Identify the urogenital diaphragm.
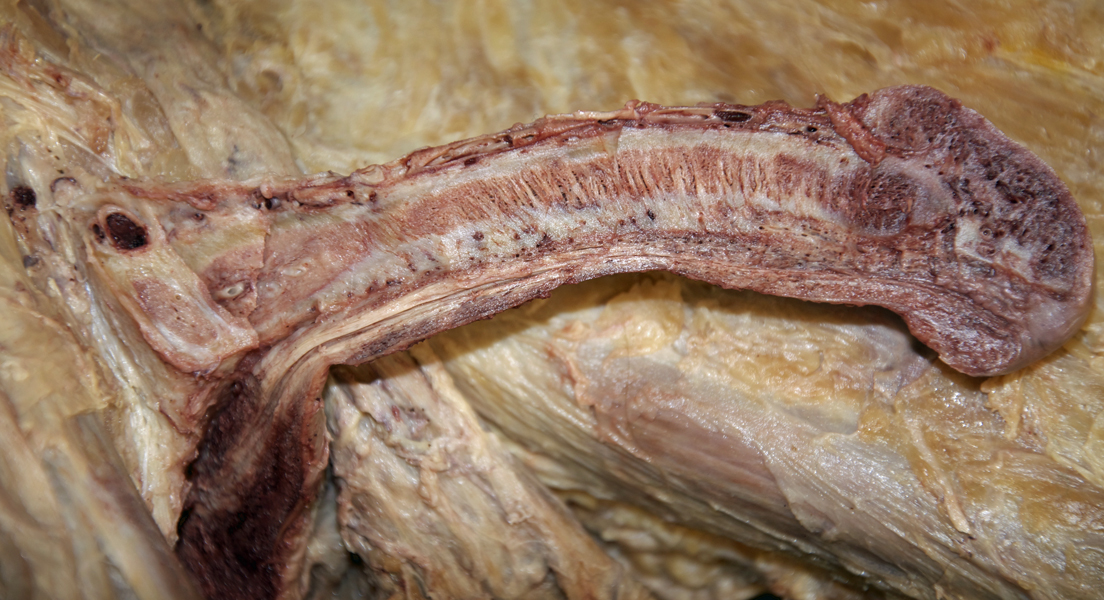
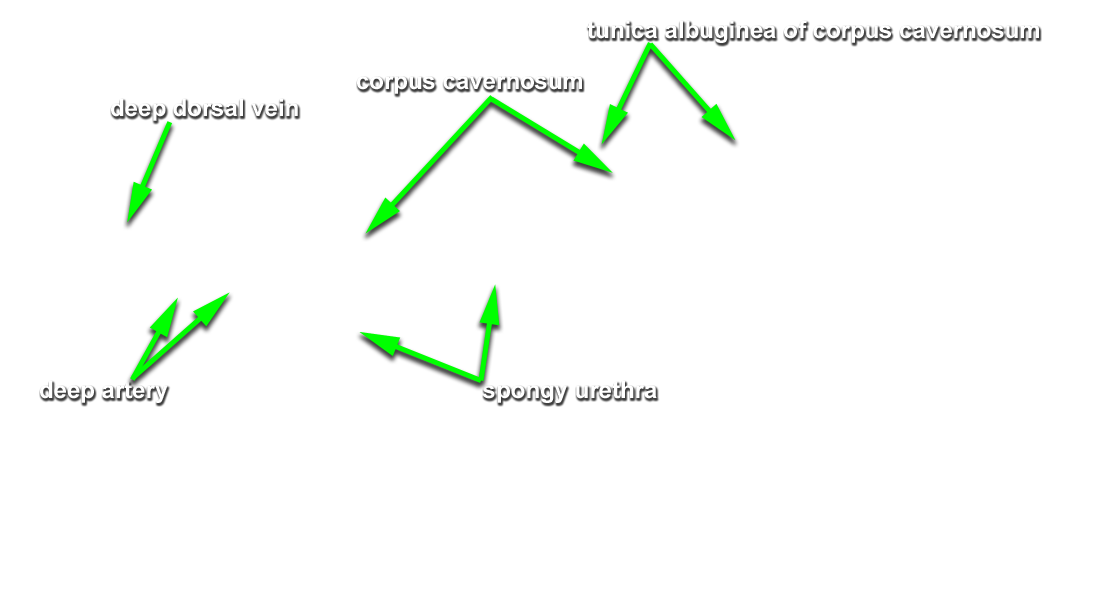
- Place a blunt probe in the penile urethra. With the probe as a guide, use a scalpel to slit open the urethra. (G 5.15A;N 363;Gl 21.28B) Identify the spongy urethra.
- Extend the incision in the posterior and superior direction through the glans, corpus spongiosum and bulb of the penis to the perineal body.
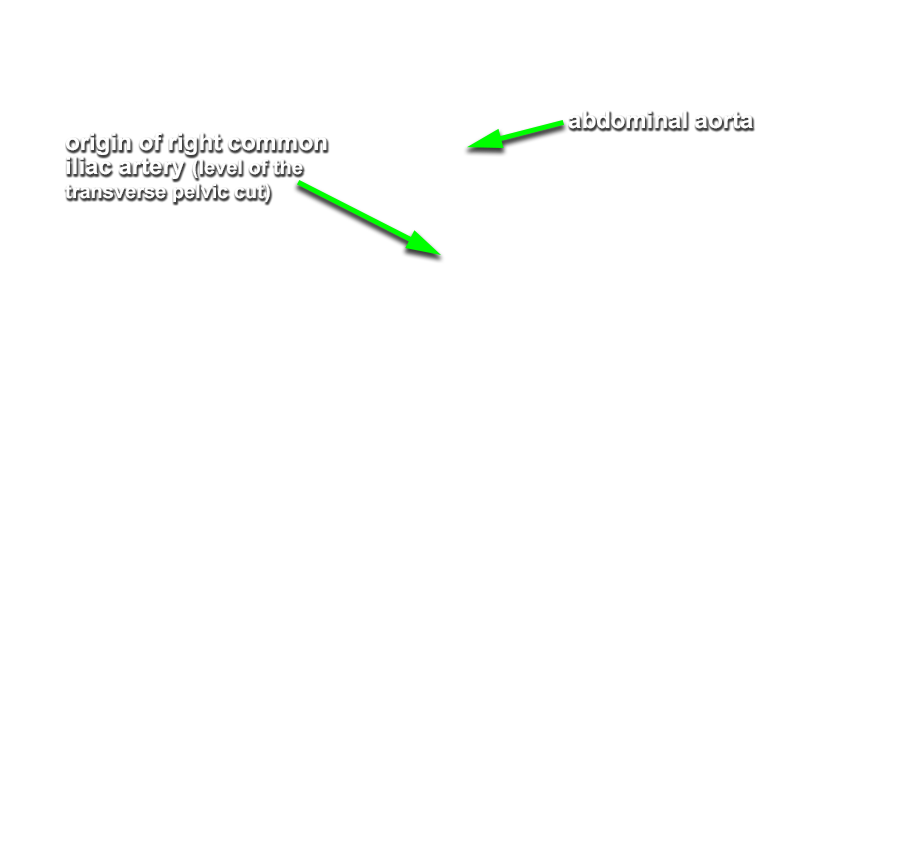
(RIGHT SIDE ONLY) Use a saw to make two cuts through the pelvis. Make a median cut through the pelvis following the incision line through the penis. Extend this cut through the sacrum to the level of the origin of the right common iliac artery. Make a transverse cut from lateral to medial to meet the first saw cut along the midline (level of the origin of the right common iliac artery). Remove the right hemipelvis and lower extremity. Do not extend the transverse cut to the left side of the body. The left common iliac artery and aorta should remain intact. Attempt to identify the membranous urethra, sphincter urethrae muscle and urogenital diaphragm (deep transverse perineus muscle) in the midline cut through the pelvis. (G 5.15A;N 362;Gl 19.17)
Important Relationship
The prostate is positioned superior (deep) to the deep transverse perineal muscle and striated (external) urethral sphincter.