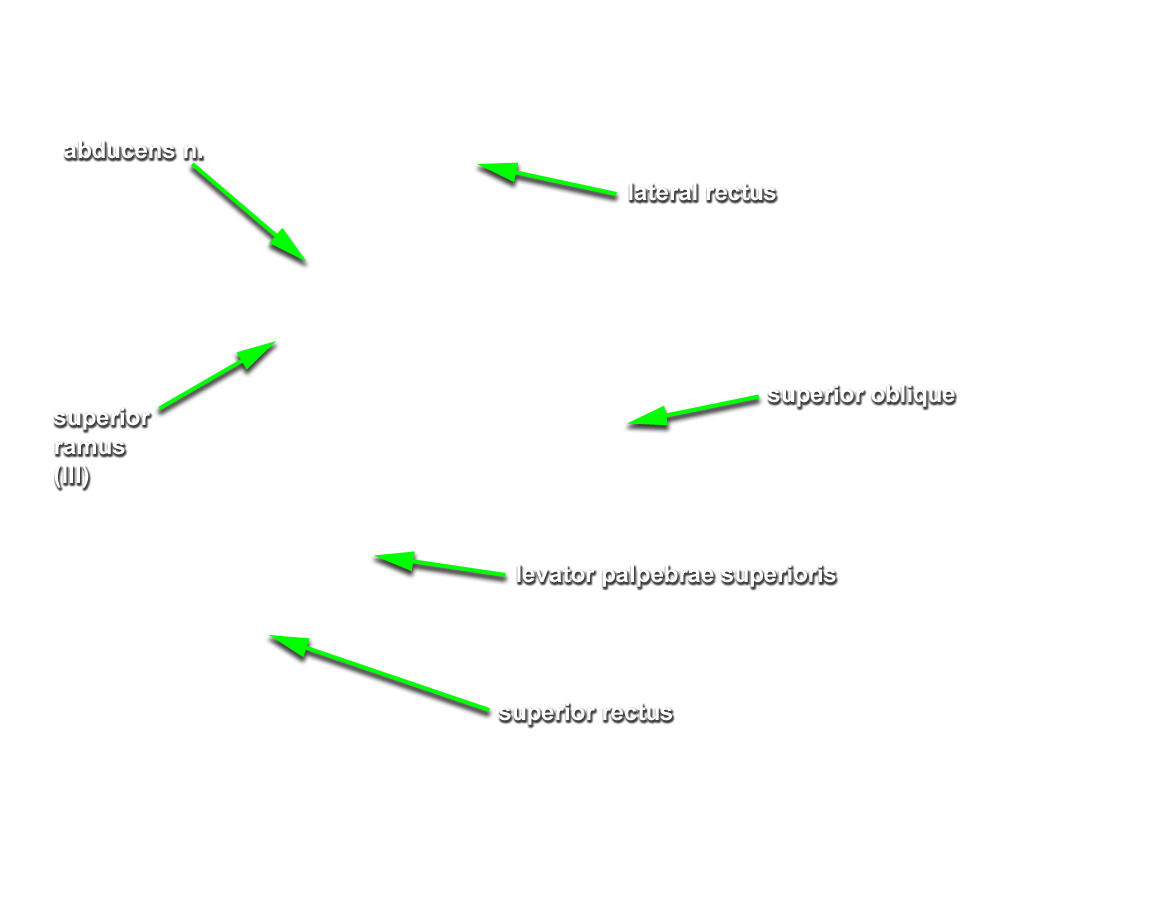
Use a superior approach (Steps 9 and 10) to dissect and identify the contents of the orbit on one side of the head and the anterior approach (Steps 11 and 12) on the opposite side.
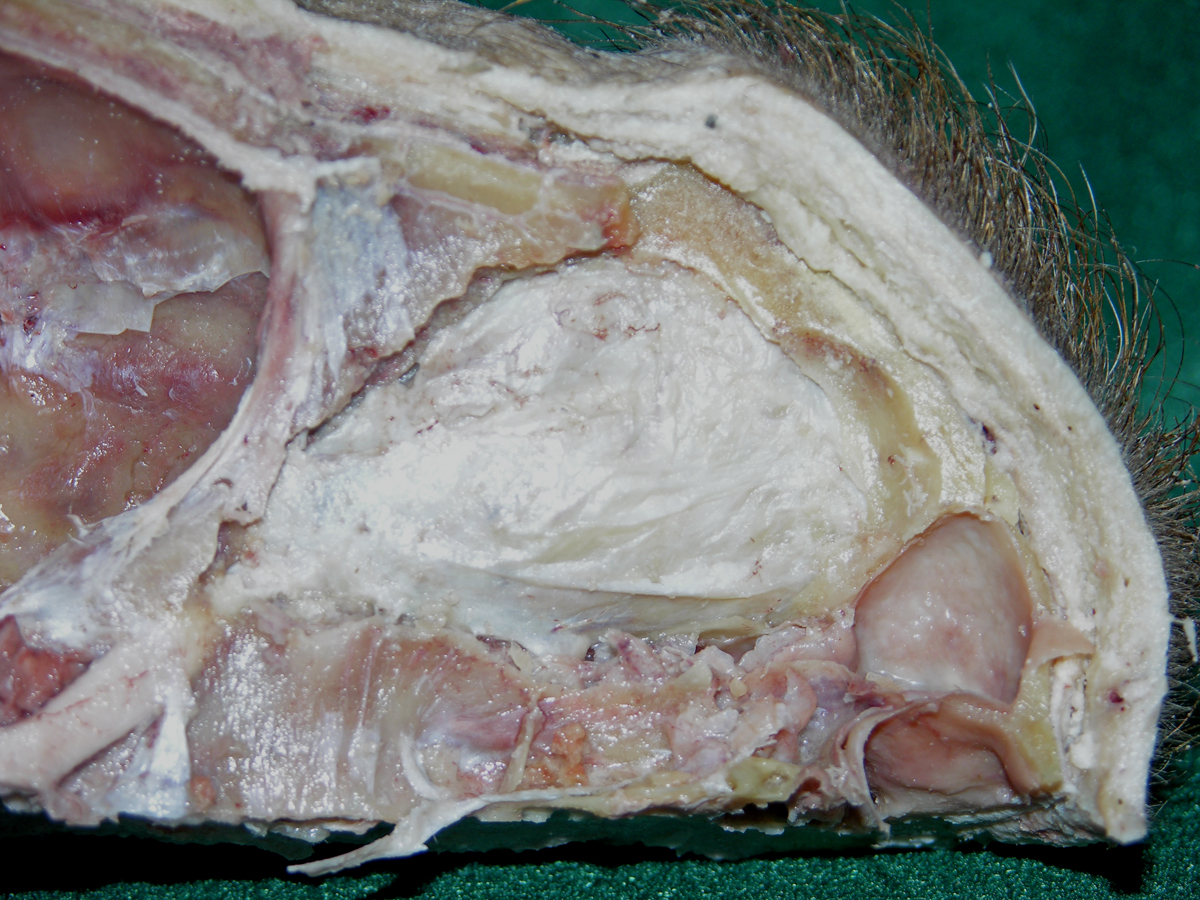
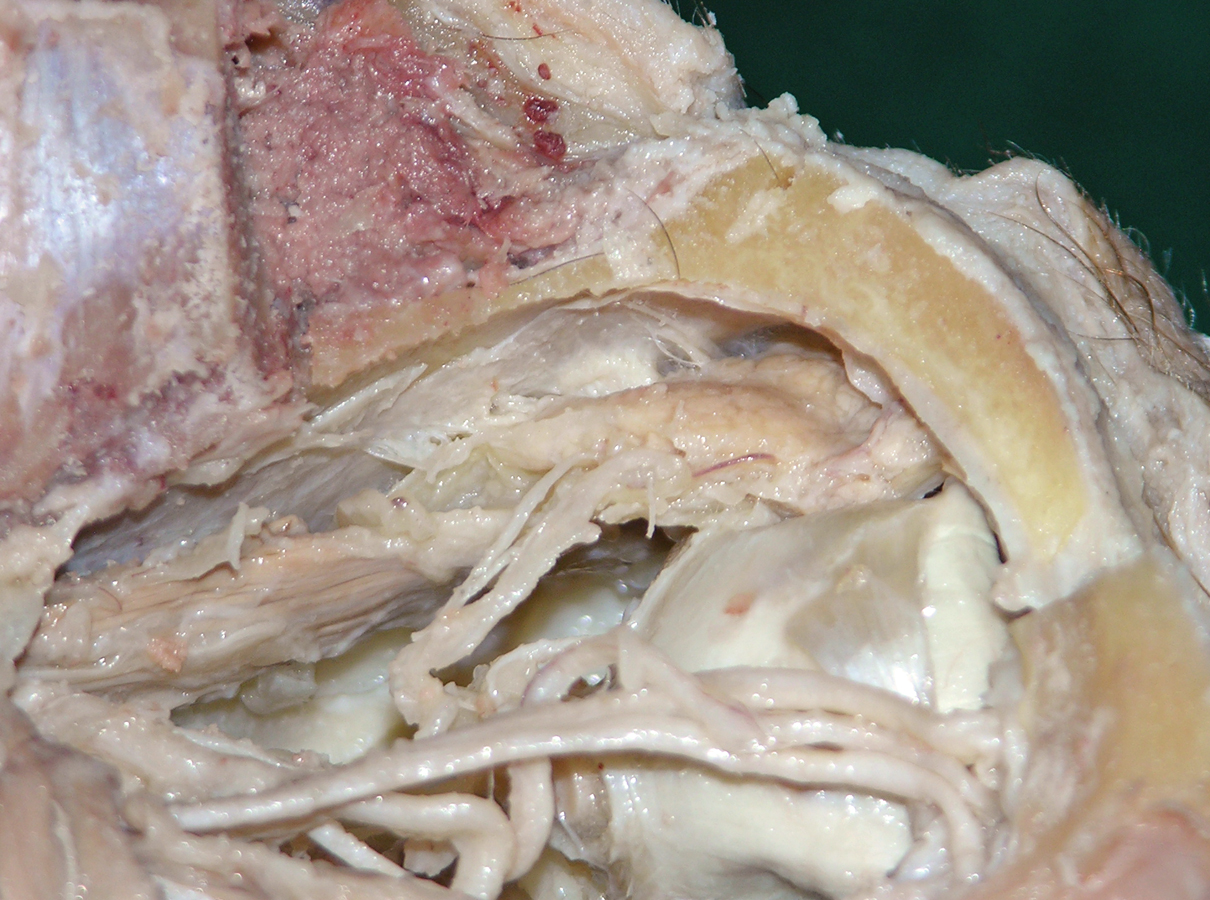
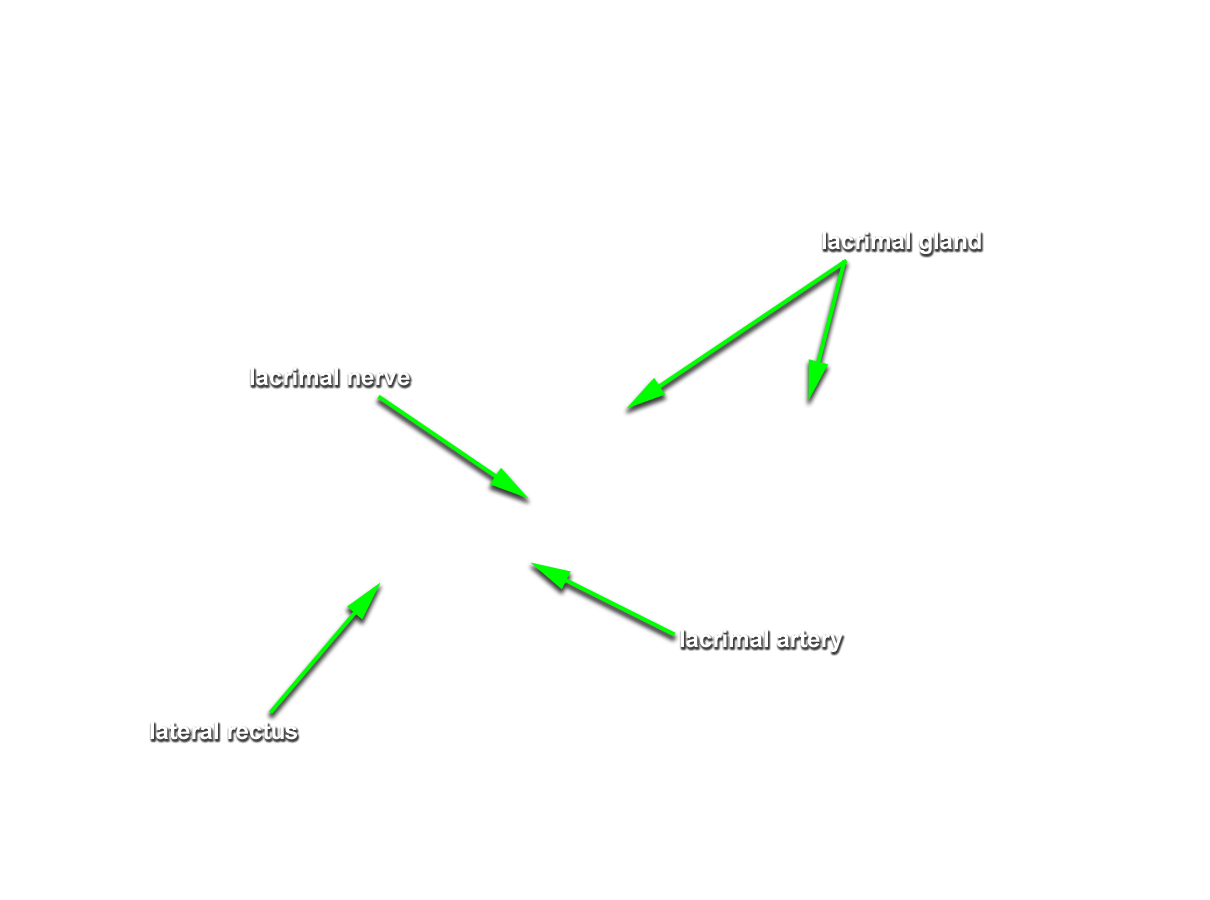
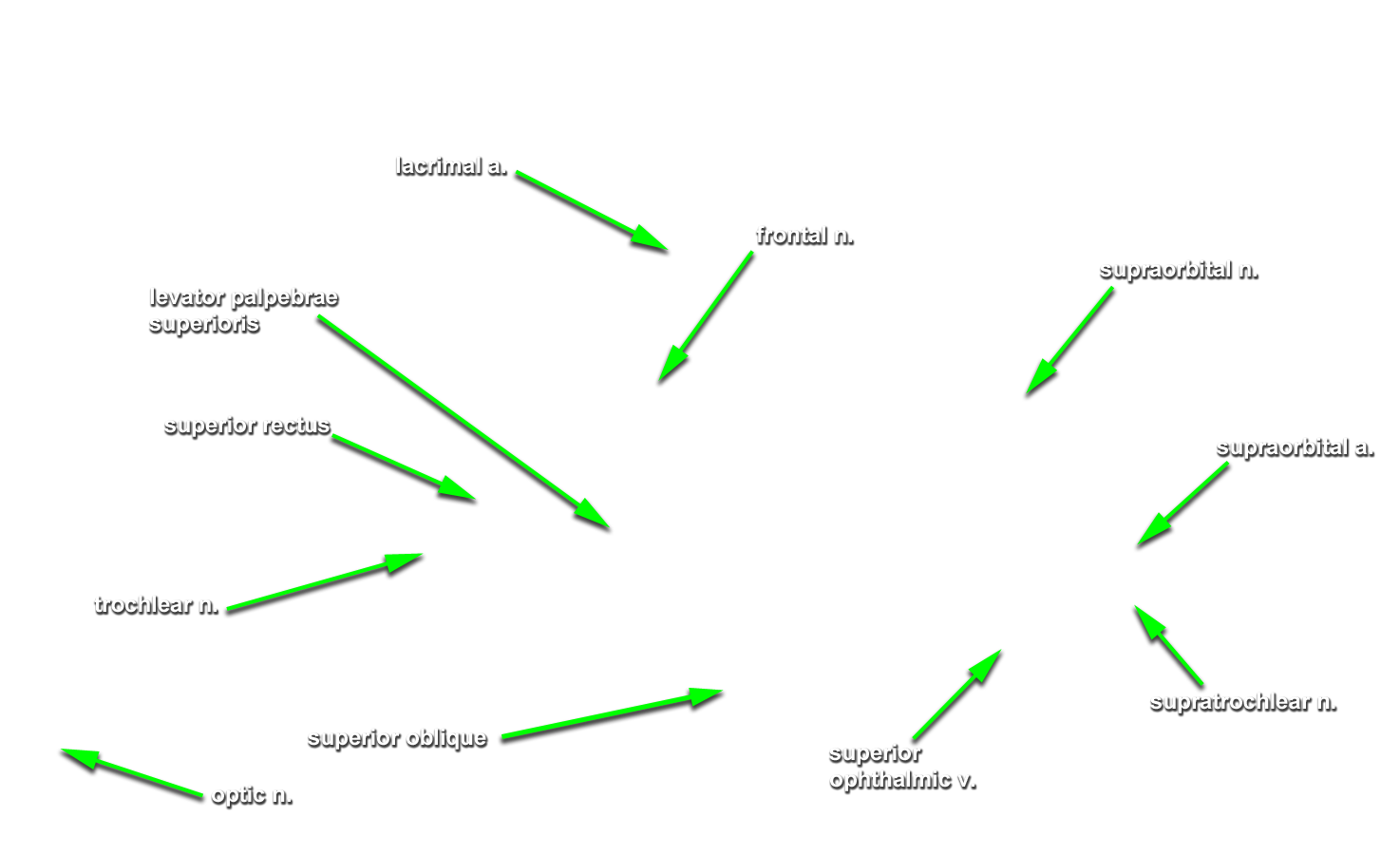
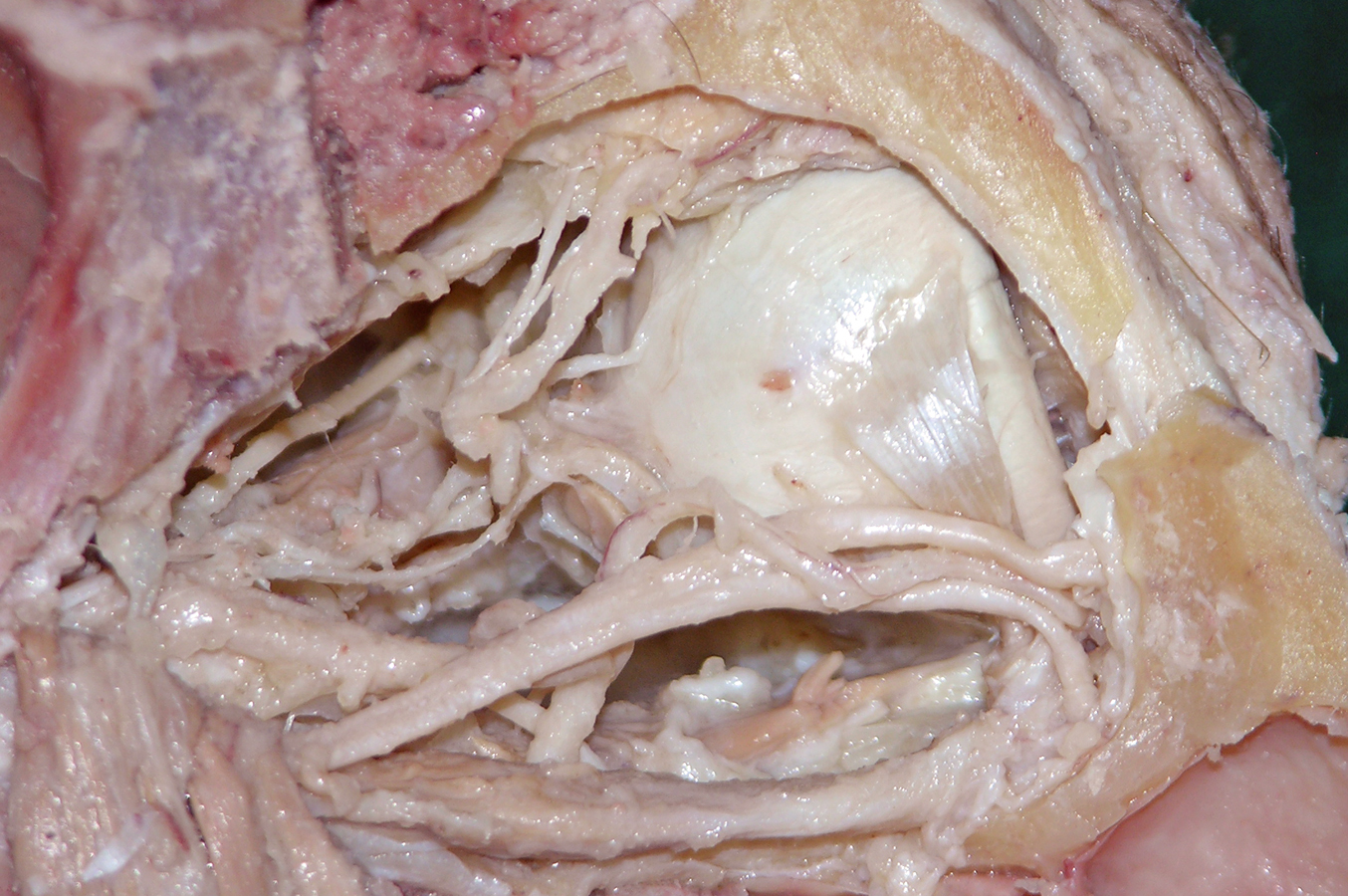
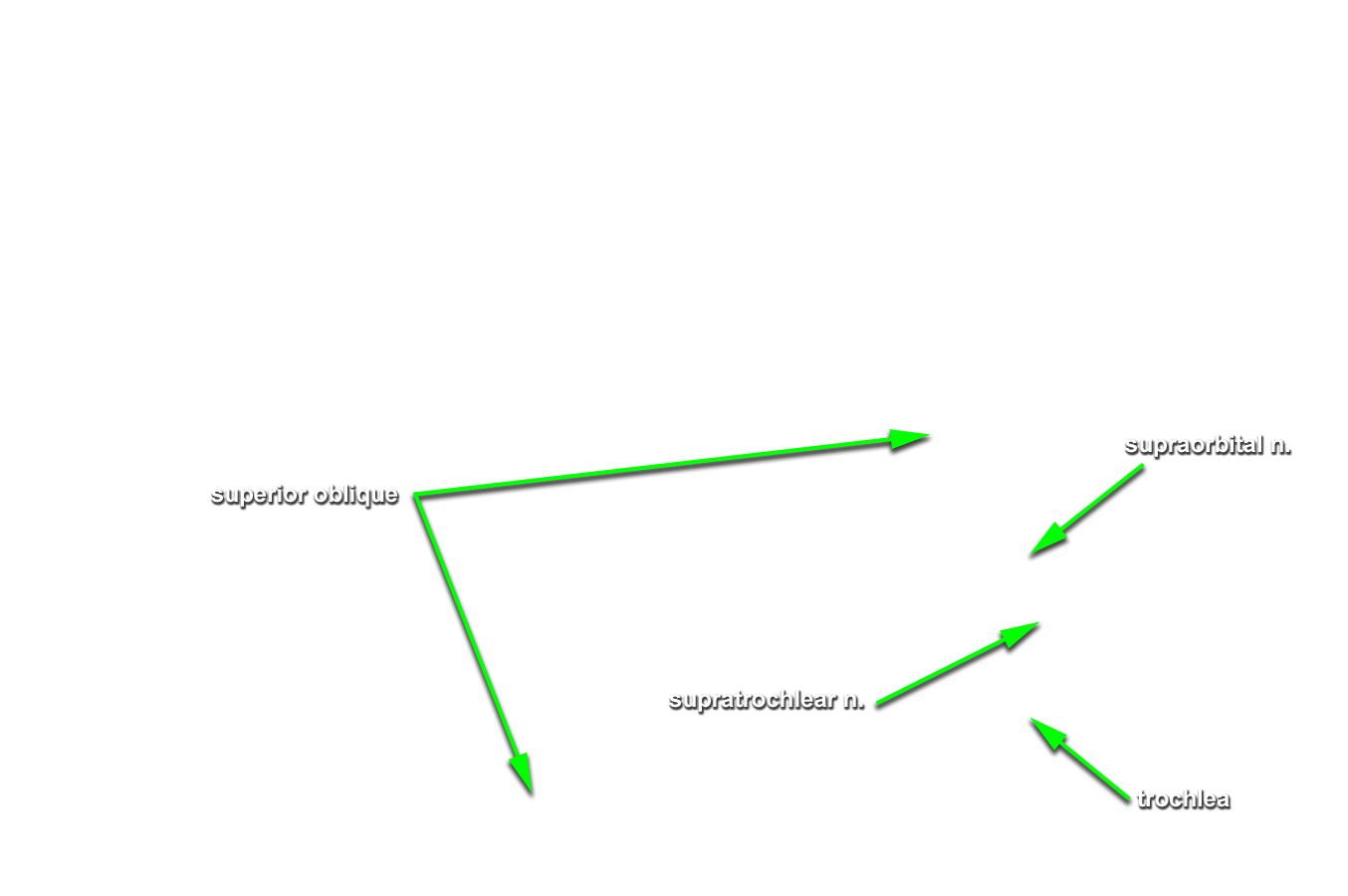
- Use a chisel handle and bone cutting shears to remove the roof of the orbit. Use sharp scissors to remove the periosteum of the orbital roof . (G 7.33A;N 86;Gl 35.9) Identify and clean the lacrimal gland, frontal nerve, supraorbital nerve and artery, and superior ophthalmic vein. Attempt to identify the lacrimal nerve.
-
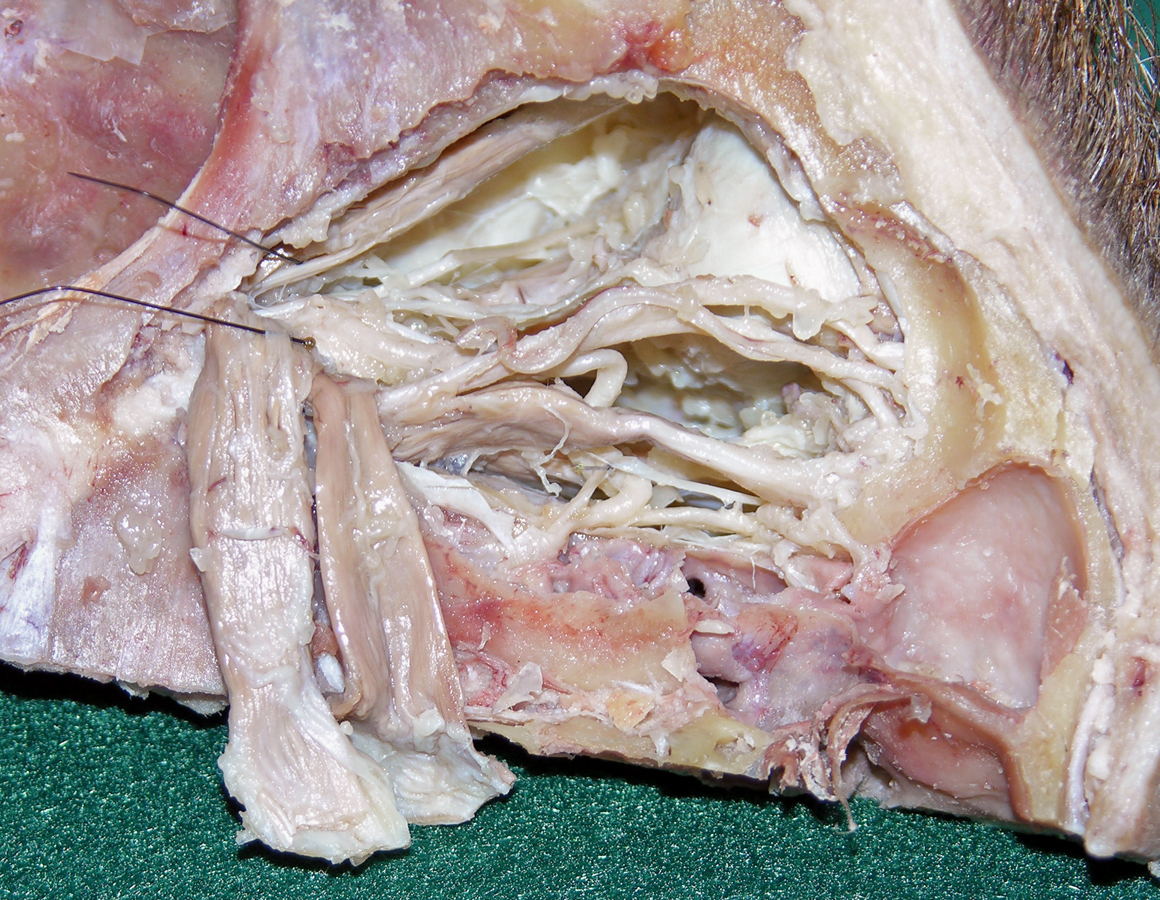
Use the scissor technique to break the orbital fat into small lobules. Carefully remove the fat lobules with forceps. Identify the
levator palpebrae superioris,
superior rectus and
superior oblique muscles. (G 7.33A;N 84;Gl 35.12) Identify the
trochlear nerve entering the proximal (posterior) superior aspect of the superior oblique muscle.
Important Relationship
- The superior oblique (tendon) muscle passes inferior to the superior rectus muscle.
- The superior oblique muscle is positioned superior to the medial rectus muscle.
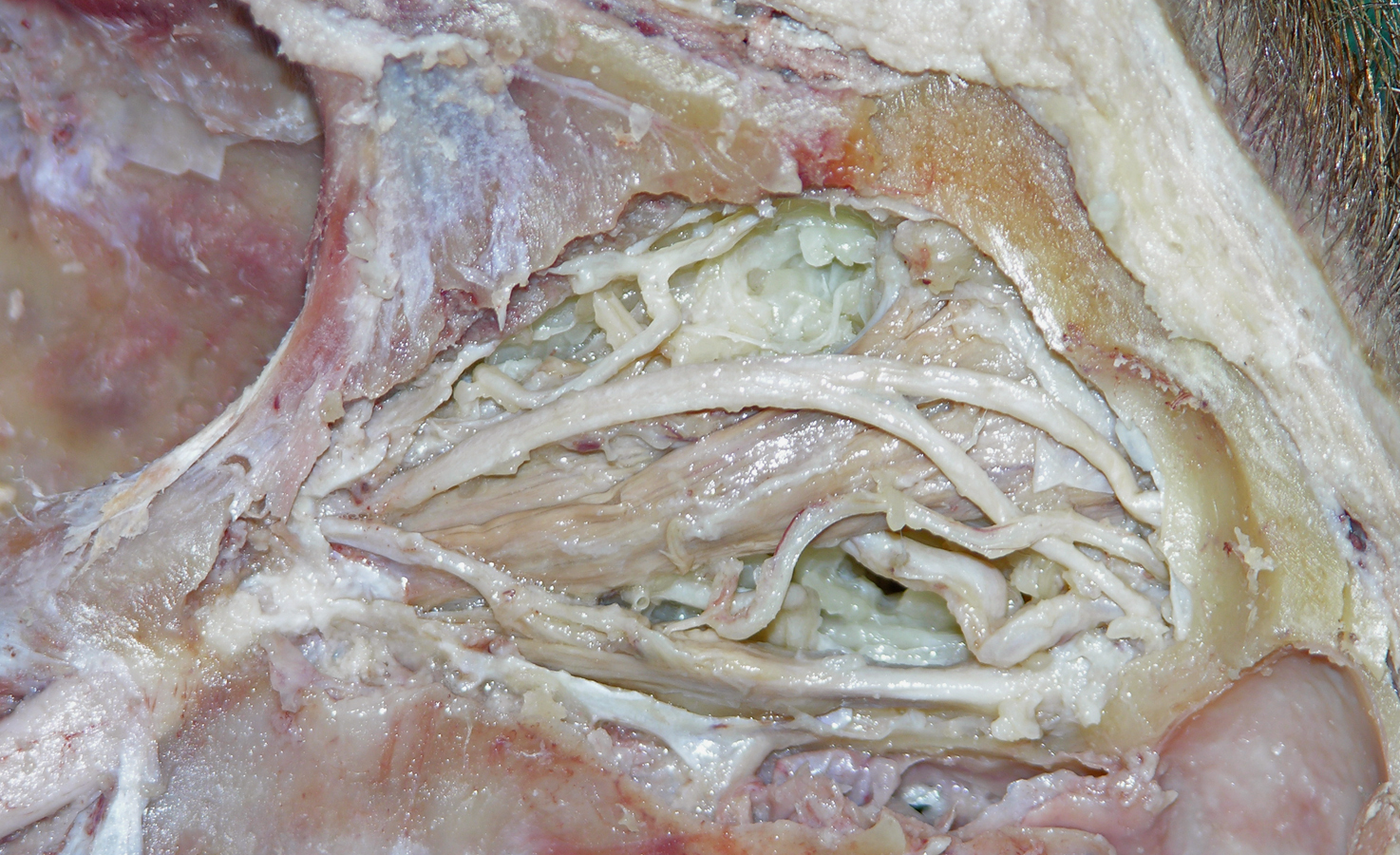
- Cut the levator palpebrae superioris and superior rectus muscles as far anterior as possible. Reflect the muscles in the posterior direction and identify the superior ramus of the oculomotor nerve. (G 7.33A;N 86;Gl 35.12B)