Identify the proximal segments of the cranial nerves emerging from the base of the skull.
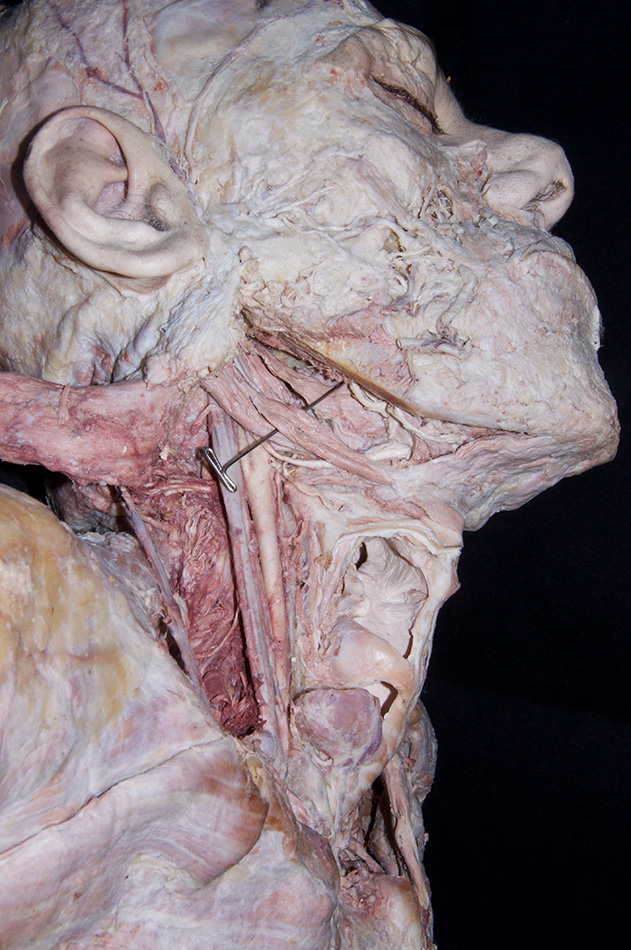
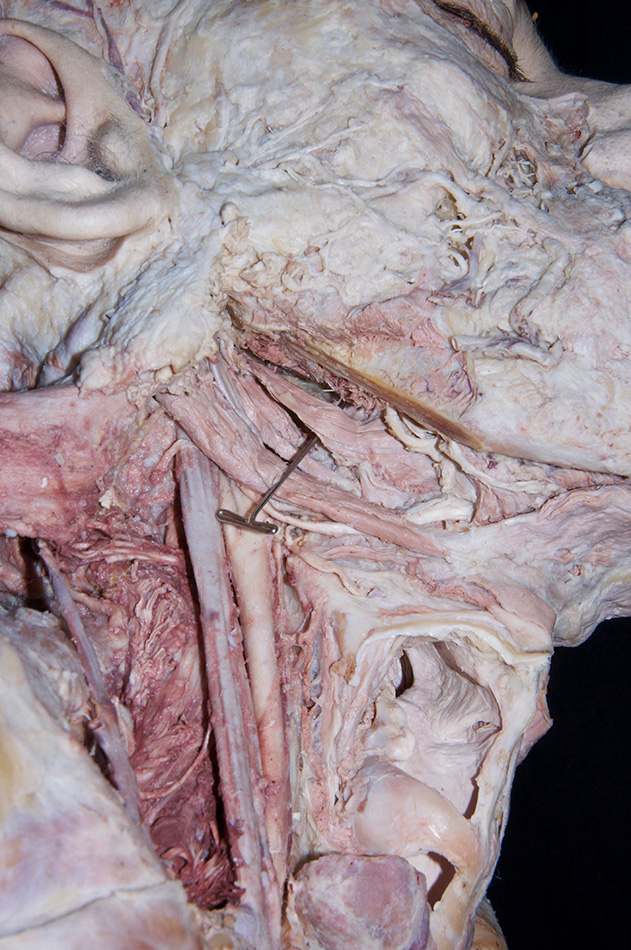
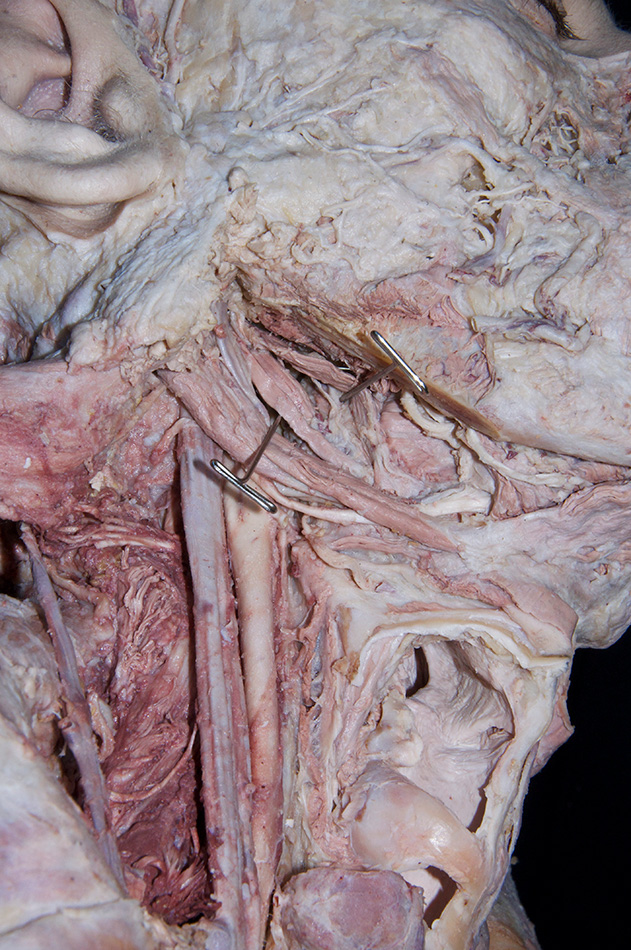
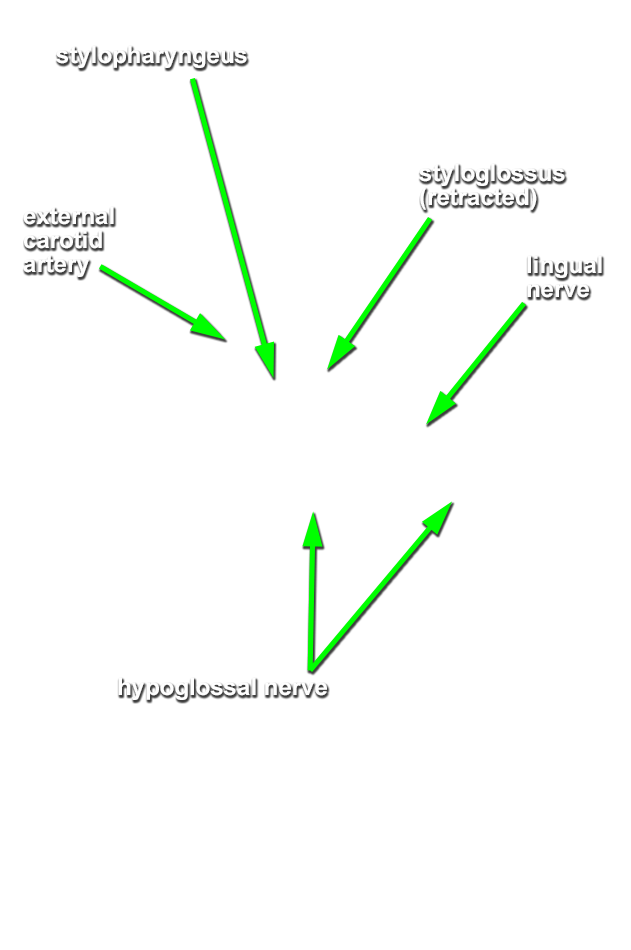
- (ON THE RIGHT SIDE ONLY) Identify the stylohyoid, styloglossus and stylopharyngeus muscles attaching to the styloid process. (G 8.19D;N 68;Gl 38.30) Return to the dangling facial nerve branch. Trace the facial nerve to the stylomastoid foramen. (G 7.39C;N 71;Gl 34.22) The stylomastoid foramen is typically in the same plane as the posterior border of the external auditory meatus.
-
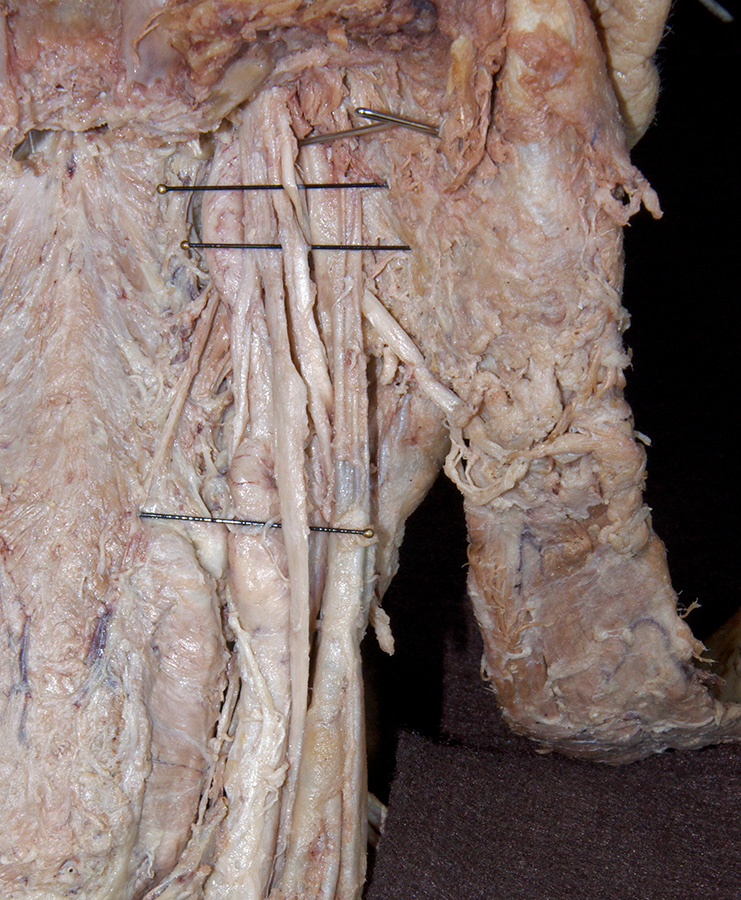
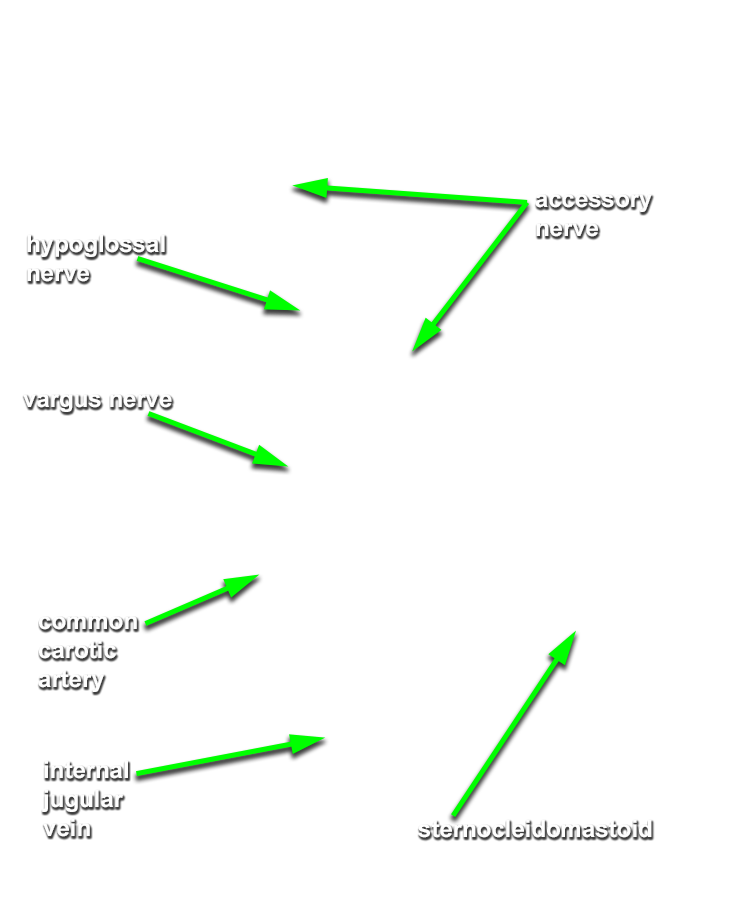
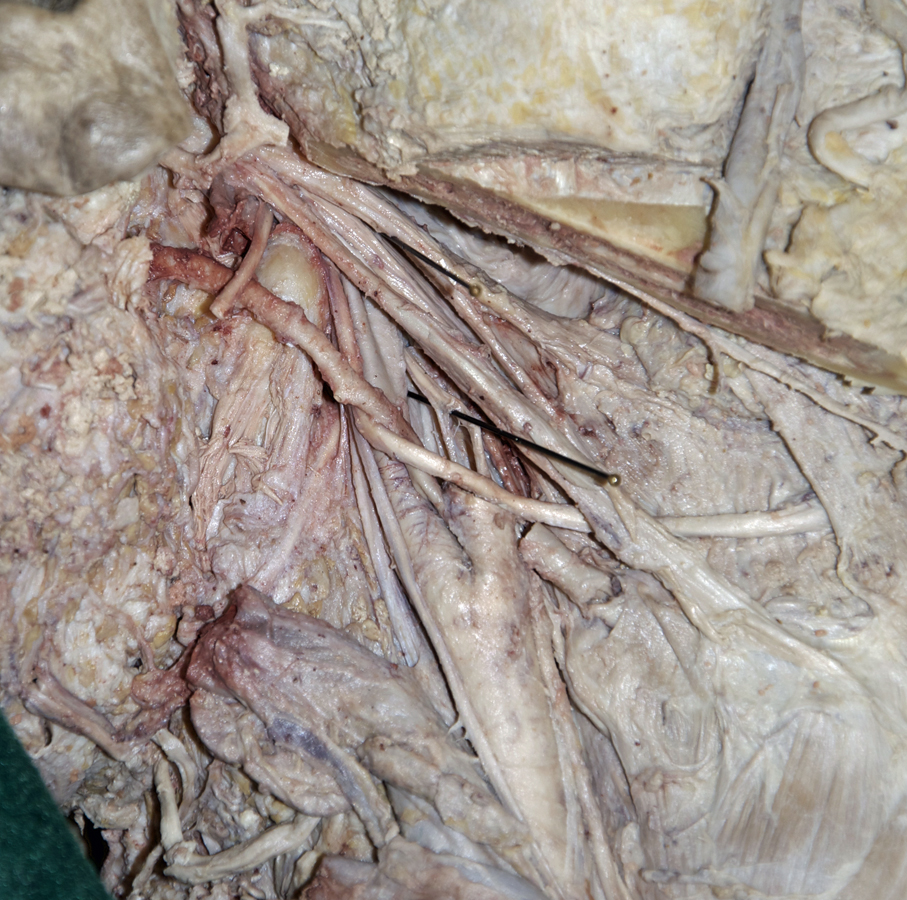
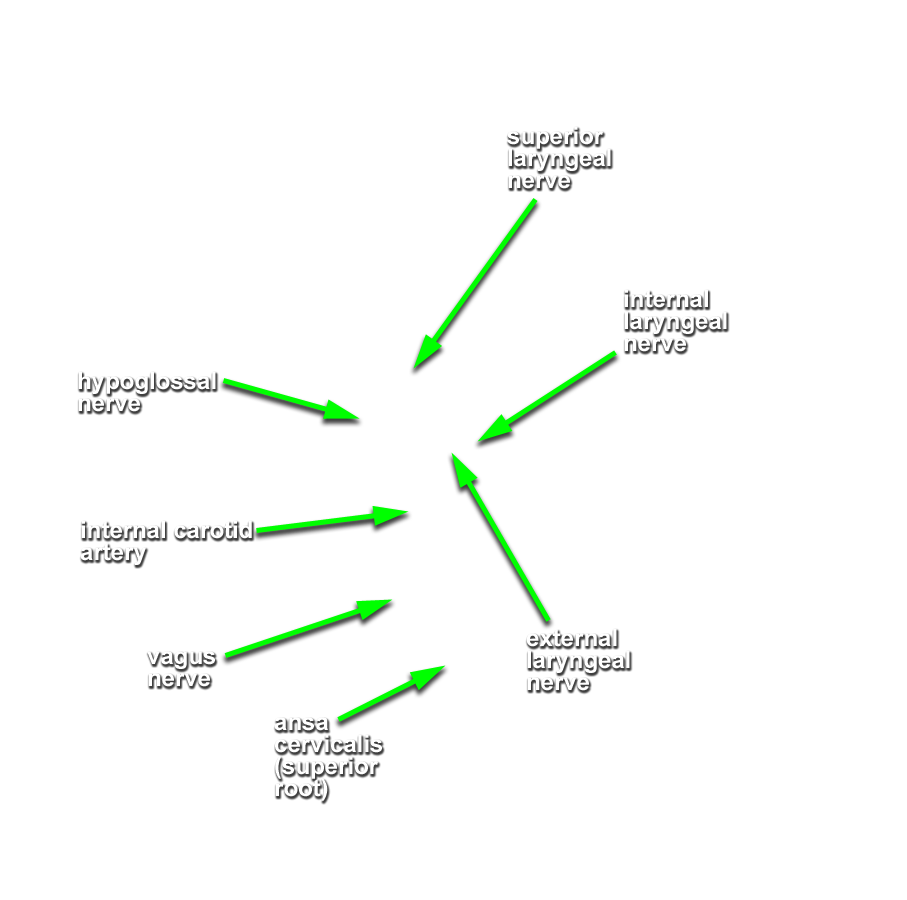
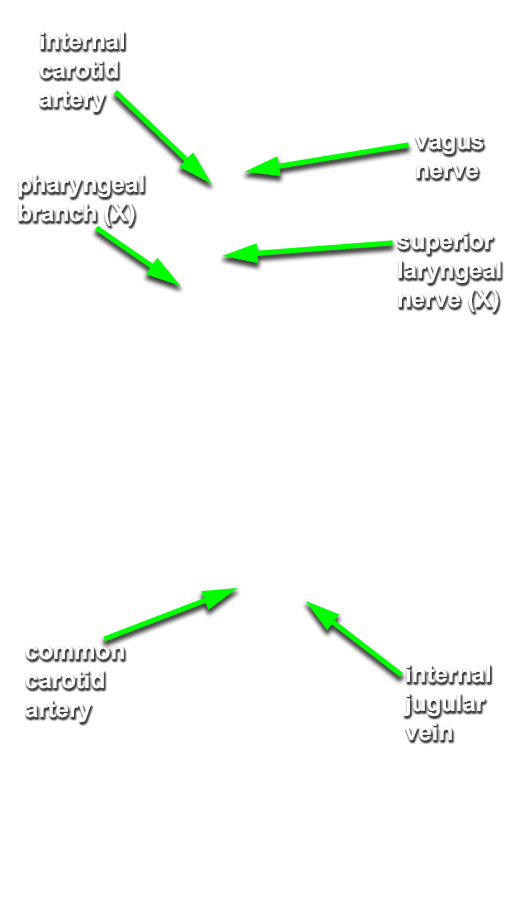
Identify the common, external and internal carotid arteries and internal jugular vein.
(G 8.31B;N 70 & 71;GI 38.32) Trace the internal carotid artery and internal jugular vein to the base of the skull. Identify the
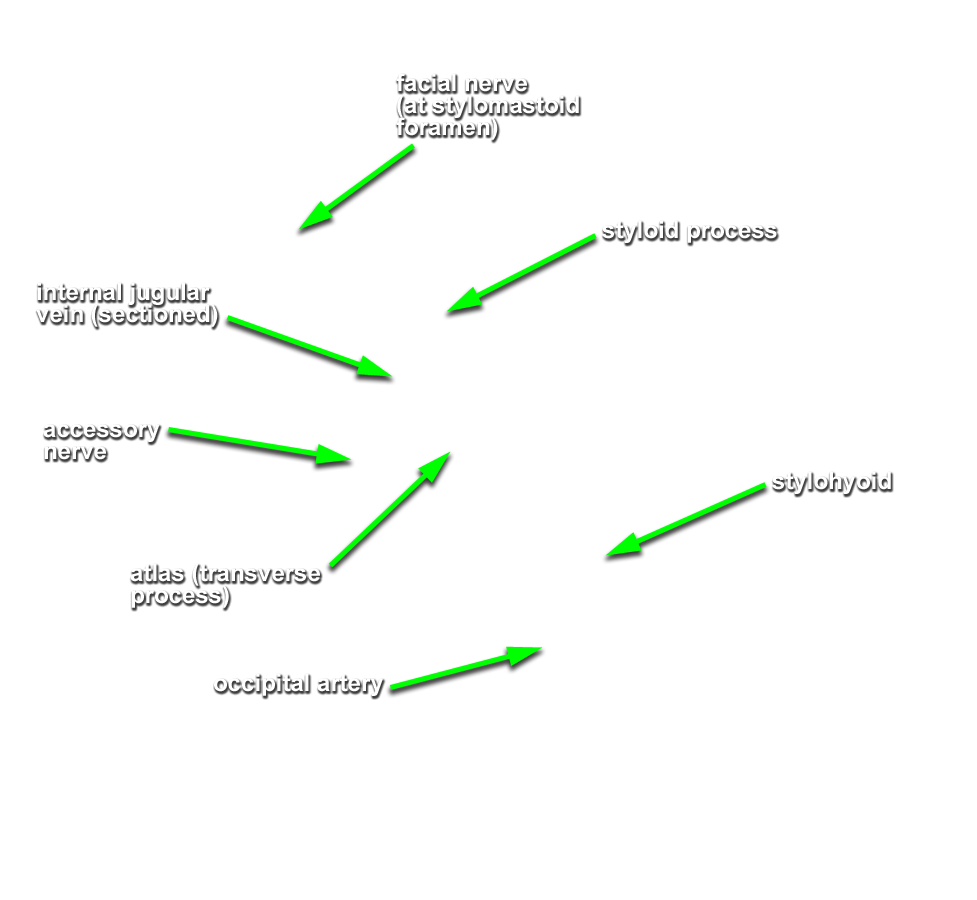
accessory nerve emerging from the jugular foramen and passing lateral into the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Identify the
vagus and
hypoglossal nerves. The hypoglossal nerve will appear to be a branch of the vagus and pass lateral to the internal and external carotid arteries.
Important Relationship
- The hypoglossal nerve passes lateral to the internal and external carotid arteries, and medial to the internal jugular vein.
-
Identify the superior laryngeal nerve branching from the vagus.
If necessary, trace the superior laryngeal nerve back from its internal laryngeal branch.
Important Relationship
- The superior laryngeal nerve passes medial to the internal and external carotid arteries.
-
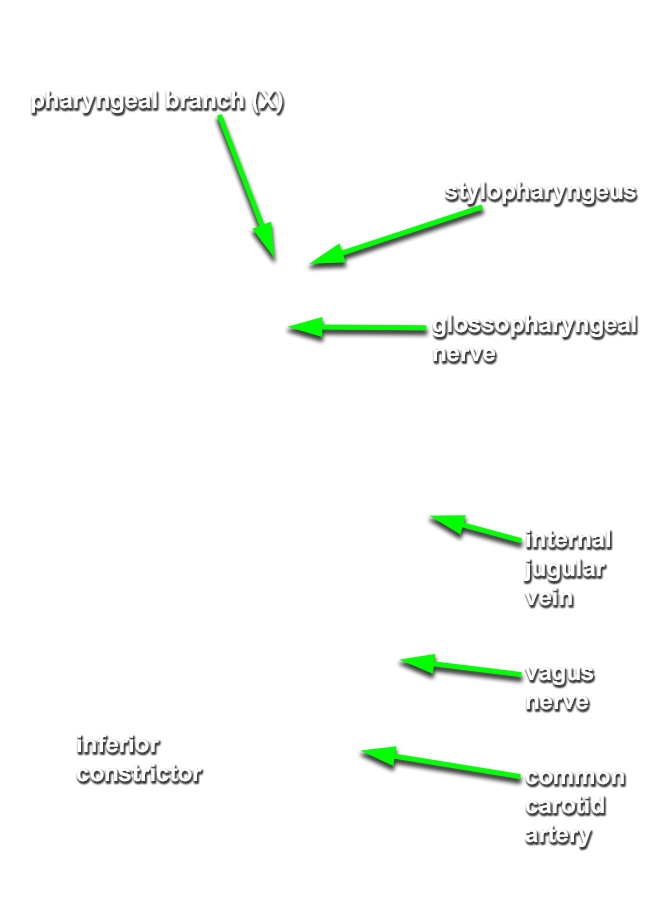
Identify the stylopharyngeus muscle and glossopharyngeal nerve. Attempt to identify the
pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve.
Important Relationship
- The glossopharyngeal nerve (and pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve) passes between the internal and external carotid arteries.