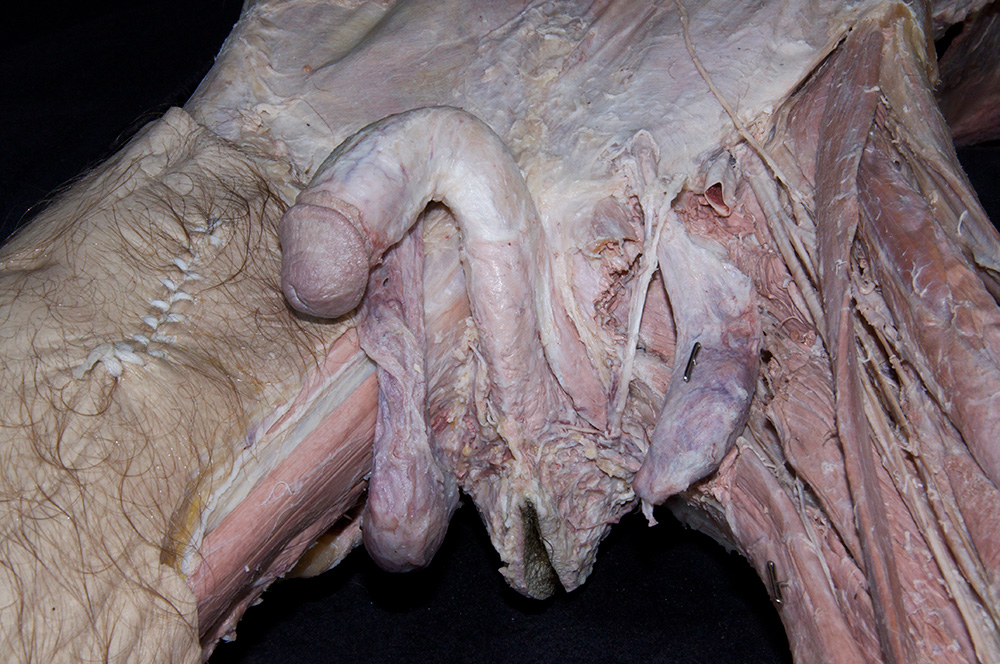
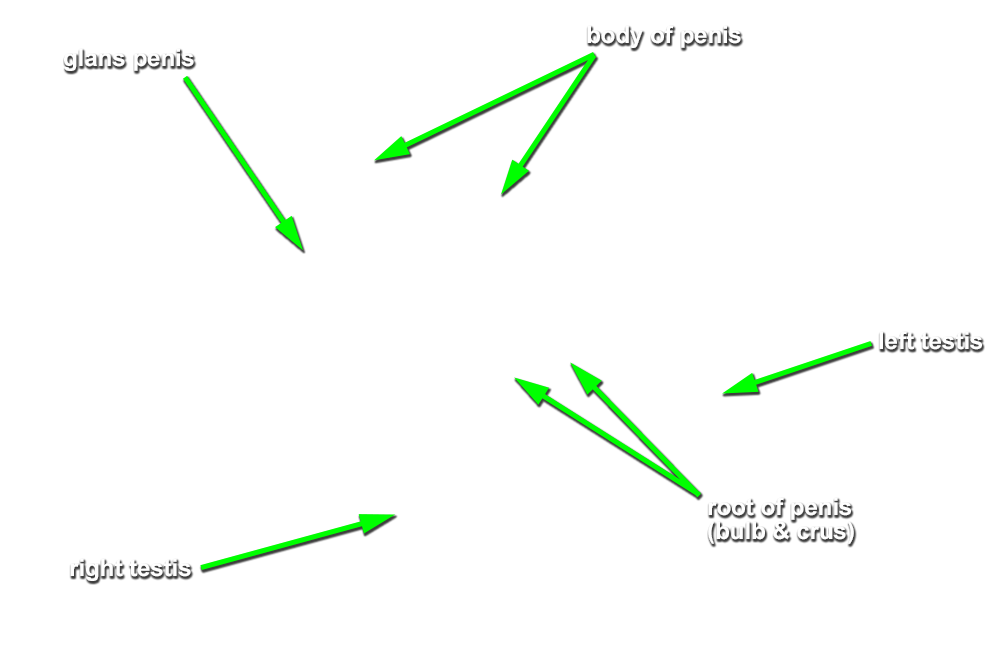
- Identify the perineal body (central tendon) intermediate between the penis and the anus. (G 5.50;N 373;Gl 22.25)
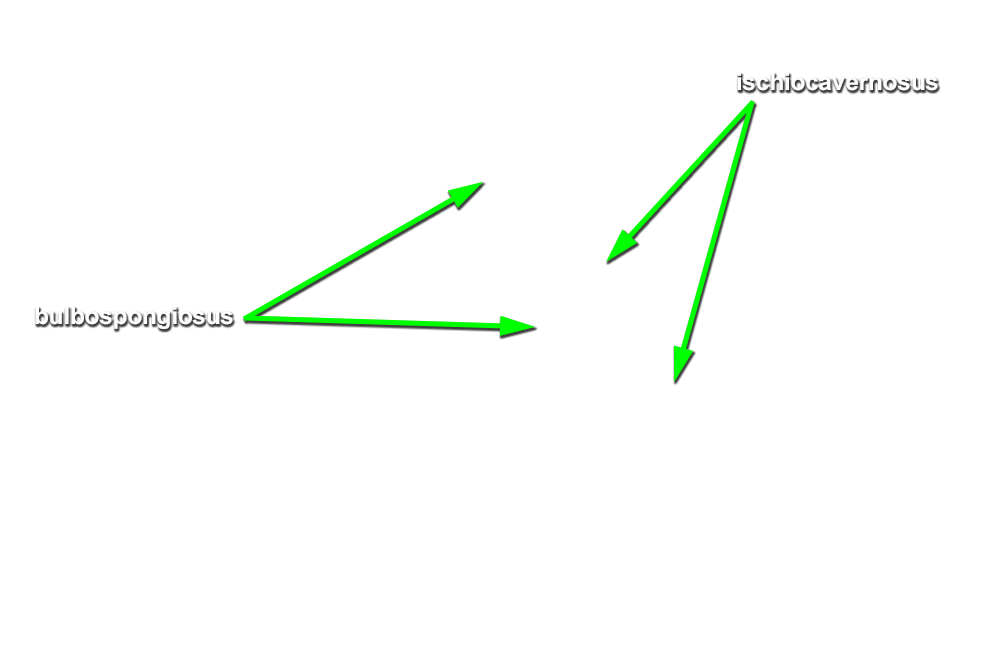
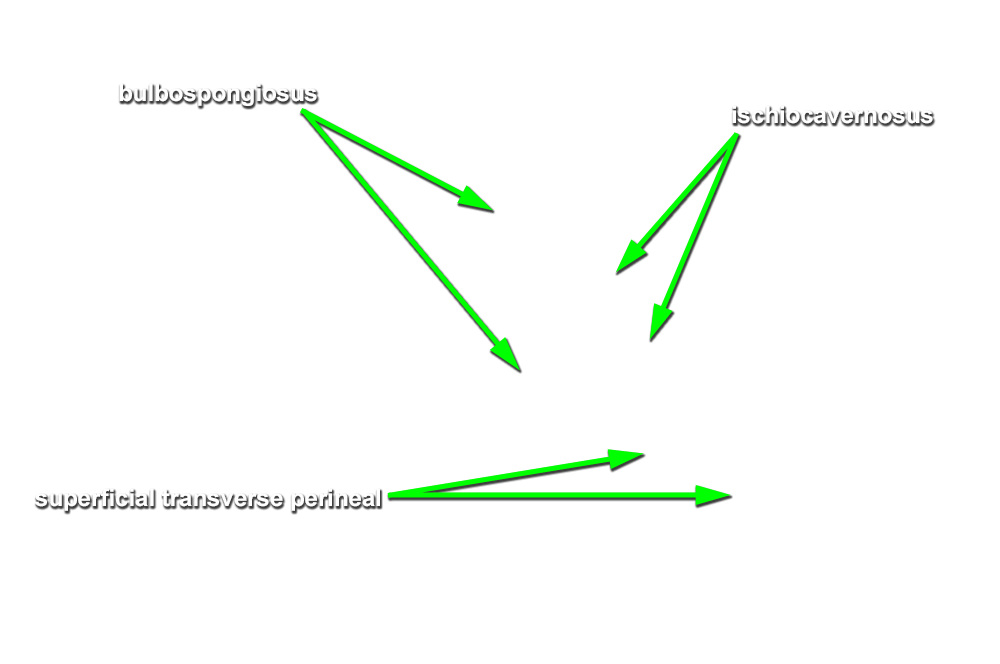
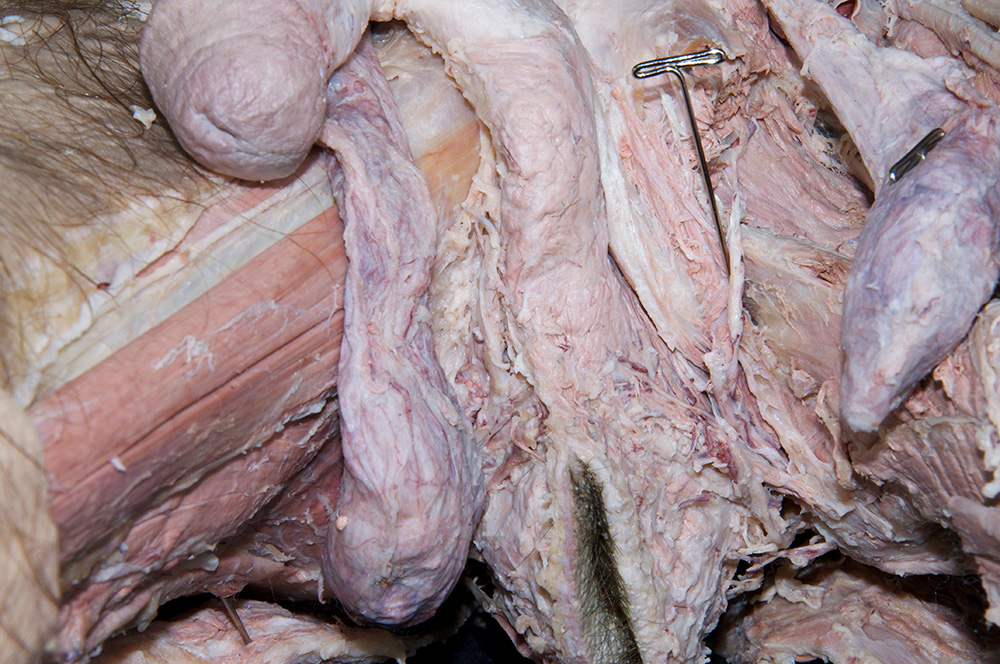
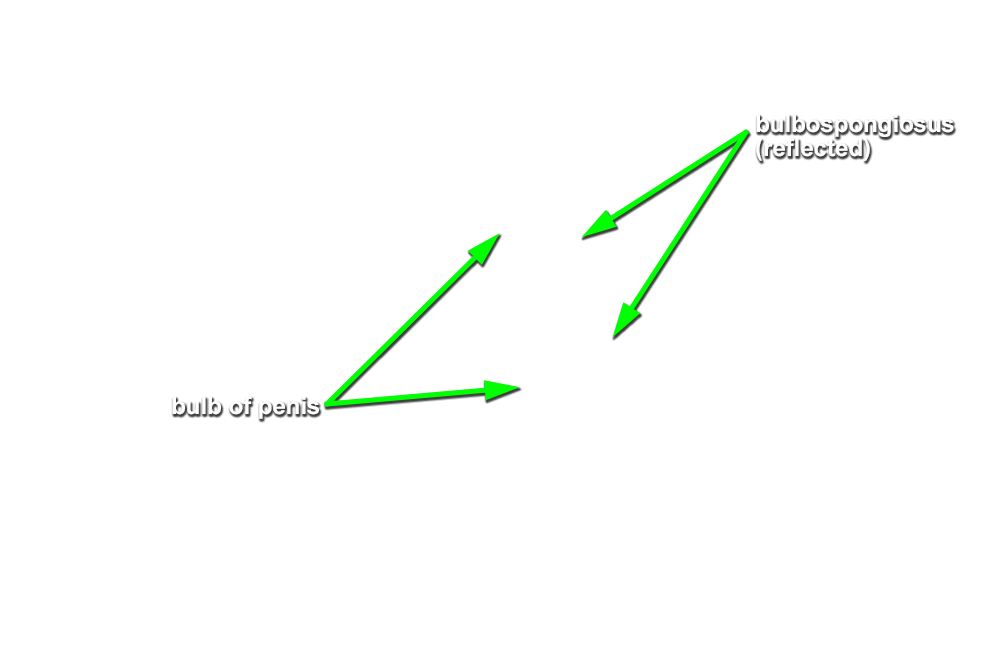
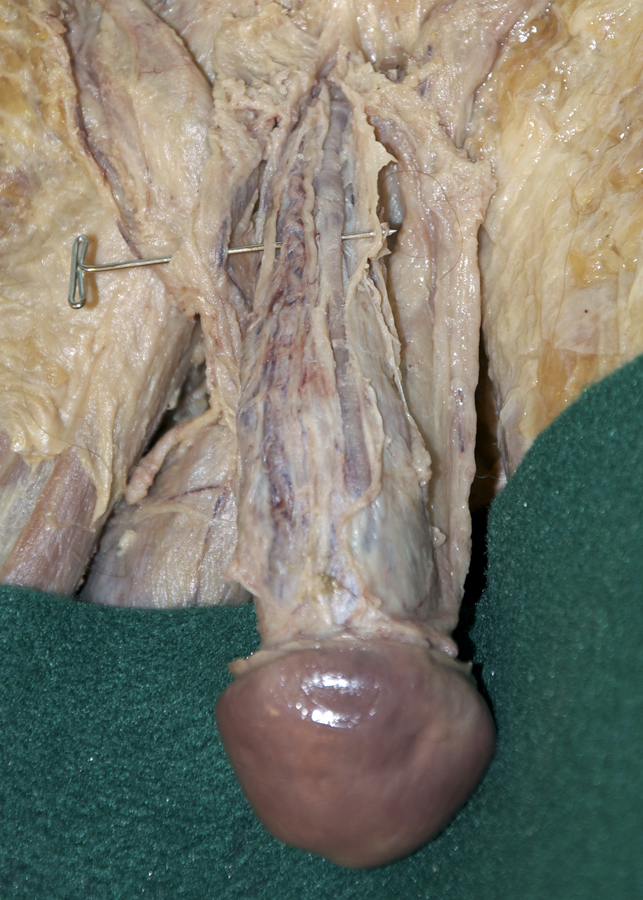
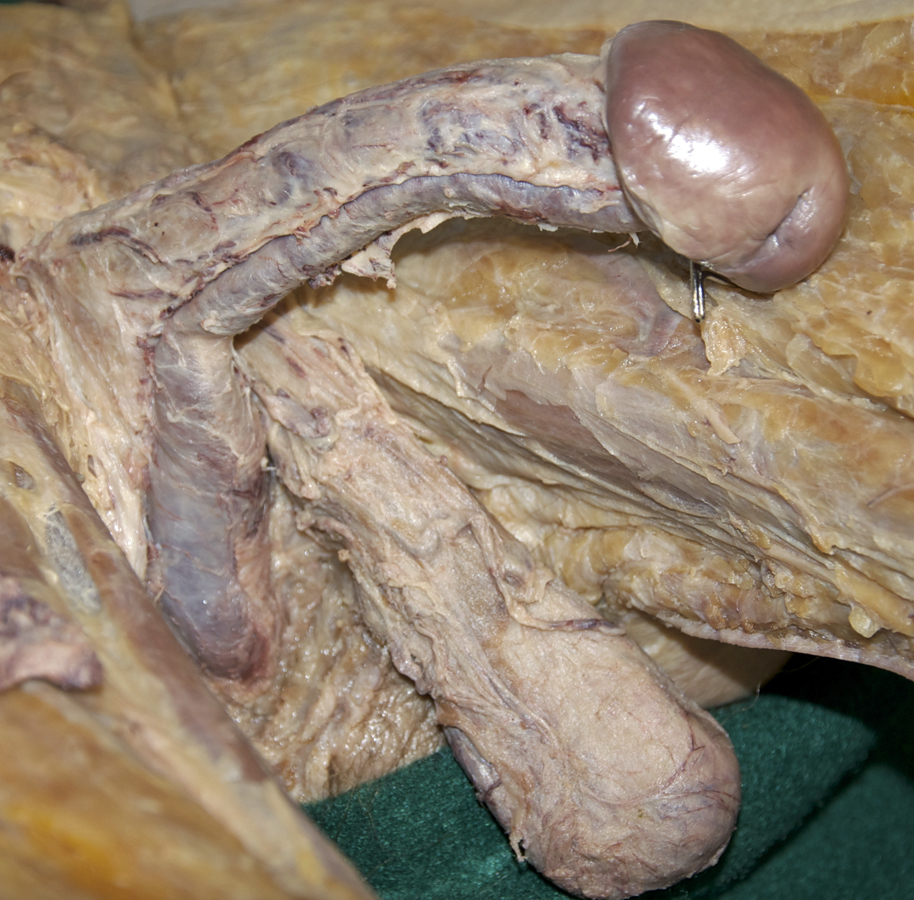
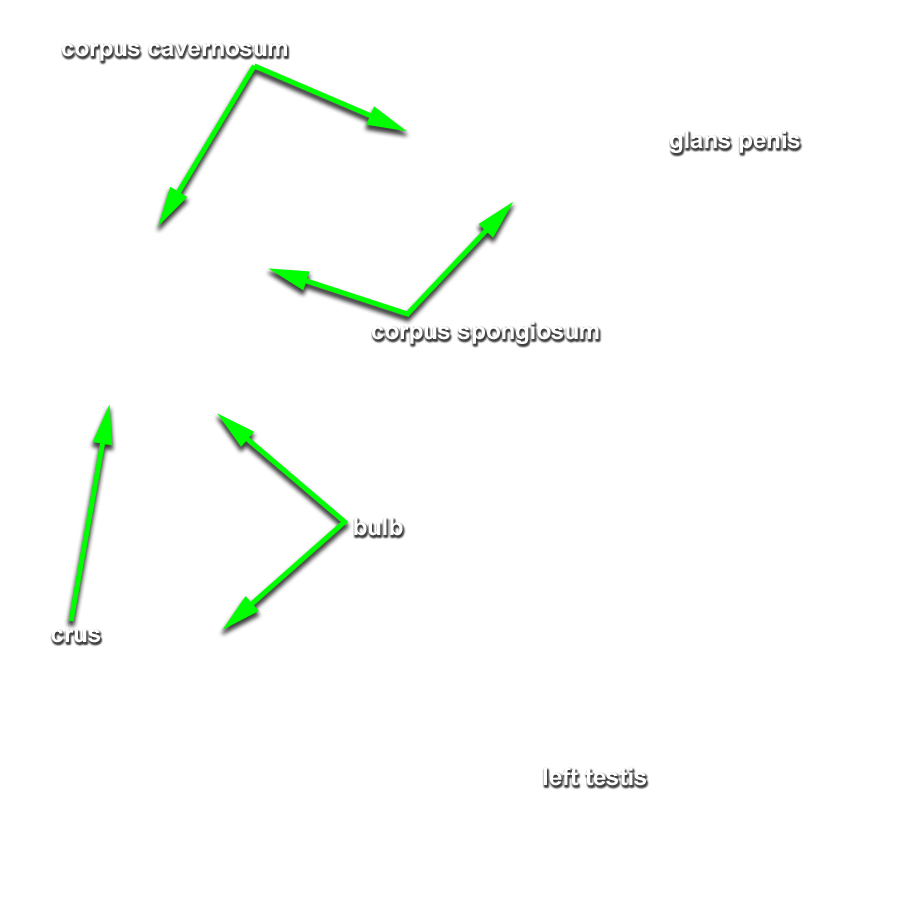
- Identify the bulb of the penis. (G 5.51;N 359;Gl 21.28) Start at the perineal body and carefully blunt dissect along the lateral aspect of the bulb of the penis to identify the bulbospongiosus muscle. (G 5.50;N 359;Gl 21.28) Attempt to completely expose the bulbospongiosus muscle. During this process you are removing the superficial perineal fascia.
- Blunt dissect approximately 2 cm lateral to the bulbospongiosus to expose and identify the ischiocavernosus muscle. (G 5.50;N 359;Gl 21.28)
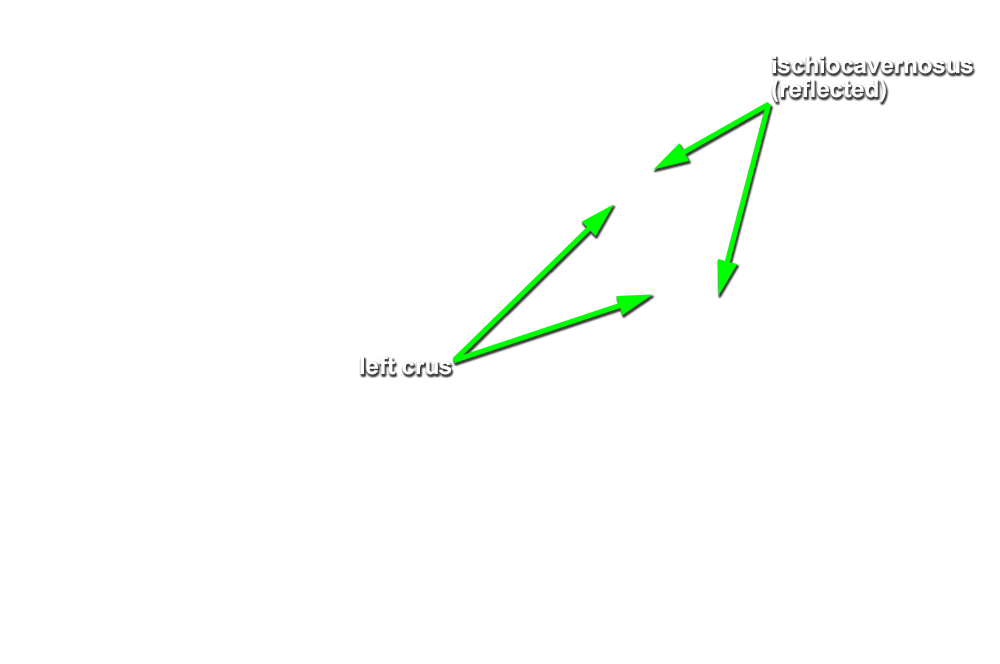
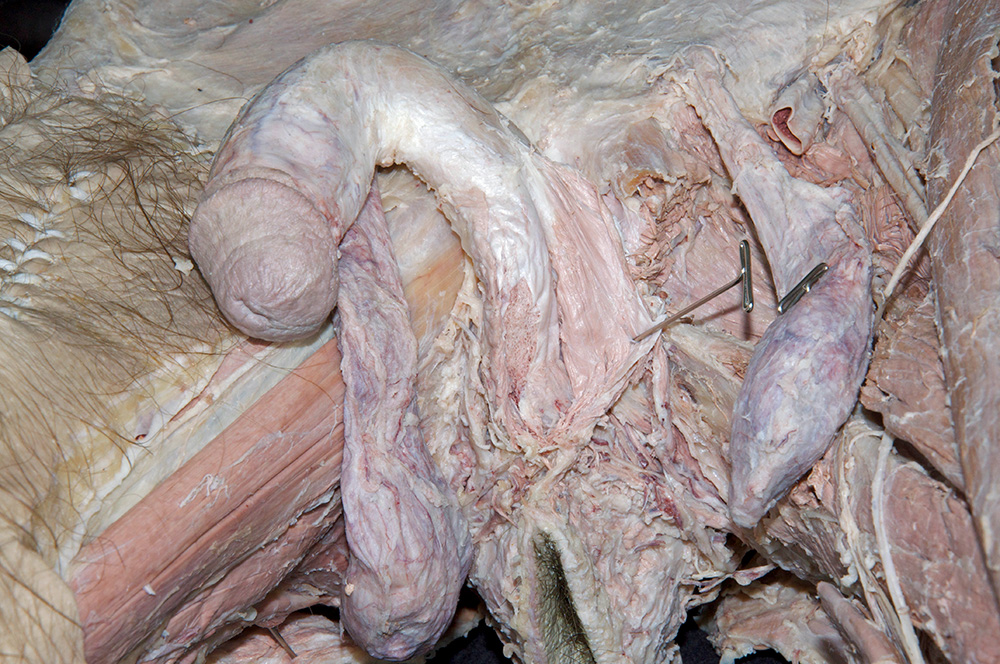
- (ON ONE SIDE ONLY) Carefully (blunt dissect) remove the ischiocavernosus muscle from the perineum. Identify the crus of the penis. (G 5.51;N 360;Gl 21.28) On the same side, reflect the bulbospongiosus muscle to expose the bulb of the penis.
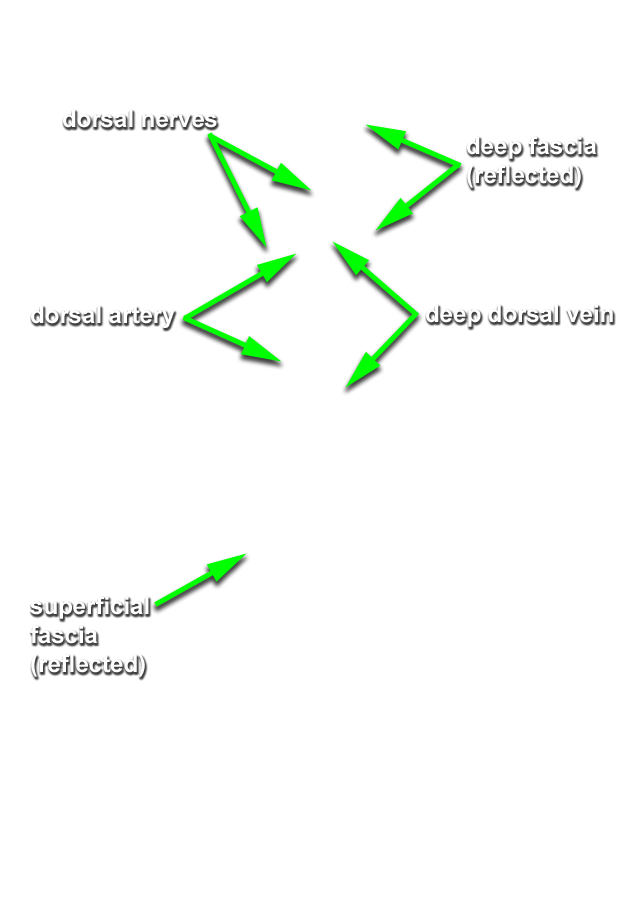
- Identify the body and glans of the penis. (G 5.55;N 360;Gl 21.29) Identify the deep fascia of the penis. (G 3.56;N 360;Gl 22.24) Carefully remove the deep fascia from the penis. Identify the deep dorsal vein (we will not remove this vein), dorsal arteries and dorsal nerves of the penis. (G 5.54;N 359;Gl 22.24) Trace the deep dorsal vein, dorsal arteries and dorsal nerves to the pubic symphysis. Identify the paired corpora cavernosa and the unpaired corpus spongiosum of the penis.
Important Relationships
- The bulbospongiosus muscle is positioned directly superficial to the bulb of the penis.
- The ischiocavernosus muscle is positioned directly superficial to the crus of the penis.
- The deep dorsal vein of the penis passes inferior to the pubic symphysis.