Identify the coverings and structures of the spermatic cord and testes. Refer to an illustration of the anterior abdominal wall, spermatic cord and testis. (G 4.16;N 256;Gl 13.14) Note how each layer of the anterior abdominal wall contributes a covering of the spermatic cord and testes.
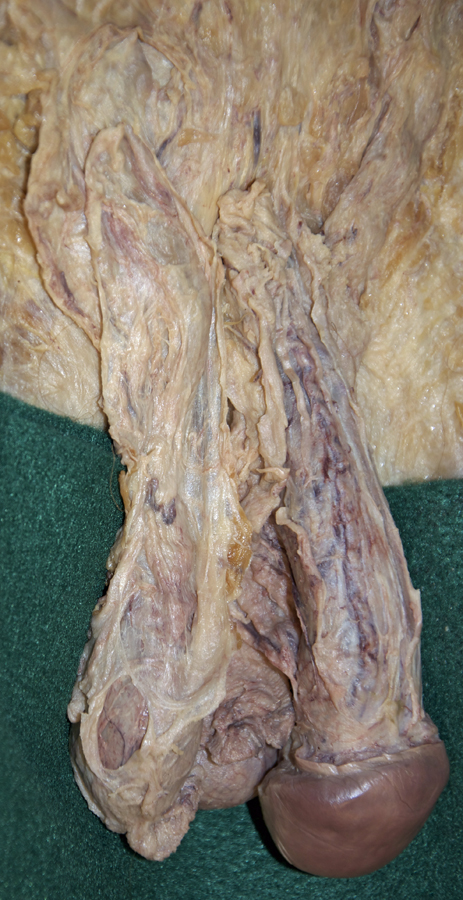
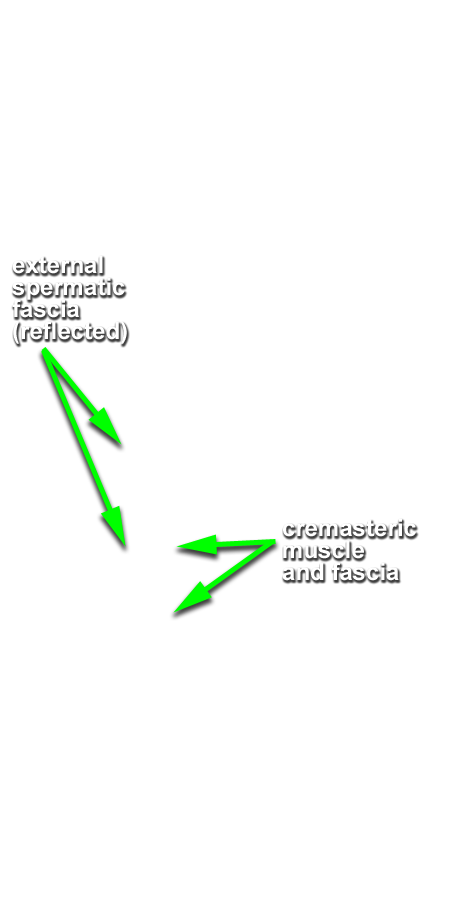
- Identify the external spermatic fascia (G 4.16;N 365;Gl 13.14) covering the spermatic cord and testis.
- Identify the cremaster muscle and fascia. (G 4.16;N 365;Gl 13.14)
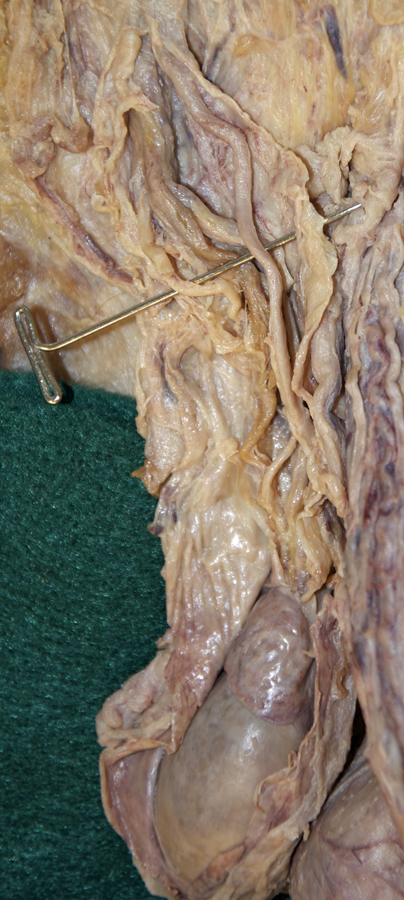
- Identify the internal spermatic fascia. (G 4.16;N 365;Gl 13.14) The cremaster, cremaster fascia and internal spermatic fascia may be fused. The outer surface is then the cremaster and the inner surface is the internal spermatic fascia.
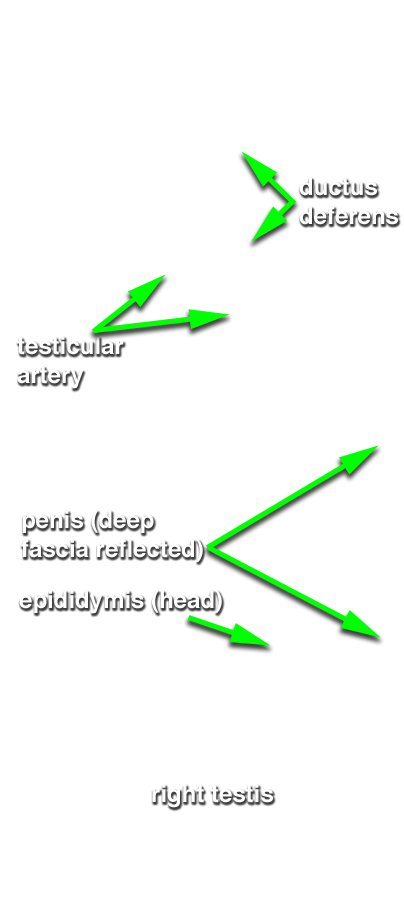
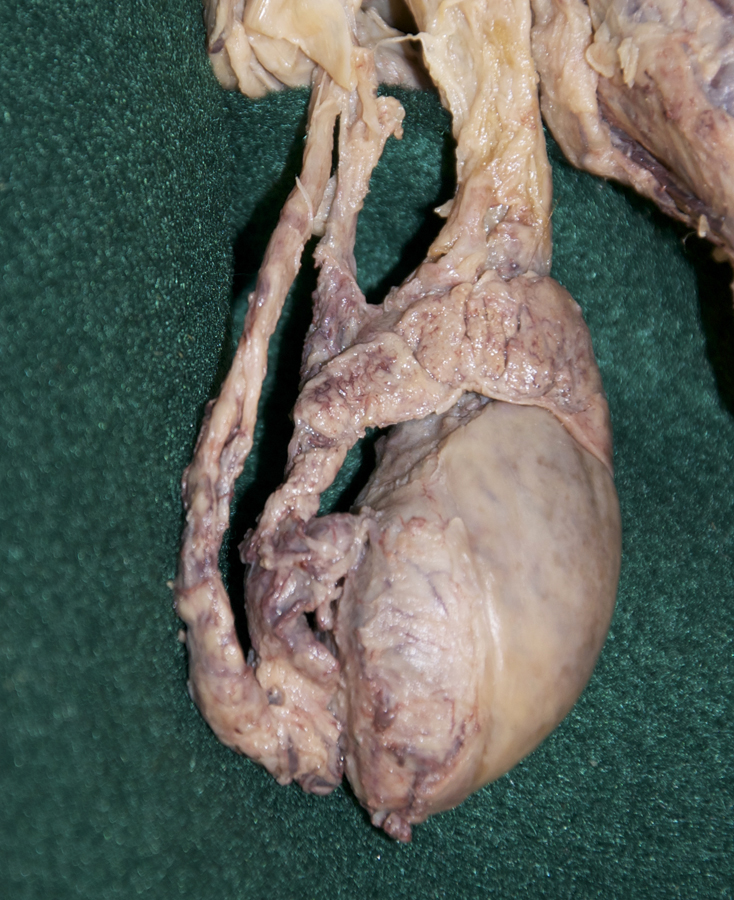
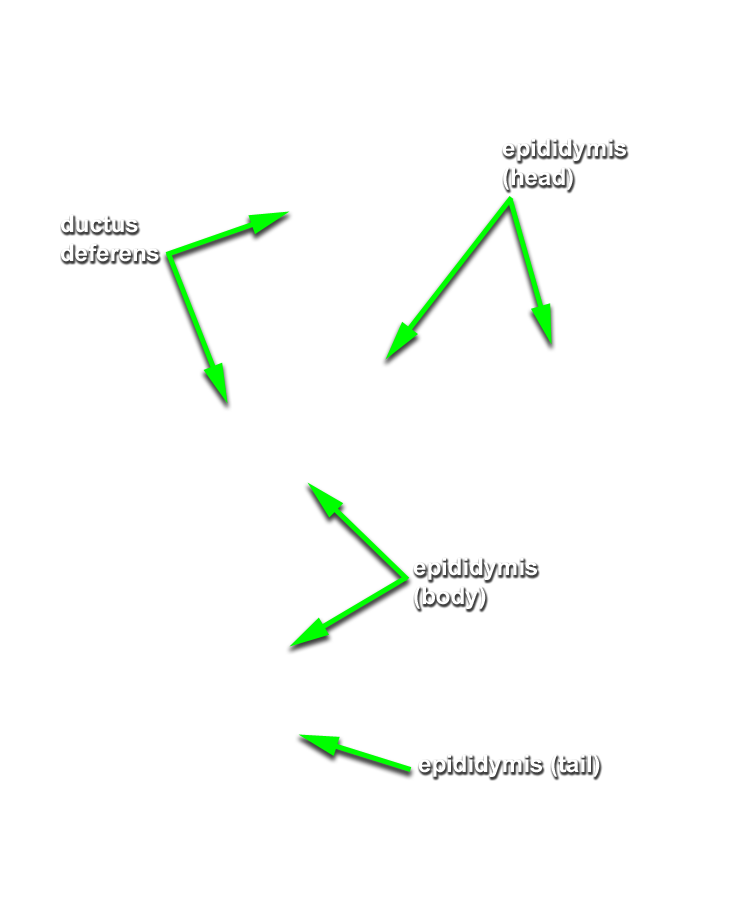
- Identify the ductus deferens, testicular artery and testicular vein (pampiniform plexus). (G 4.19A;N 365;Gl 13.14) Attempt to identify the genitofemoral nerve and cremasteric and ductus deferens arteries.
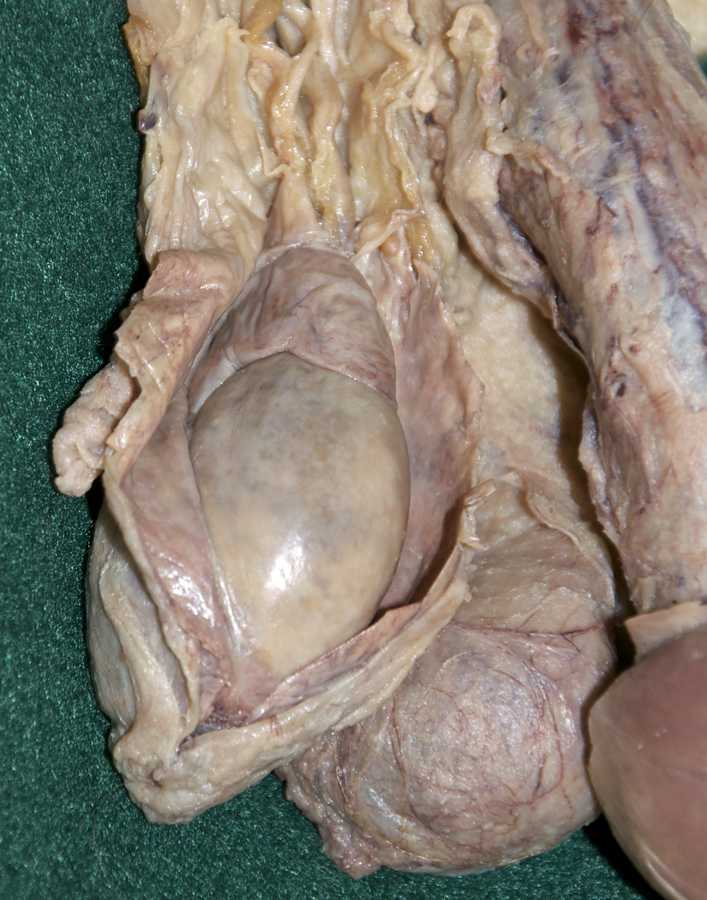
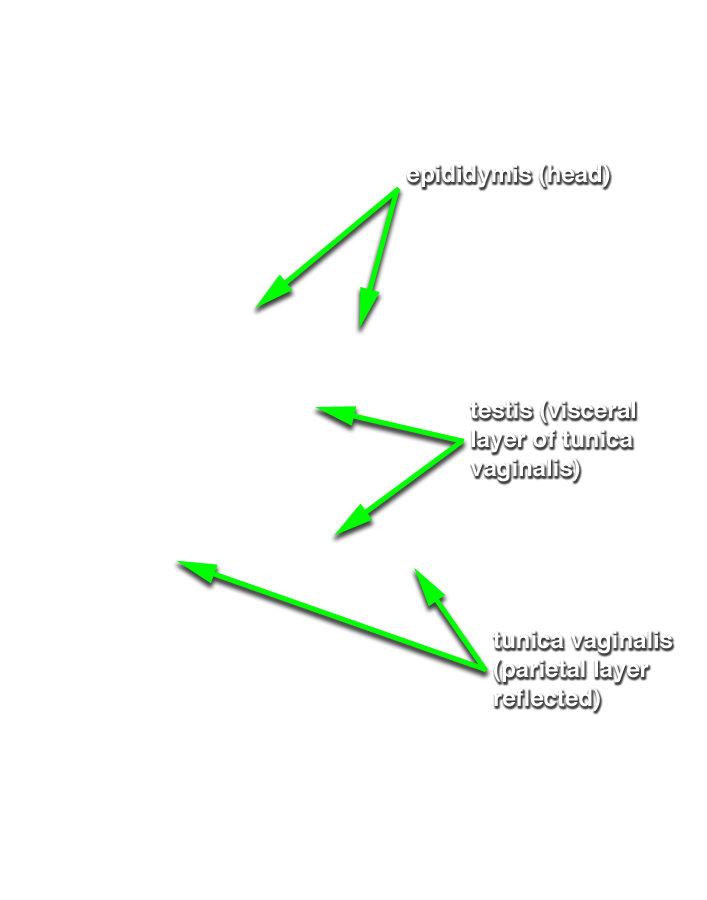
- Identify the tunica vaginalis, testis and epididymis. (G 4.19B;N 365;Gl 13.16) Identify the tail, body and head of the epididymis. (G 4.20A;N 368;Gl 13.16) Identify the tunica albuginea. (G 4.20B;N 368;Gl 13.16) Attempt to identify one or more efferent ductules extending from the testis to the head of the epididymis.