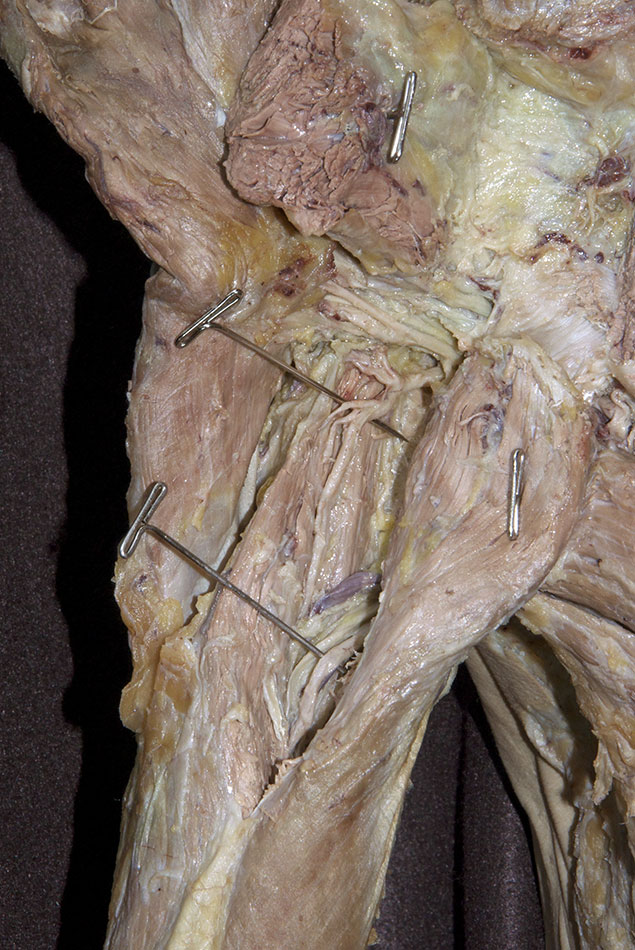
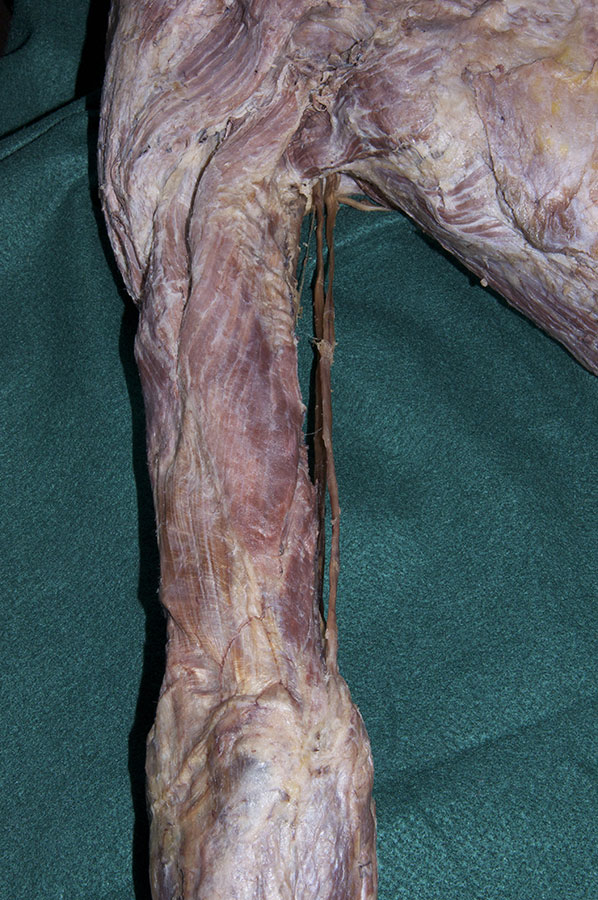
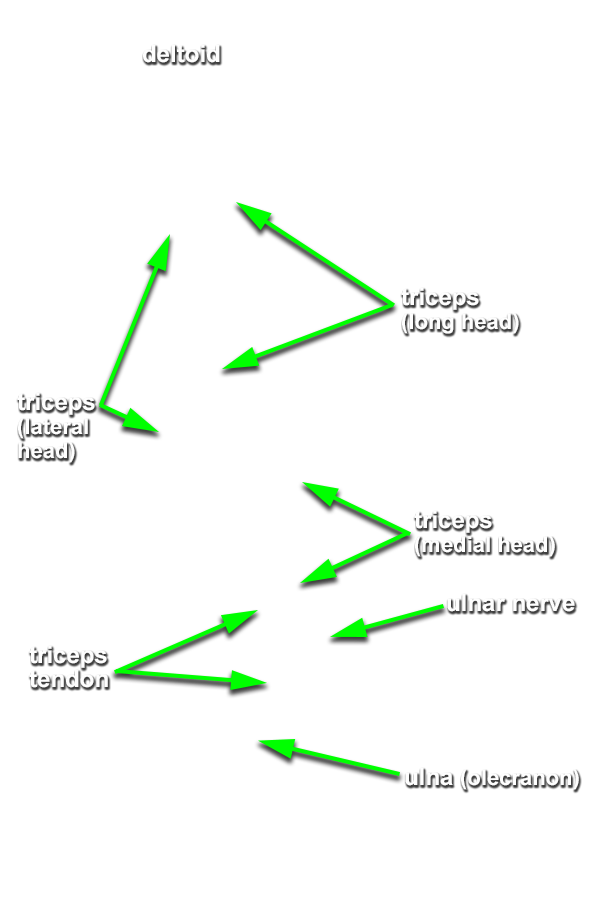
Return to the posterior compartment of the arm. (G 2.41;N 418;Gl 28.30B)
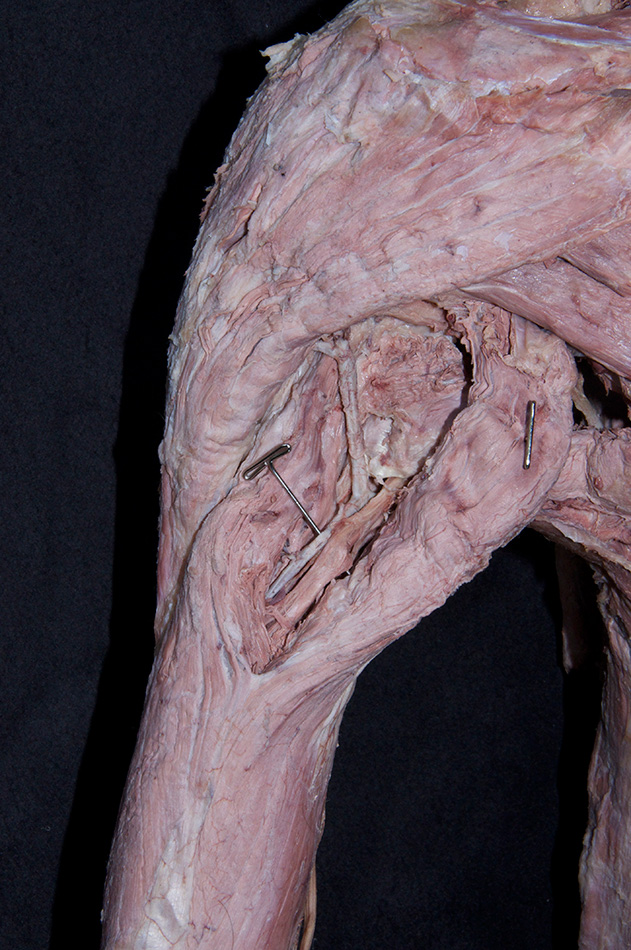
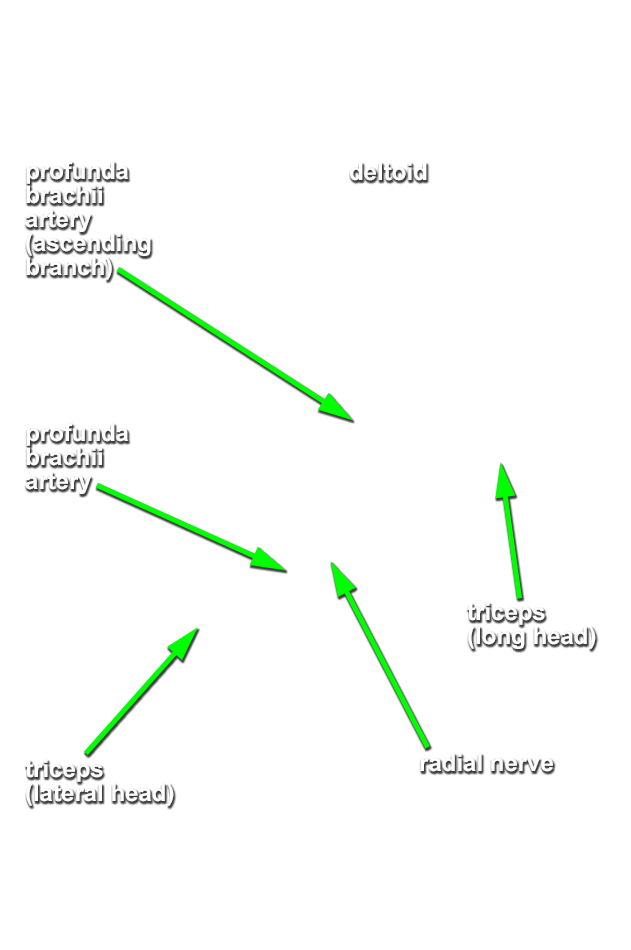
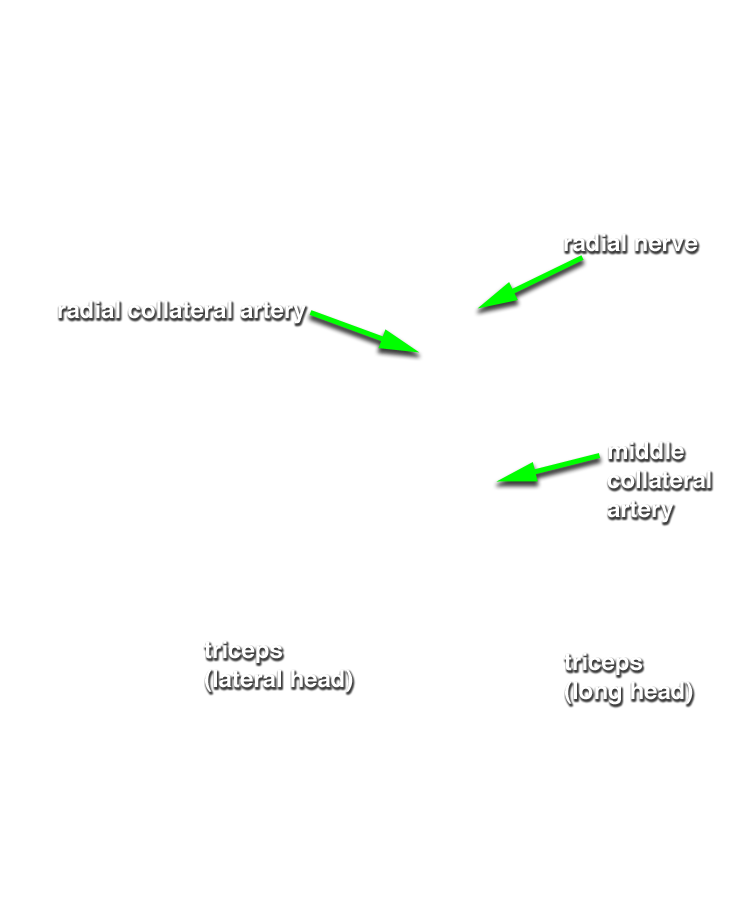
- Identify the long and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle. The space between the two heads is the triangular interval.
- Identify the radial nerve in the floor of the triangular interval.
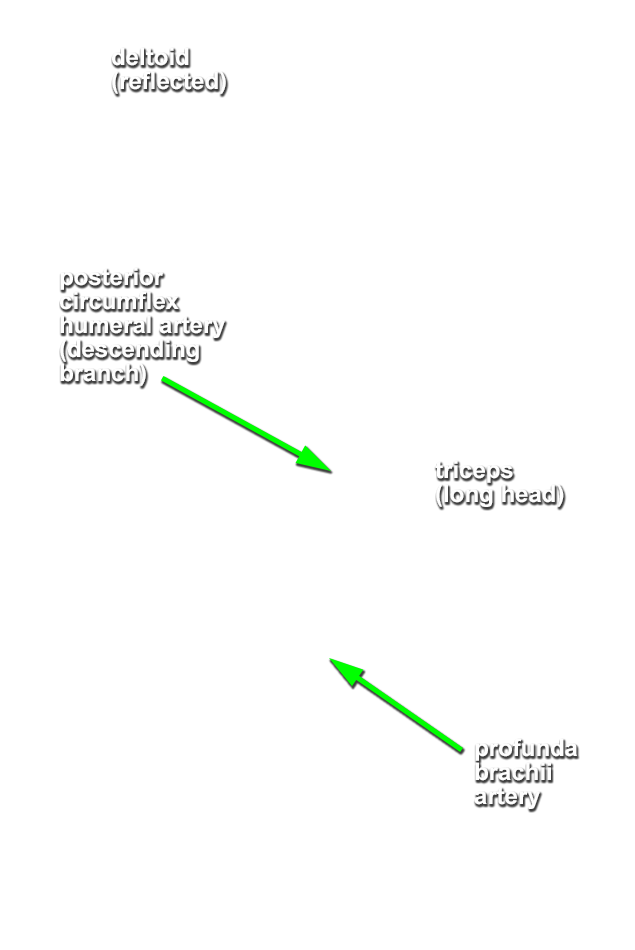
- Identify the profunda brachii artery and its two terminal branches, the radial and middle collateral arteries, accompanying the radial nerve. This artery often divides into its two terminal branches before passing posterior to the humerus.
- Attempt to identify the anastomosis between the profunda brachii and posterior circumflex humeral arteries.
- Reflect the lateral head of the triceps brachii muscle and trace the radial nerve and radial collateral artery distally until they disappear deep to the brachialis muscle.
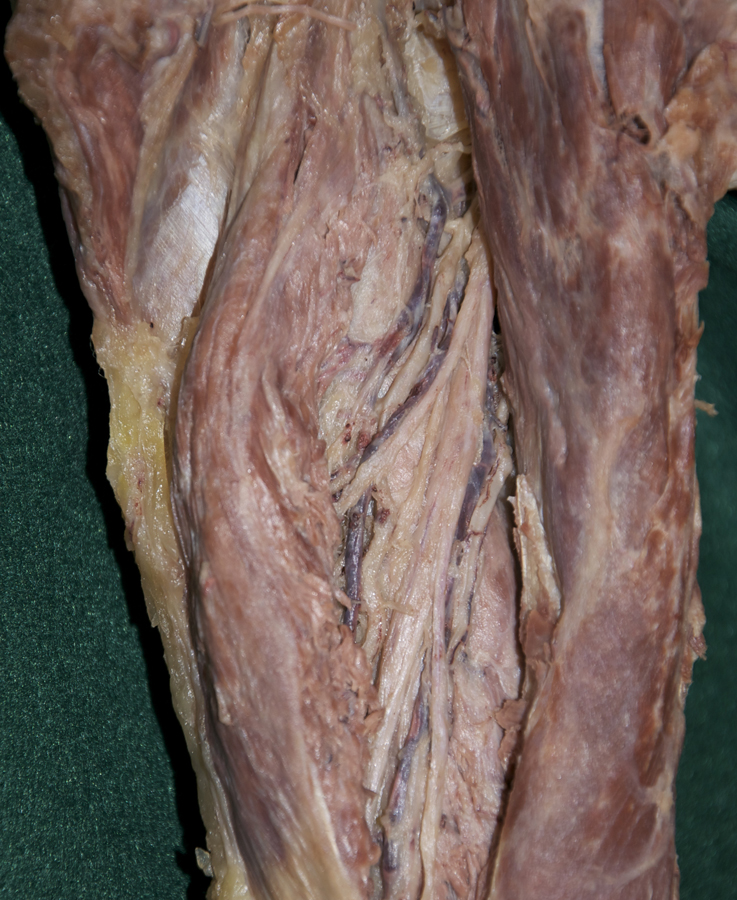
- Trace the triceps brachii muscle to its distal attachment to the olecranon.
- Identify the medial head of the triceps brachii muscle adjacent to the ulnar nerve. (G 2.41;N 419;Gl 25.21C)
Important Relationships
- The radial nerve passes directly posterior to the humerus (shaft) and directly anterior to the humerus (lateral epicondyle).
- The profunda brachii artery passes directly posterior to the humerus (shaft).
- The middle collateral (or interosseous recurrent) artery passes directly posterior to the humerus (lateral epicondyle).