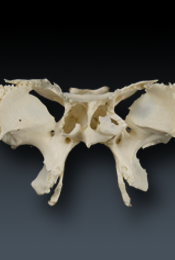
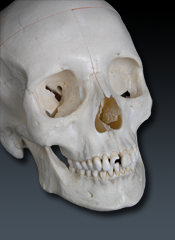
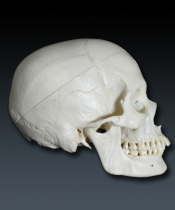
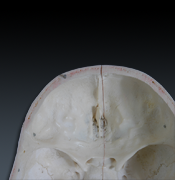
Sphenoid (L. wedge)
Body
Sulcus chiasmatis
(G. chiasma, two crossing lines, from the letter chi)
function - houses the optic chiasm
Optic canal
function - transmits the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery
Sella turcica
(L. saddle)
Hypophyseal fossa
(G. an undergrowth)
function - houses the pituitary gland
Dorsum sellae
Posterior clinoid processes
(G. klino, to slope, incline or bend)
Carotid groove
function - houses internal carotid artery and carotid nerve
Sphenoid sinus
Greater wings
Cerebral surfaces
Foramen rotundum
function - transmits the maxillary nerve
Foramen ovale
function - transmits the mandibular nerve and accessory meningeal artery
Spine (of sphenoid)
attachments - sphnomandibular ligament
Foramen spinosum
function - transmits the middle meningeal artery and the meningeal (recurrent) branch of the mandibular nerve
Lateral surface
attachments - temporalis and lateral pterygoid muscles
Orbital surface
Superior orbital fissure
function - transmits the ophthalmic, oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nerves and the ophthalmic vein
Foramen lacerum
(L. lacero, to tear)
Lesser wings
Anterior clinoid processes
attachments - tentorium cerebelli
Pterygoid process
Pterygoid fossa
attachments - medial pterygoid muscle
Scaphoid fossa
(G. skaphe, skiff, boat)
attachments - tensor palatini muscle
Pterygoid canal
function - transmits the nerve of the pterygoid canal
Lateral pterygoid plate
attachments - lateral and medial pterygoid muscles
Medial pterygoid plate
Pterygoid hamulus
(L. small hook)
function - deflects the tendon of the tensor palatini muscle