(ON BOTH SIDES) Identify the arteries and nerves of the pelvis.
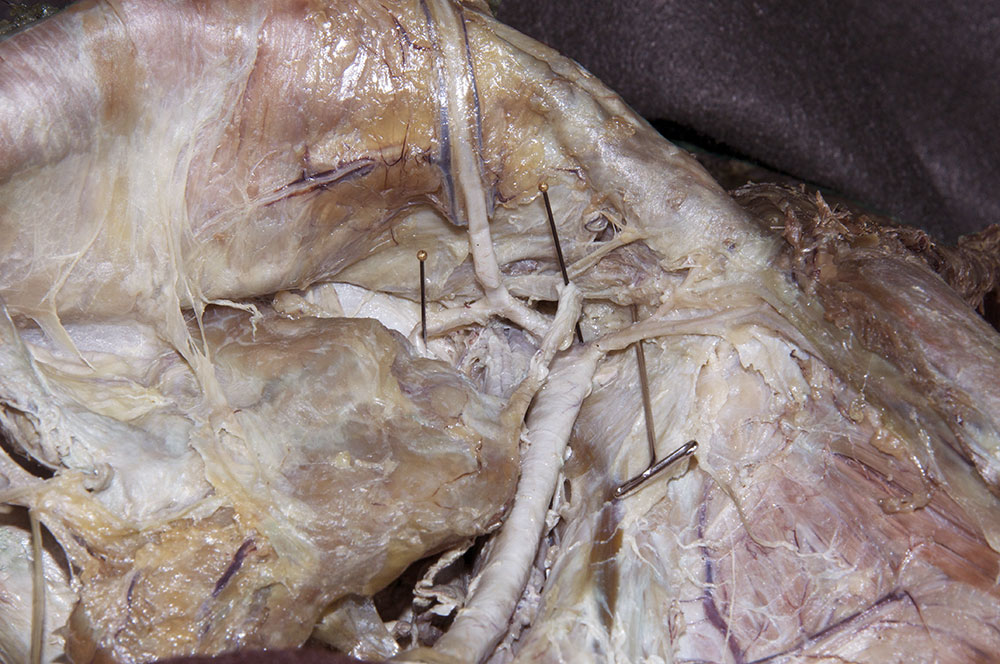
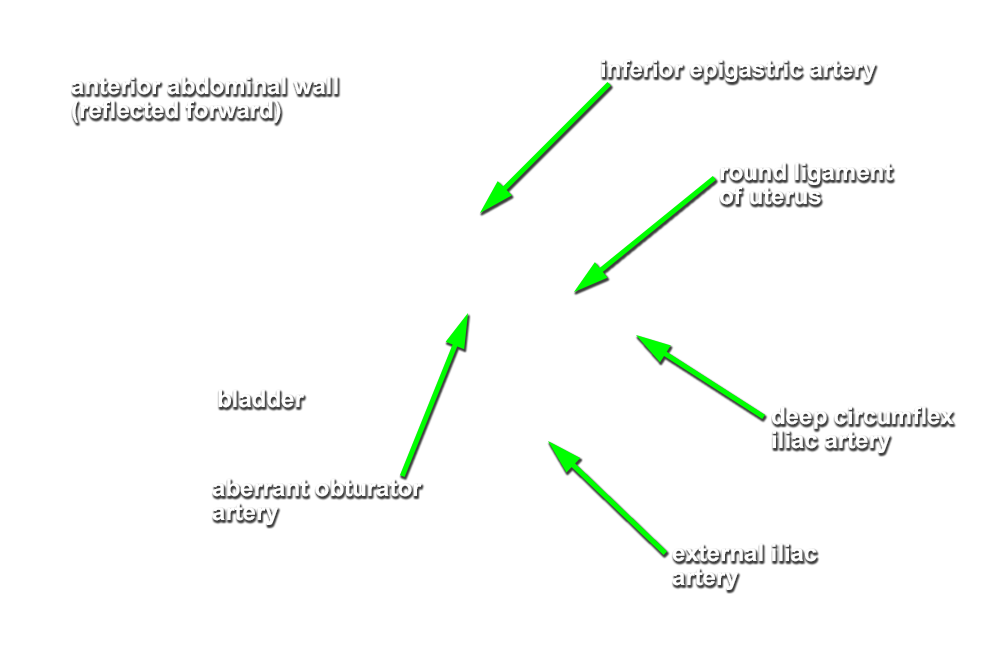
- Identify the external and internal iliac arteries. (G 5.38;N 378;Gl 21.5) Identify the inferior epigastric artery where it arises from the external iliac artery. Attempt to identify the origin of the deep circumflex iliac artery.
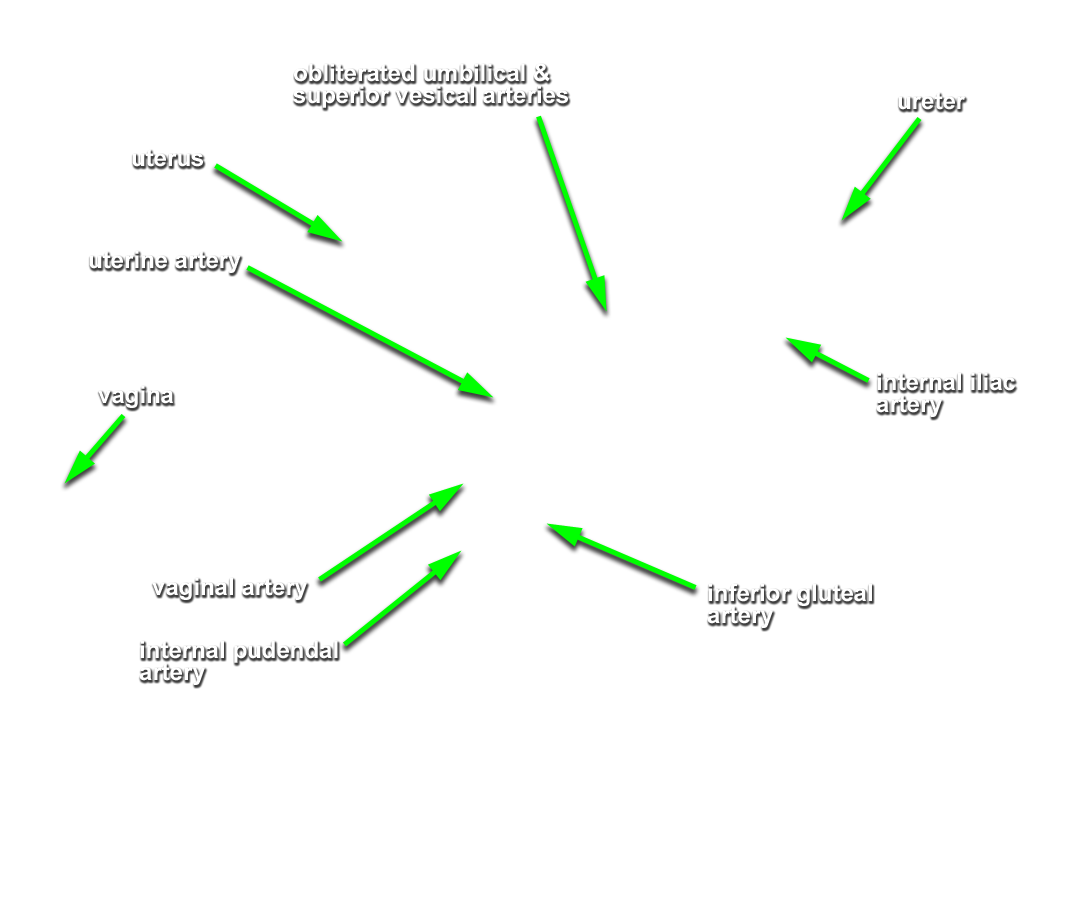
- Identify the obliterated umbilical artery extending to the anterior abdominal wall (median umbilical fold). Identify the superior vesical arteries typically arising from the proximal segment of the obliterated umbilical artery. (G 5.38;N 378;Gl 22.1B)
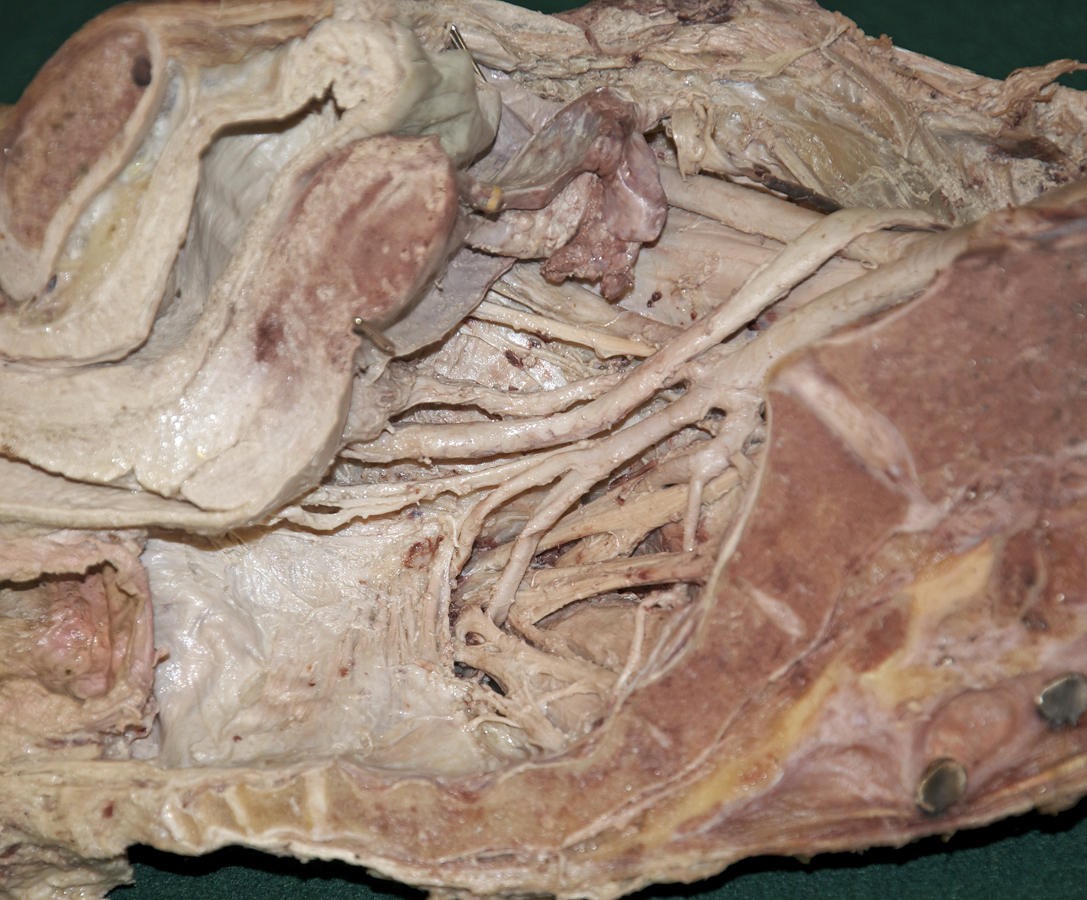
- Identify the obturator artery exiting the pelvis with the obturator nerve.
- Identify the uterine artery passing directly superior to the ureter. (G 5.32B;N 342 and 350;Gl 22.4A) Attempt to identify the vaginal artery.
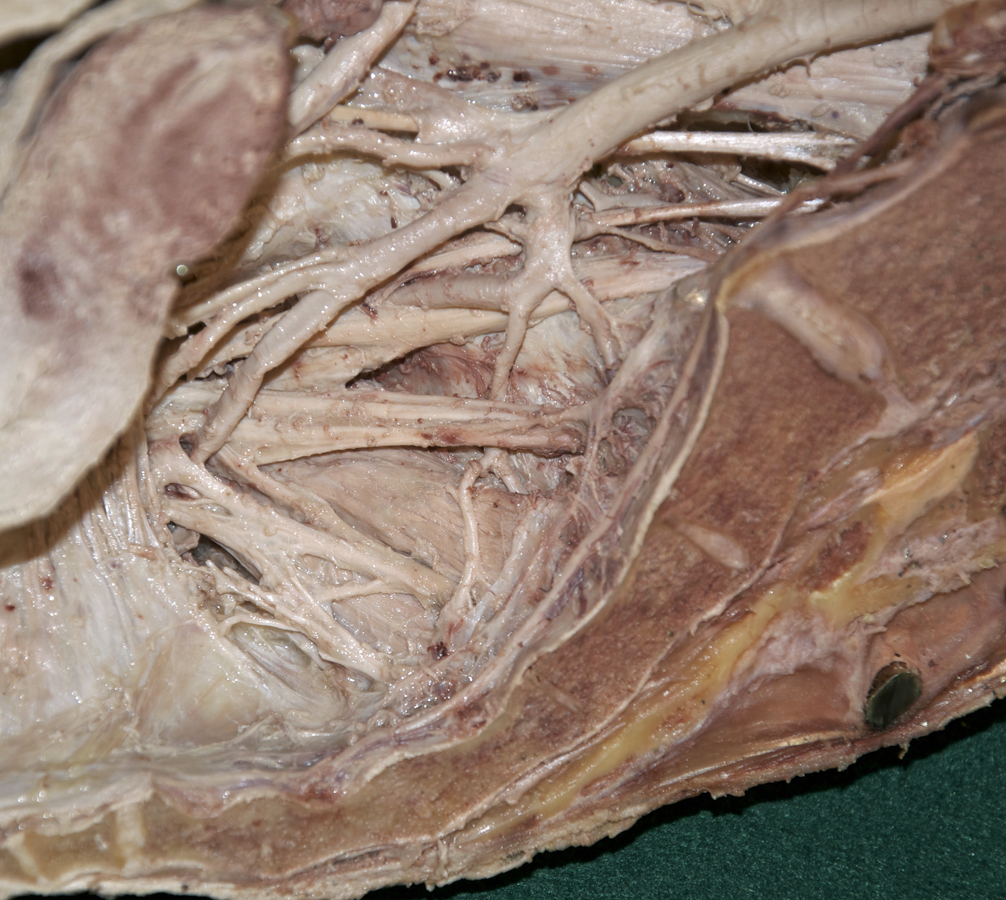
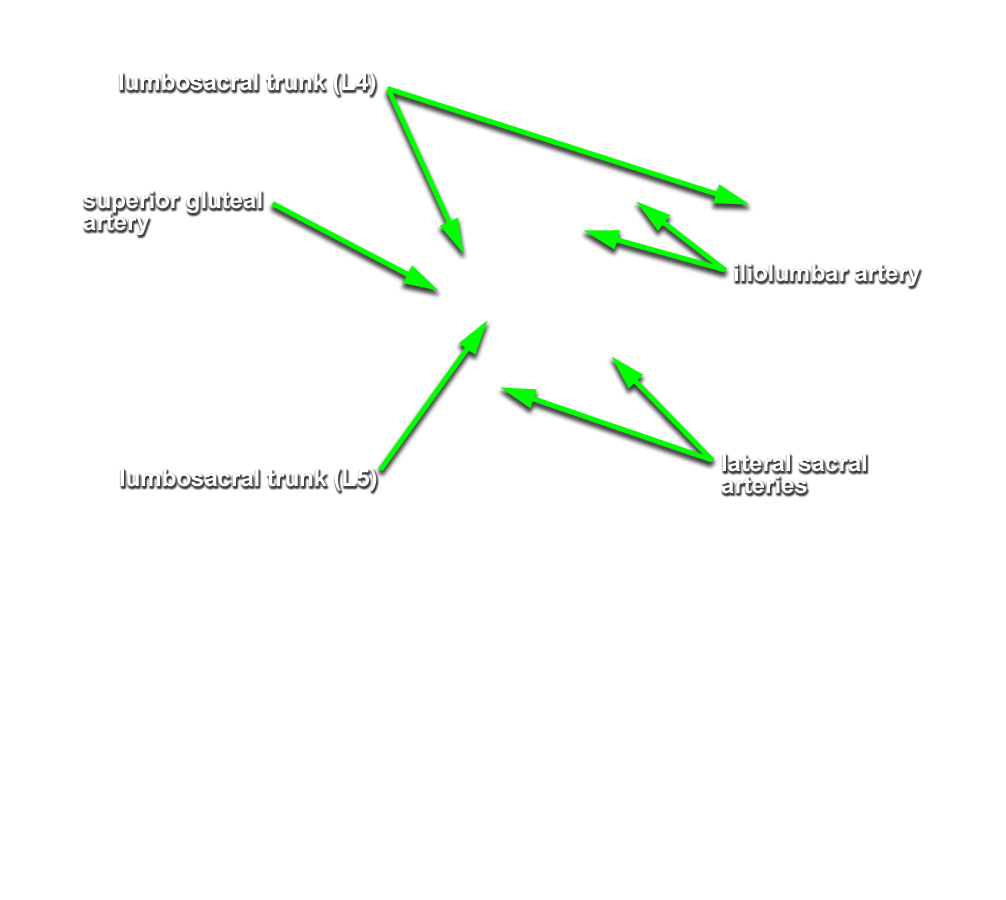
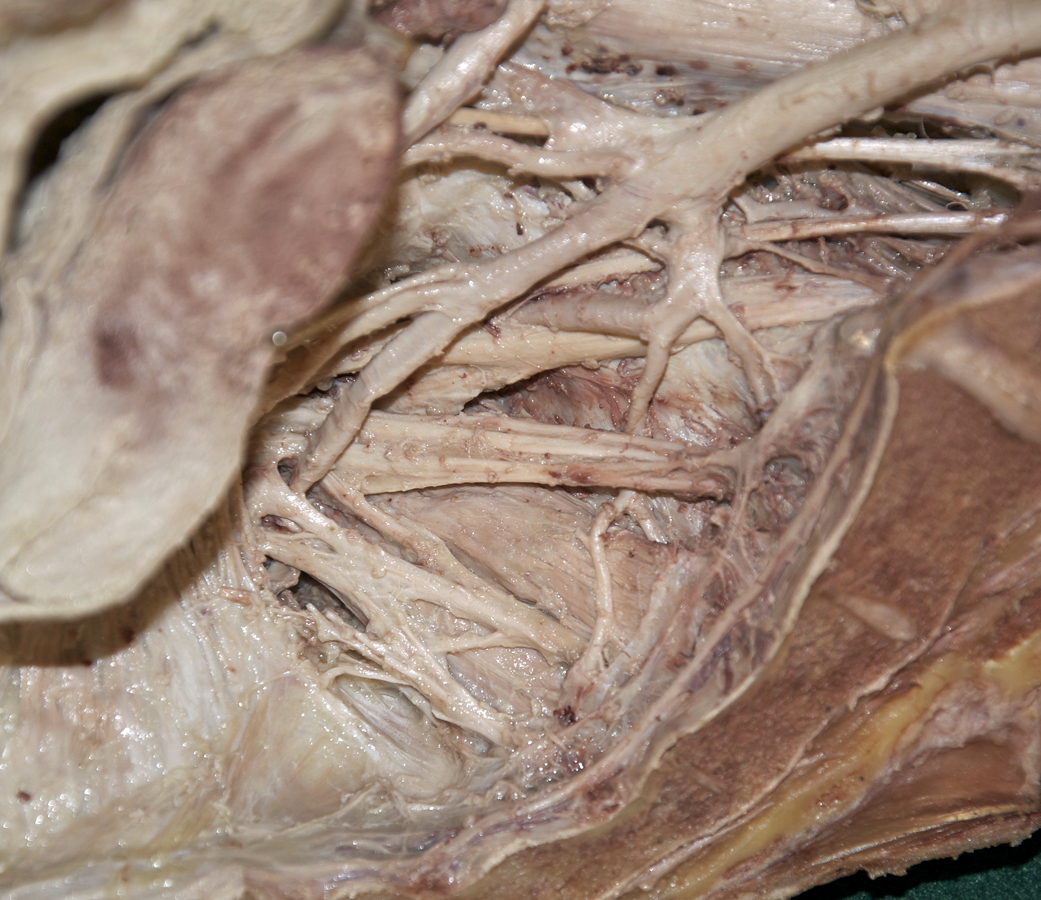
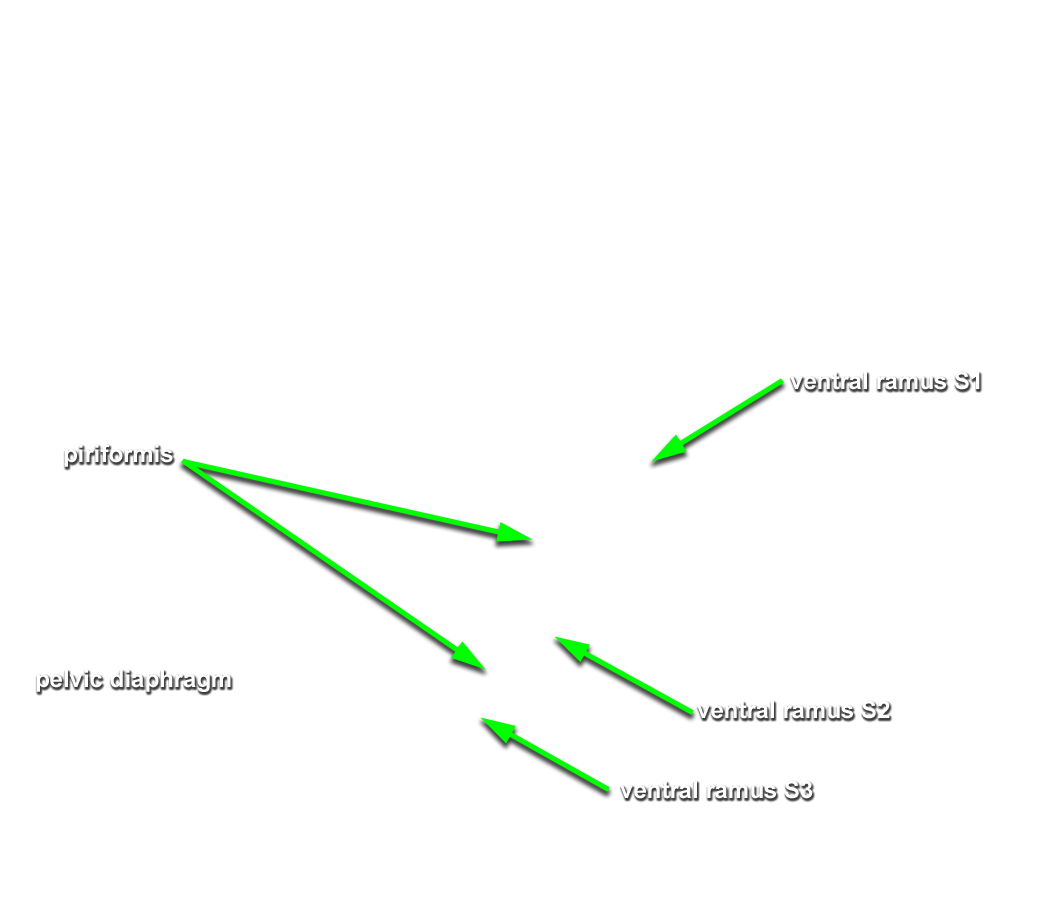
- Return to lumbosacral trunk. Trace the lumbosacral trunk distally until it is joined by ventral rami S1 and S2. (G 4.78;N 380;Gl 16.34) Identify the iliolumbar and lateral sacral arteries. (G 5.13;N 380;Gl 22.1) Identify the superior gluteal artery. (G 5.17;N 380;Gl 22.1) The superior gluteal artery typically passes between the lumbosacral trunk and ventral ramus S1. Identify the inferior gluteal artery. (G 5.17;N 380;Gl 22.1) The inferior gluteal artery often passes between ventral rami S1 and S2.
- Identify the internal pudendal artery. If you are not sure of your identification of the superior gluteal, inferior gluteal and internal pudendal arteries, then return to the gluteal region. Clamp one or more of the arteries with a hemostat and gently tug on the arteries while observing the pelvic branches of the internal iliac artery. Identify the piriformis muscle. (G 5.10A;N 338;Gl 19.13C) Attempt to identify the pudendal nerve as it arises from the sacral plexus.
Important Relationship
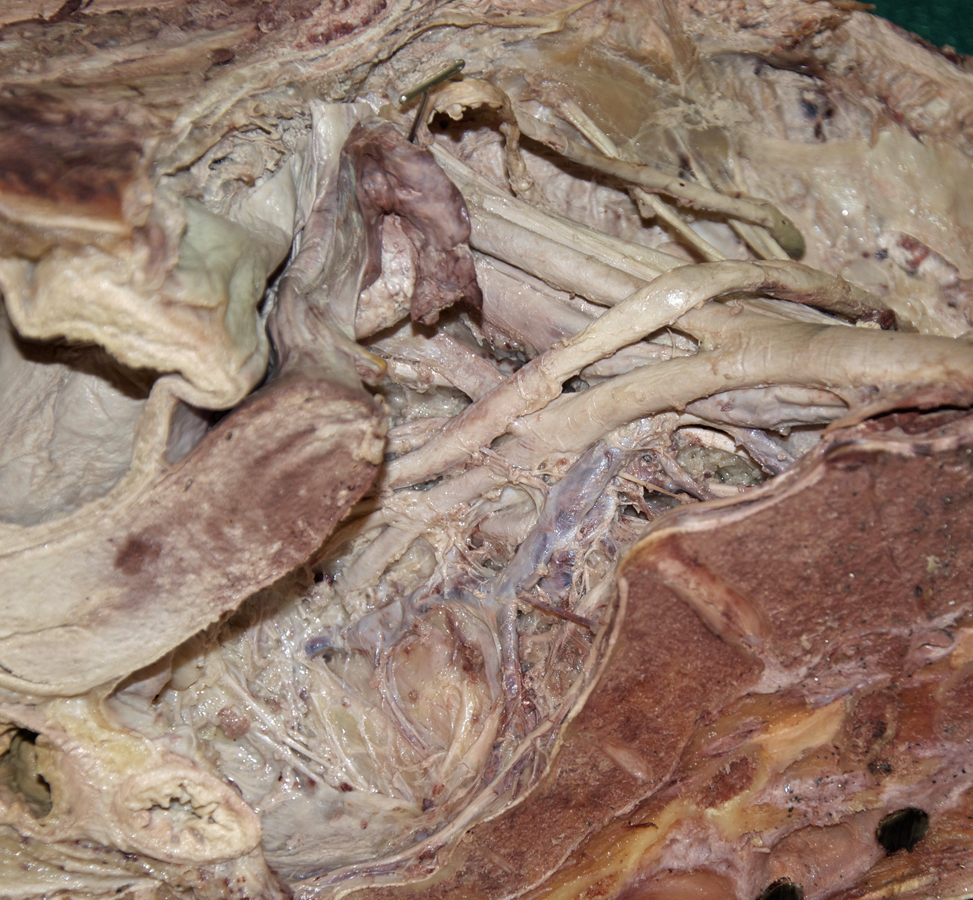
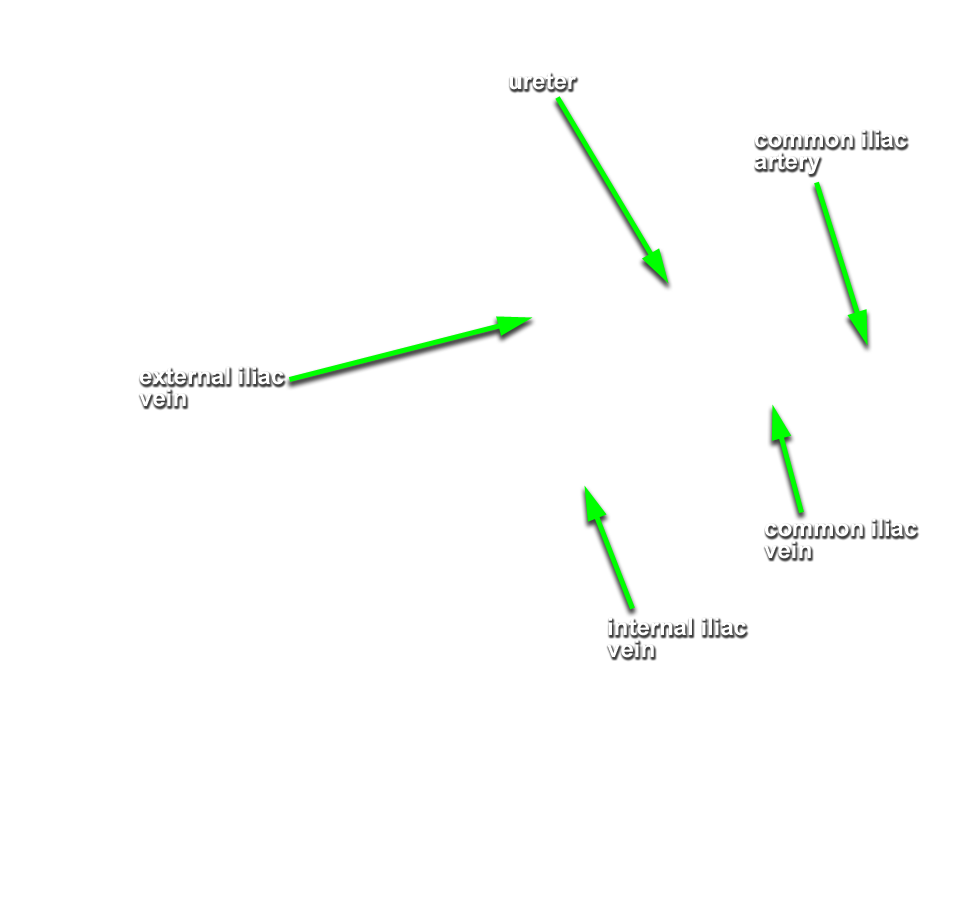
- The left common iliac vein is positioned posterior-medial to the common iliac artery.
- The external iliac vein is positioned posterior-medial to the external iliac artery.
- The obturator artery, vein and nerve pass inferior to the superior pubic ramus.
- The ureter passes posterior and inferior to the uterine artery.
- The ureter passes superior and anterior to the vaginal artery.
- The lumbosacral trunk passes anterior to the sacrum (ala).