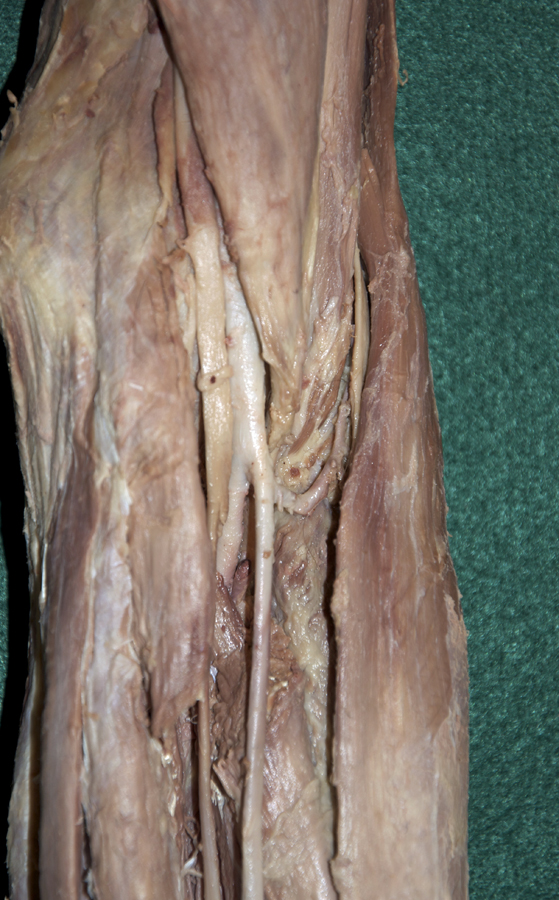
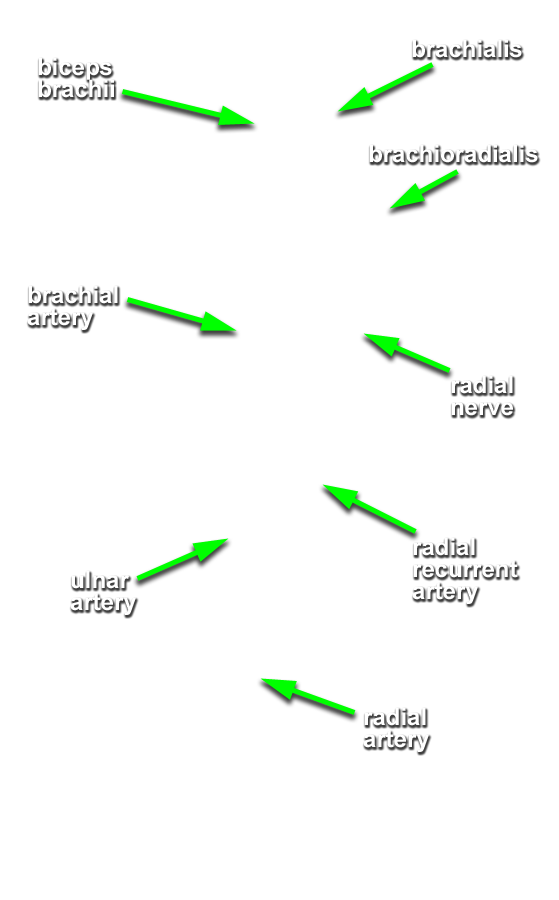
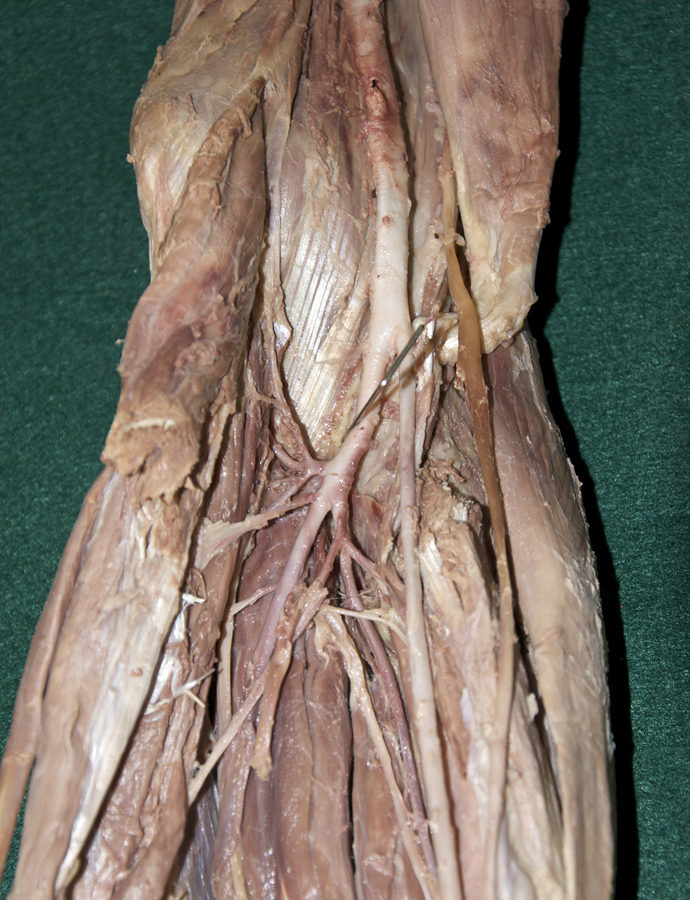
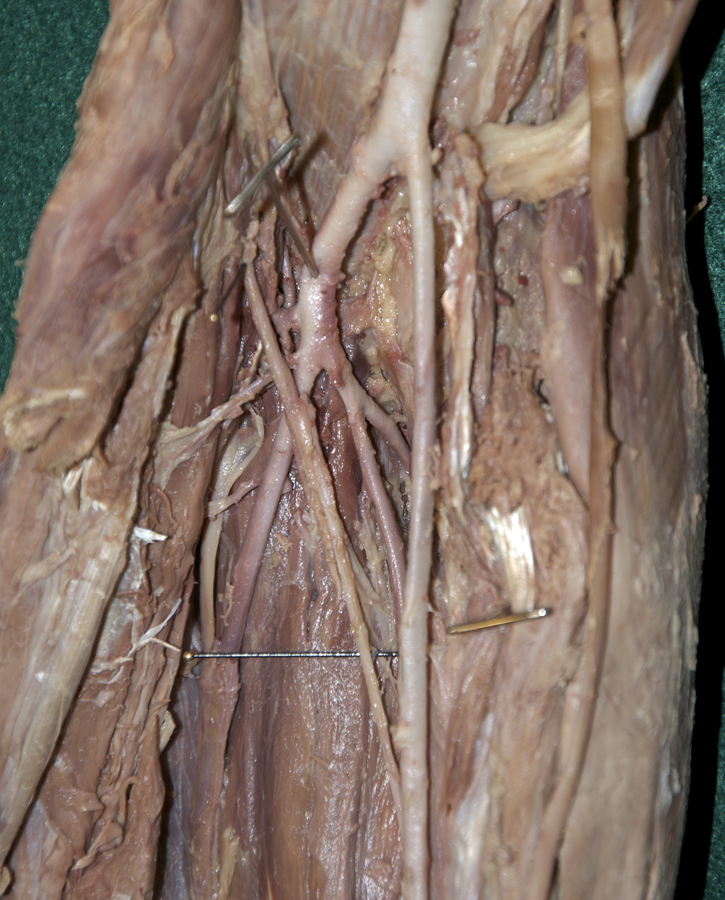
(ON THE LEFT SIDE ONLY) Identify the branches of the radial and ulnar arteries in the forearm. (G T2.11, 2.60B and 2.65B;N 433;Gl 28.37)
- Identify the brachial, radial and ulnar arteries in the cubital fossa.
- Identify the radial recurrent artery. The radial recurrent artery arises very shortly after the bifurcation and is typically adjacent to the deep branch of the radial nerve. (G 2.64B;N 433;Gl 28.37C)
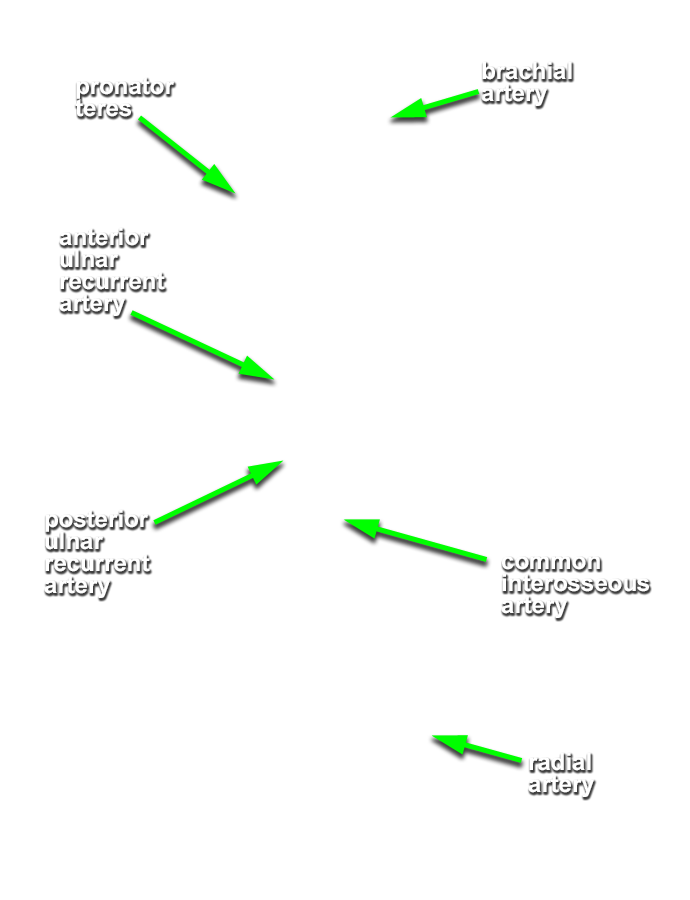
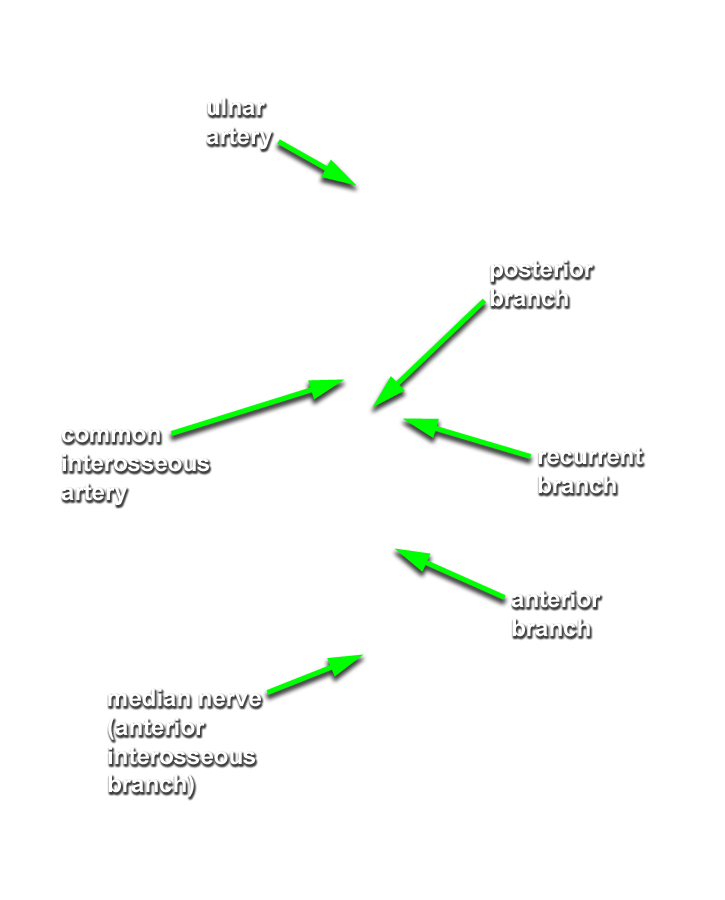
- Identify the common interosseous artery. Attempt to identify the anterior and posterior ulnar recurrent arteries. (G T2.11;N 434;Gl 28.4B) You may not be able to identify these arteries on the right forearm with the intact pronator teres and flexor digitorum superficialis. Return to the common interosseous artery and identify the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries. (G 2.60B;N 434;Gl 28.4B) Attempt to identify the posterior interosseous recurrent artery.
- Identify the median nerve and its branches innervating most of the muscles of the anterior compartment of the forearm. Attempt to identify and trace the anterior interosseous nerve.
Important Relationships
- The brachial artery passes anterior to the elbow joint.
- The brachial artery passes posterior (deep) to the bicipital aponeurosis.
- The radial collateral (or radial recurrent) artery passes directly anterior to the humerus (lateral epicondyle).
- The inferior ulnar collateral (or anterior ulnar recurrent) artery passes directly anterior to the humerus (medial epicondyle).