Identify the internal features of the heart.
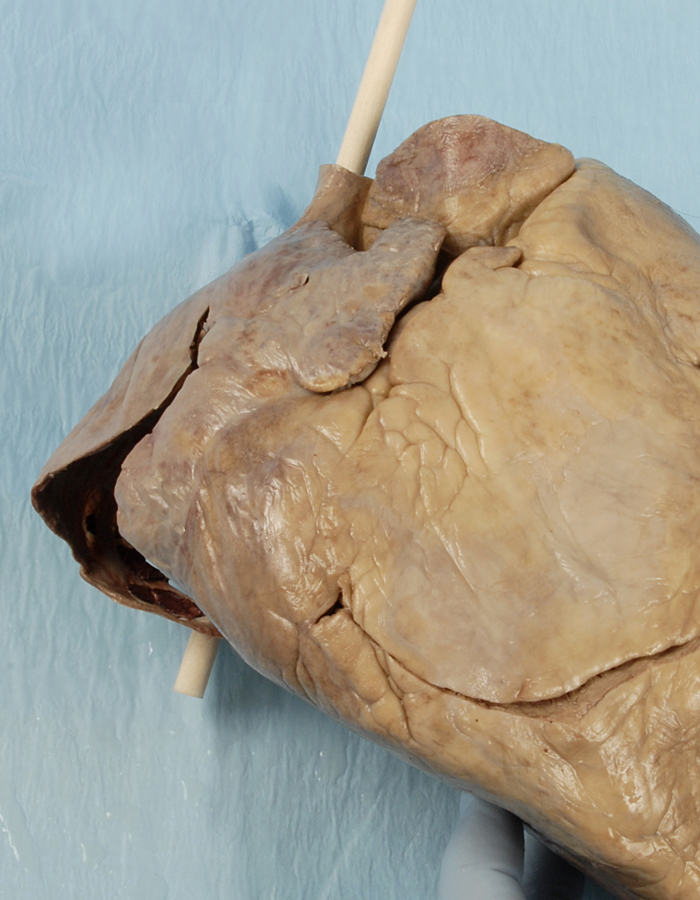
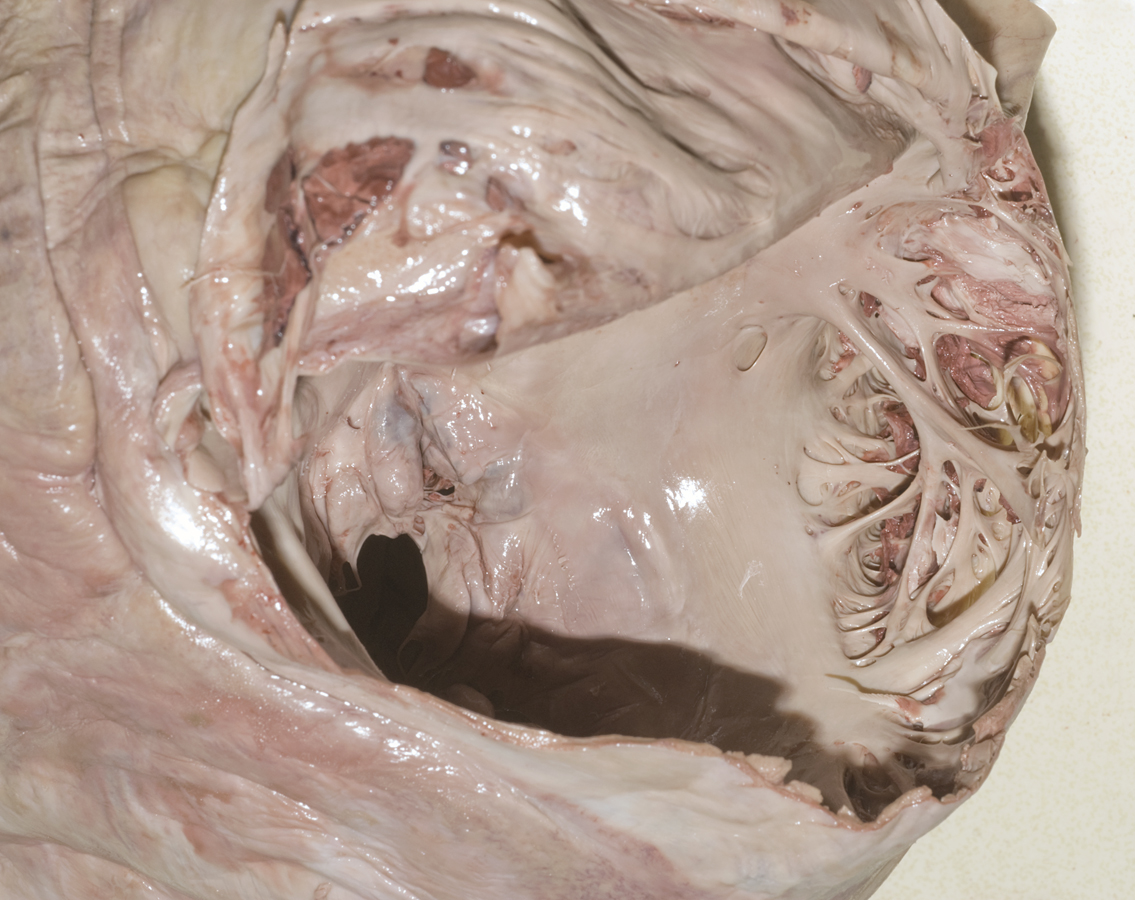
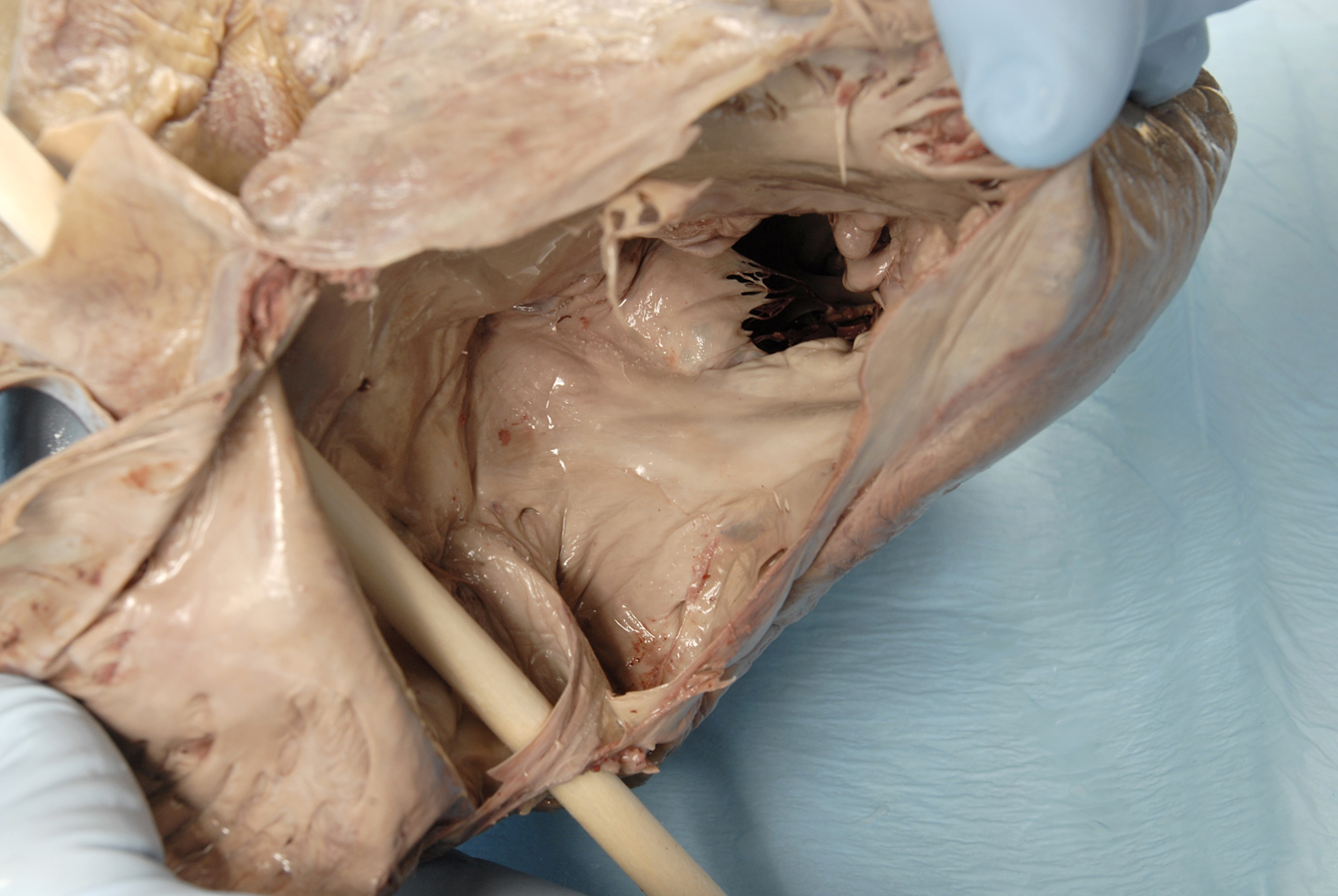
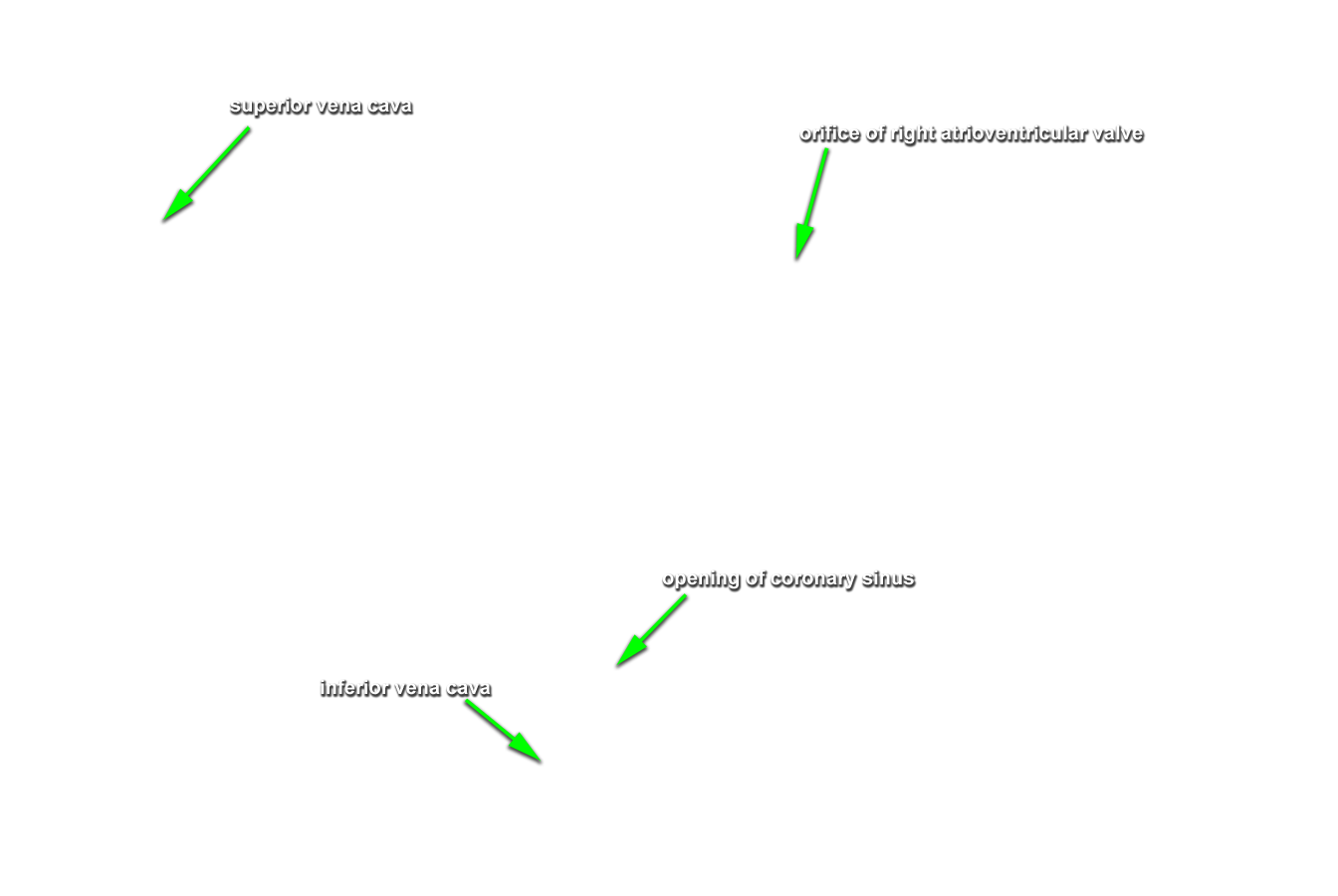
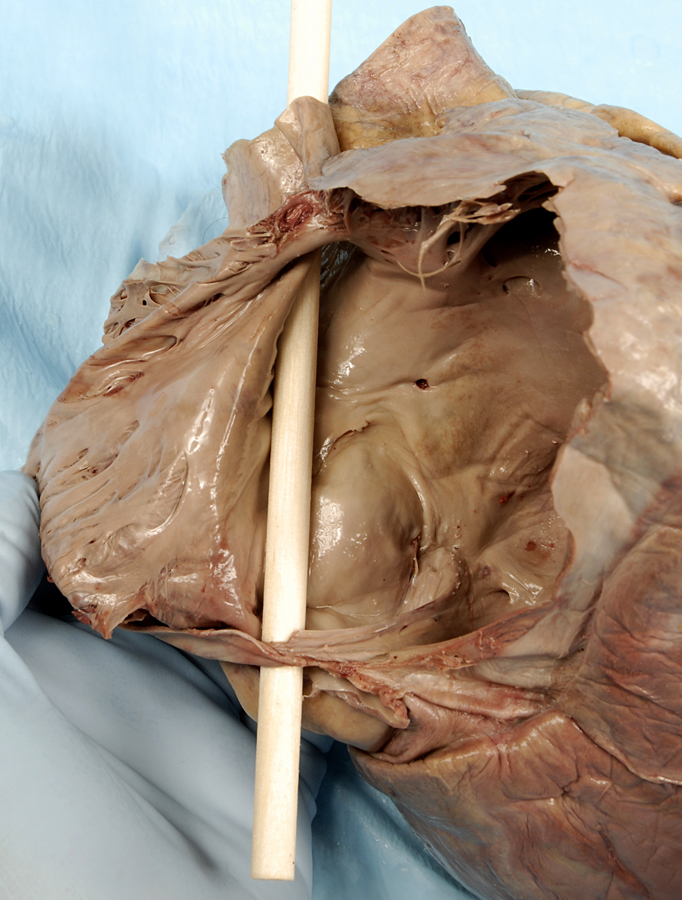
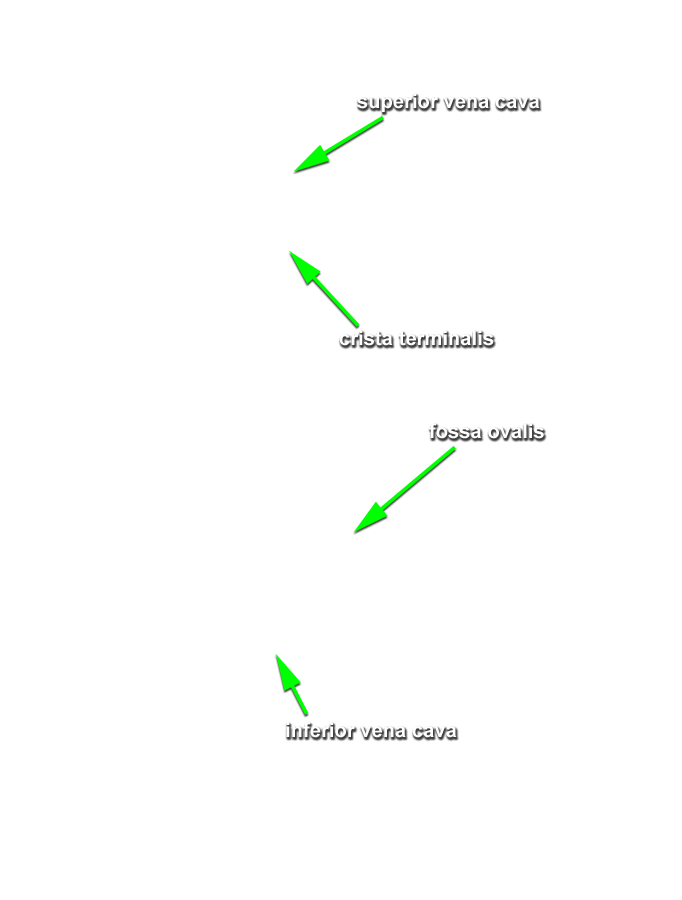
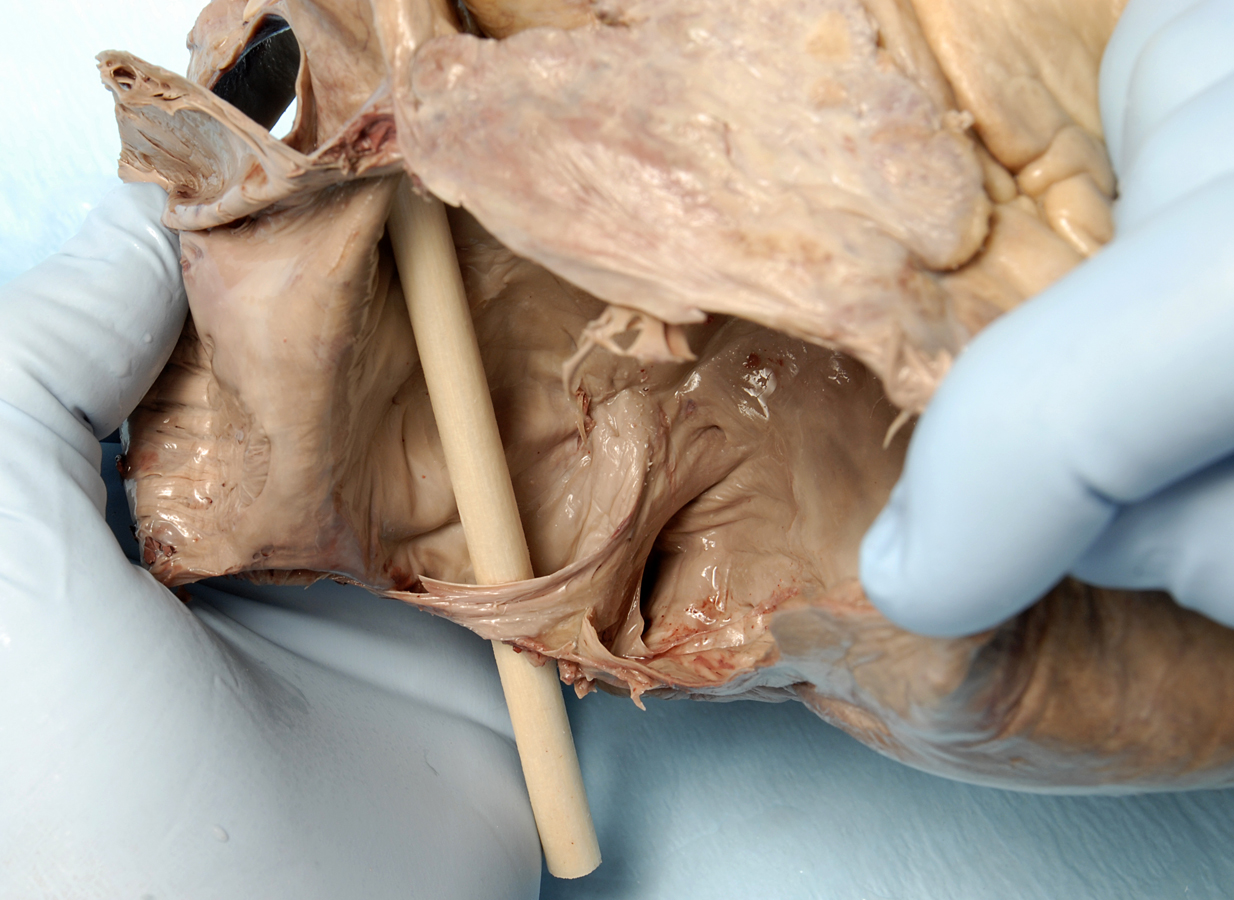
- Reflect the wall of the right atrium and identify the pectinate muscles. Identify the openings of the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. Attempt to identify the valve of the IVC. Identify the orifice of the right atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve. Identify the smooth walled interatrial septum with the fossa ovalis (oval fossa) and the opening of the coronary sinus. Identify the crista terminalis. This is a ridge of tissue where the rough and smooth walled portions of the right atrium meet. (G 3.54;N 217;Gl 9.12B) The S-A node is positioned where the crista terminalis meets the base of the SVC. The A-V node is located in the interatrial wall immediately superior to the opening of the coronary sinus.
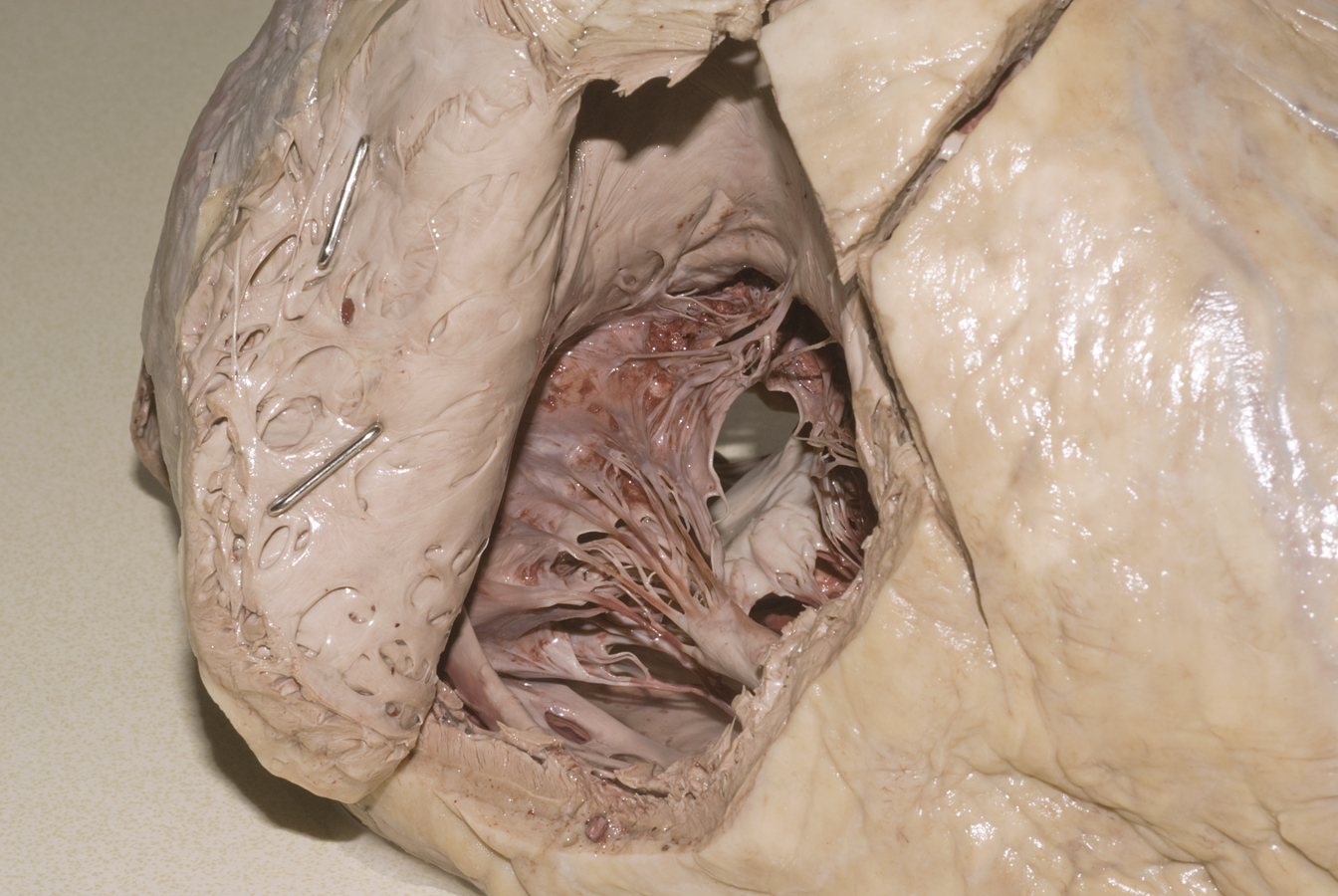
- Identify the cusps of the pulmonary (artery) valve from the superior view. (G 3.58;N 219;Gl 9.13) Open the right ventricle and identify the muscular ventricular wall with the trabeculae carnae. (G 3.55;N 217;Gl 9.12A) Identify the cusps, chordae tendinae (tendinous cords) and papillary muscles of the tricuspid valve. Attempt to identify the septomarginal trabecula extending between the base of the anterior papillary muscle and the interventricular septum. Identify the cusps of the pulmonary valve from the inferior view and the associated conus arteriosus (smooth walled region immediately inferior to the pulmonary valve).
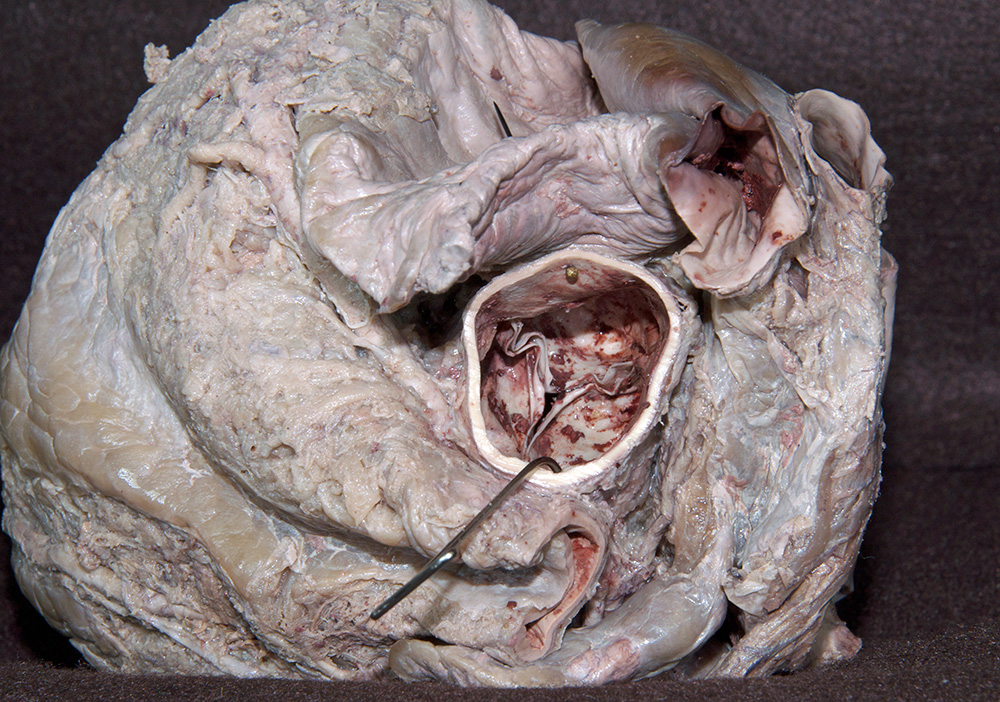
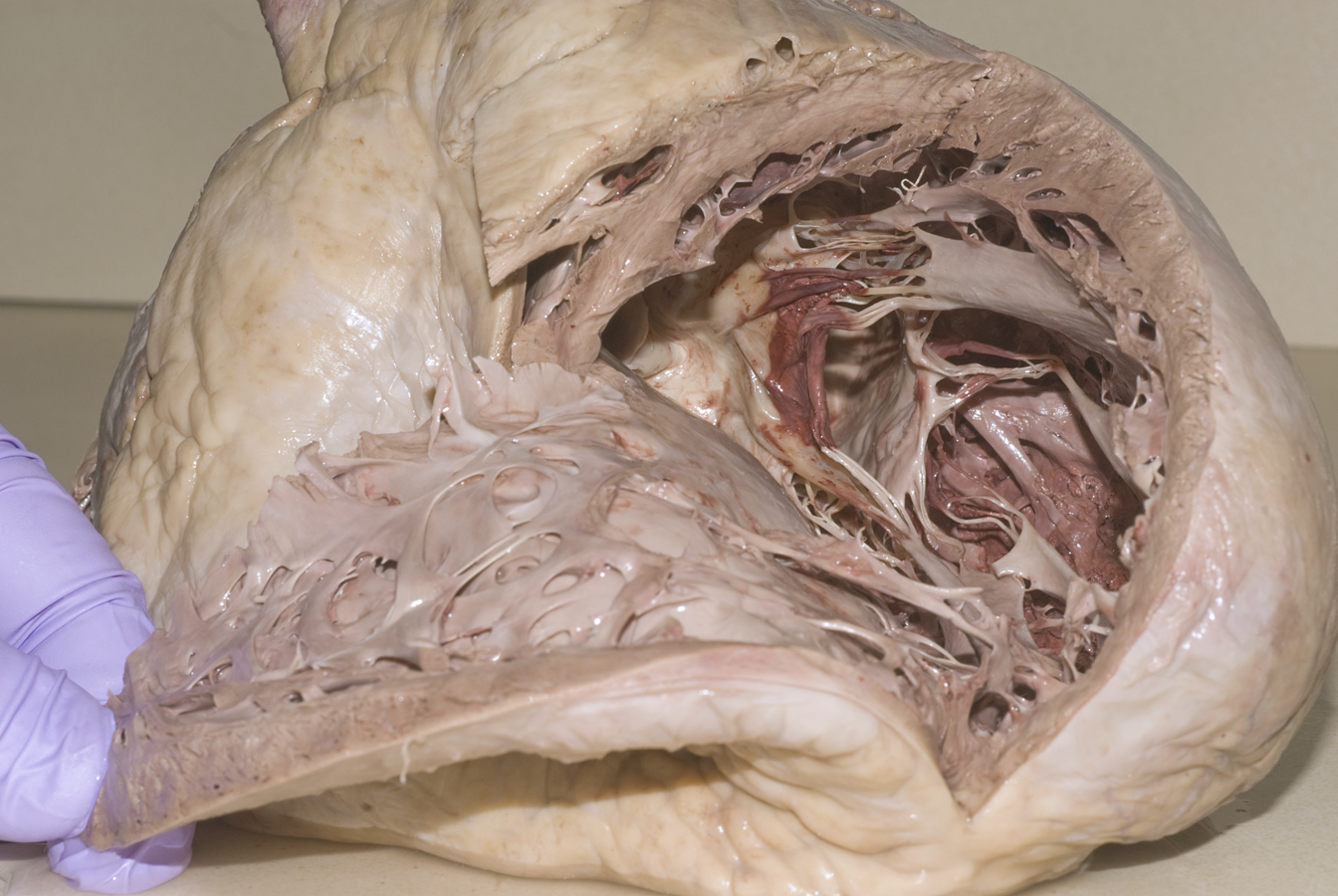
- Return to the ascending aorta. Identify the cusps of the aortic valve from the superior view. (G 3.58;N 219;Gl 9.13) Identify the orifices of the right and left coronary arteries. Identify the interventricular septum, and trabeculae carnae. Compare the thickness of the left and right ventricular walls. Identify the cusps, tendinous cords and papillary muscles of the bicuspid (mitral) valve.