Identify the internal surface features and structures associated with the oral cavity.
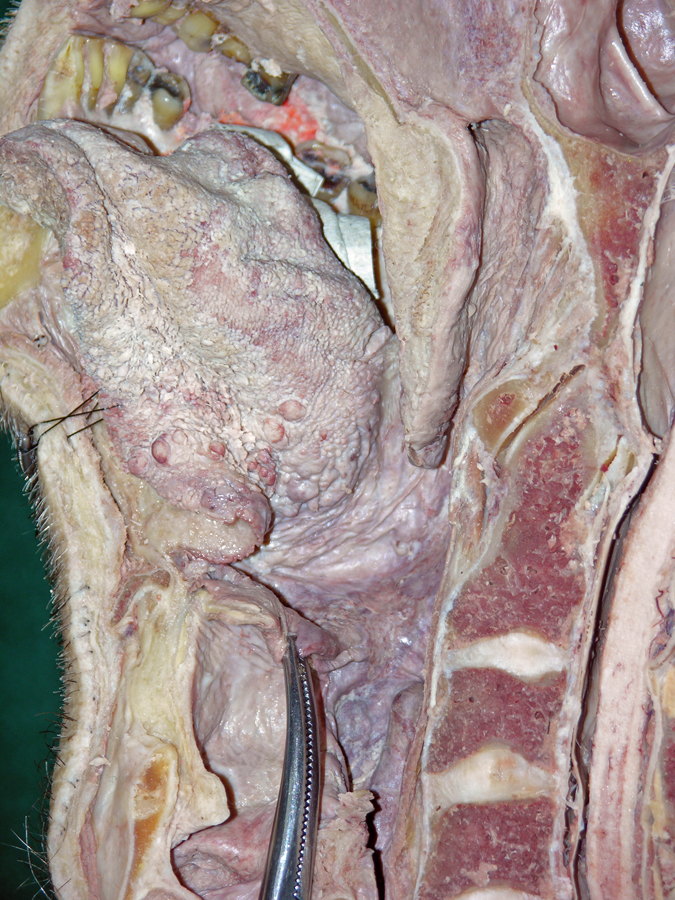
- (ON BOTH SIDES) Identify the tongue, terminal sulcus, foramen cecum, vallate papillae (the white circle at the posterior border of the tongue (not labeled)), and sublingual fold and caruncle. (G 8.24 and 8.27;N 58 and 61;Gl 38.20)
-
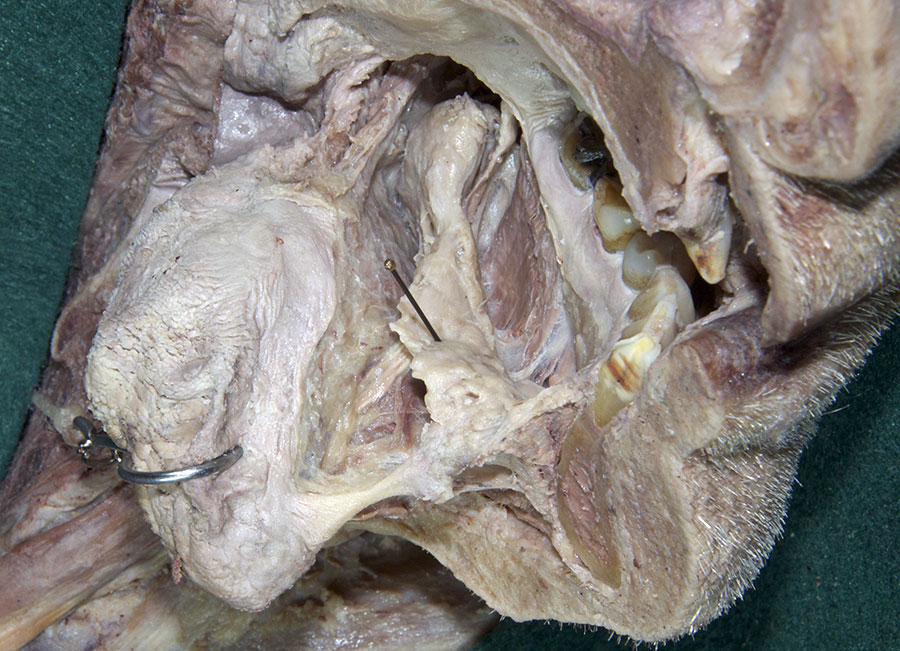
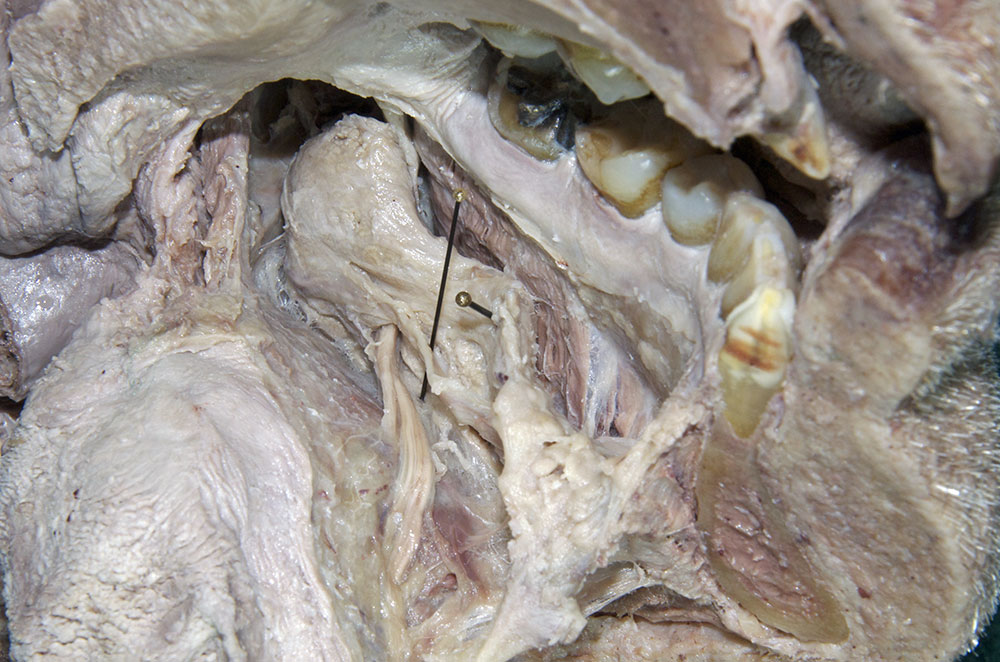
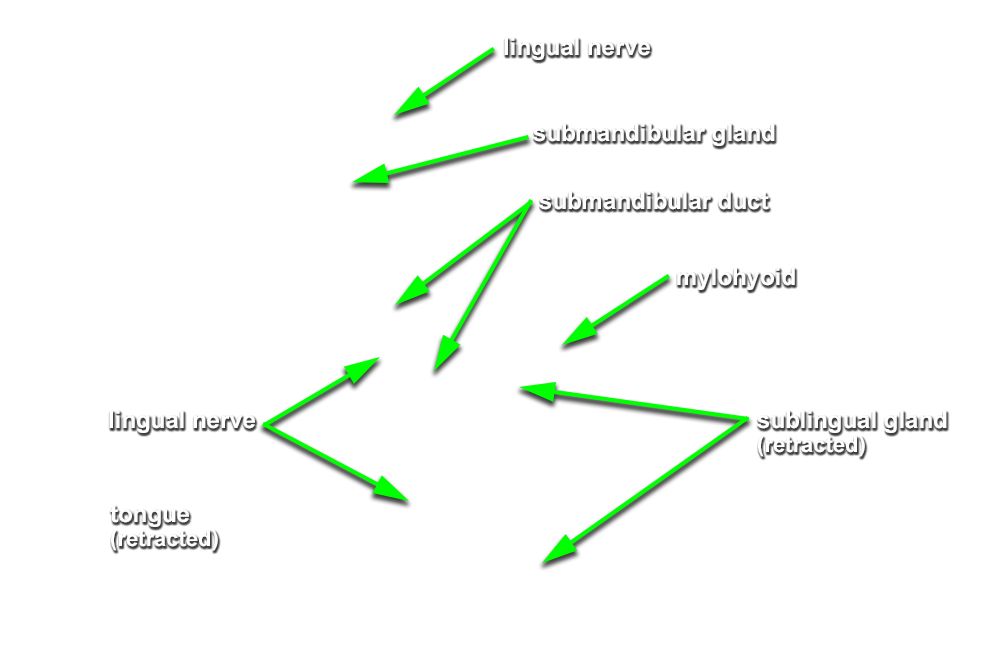
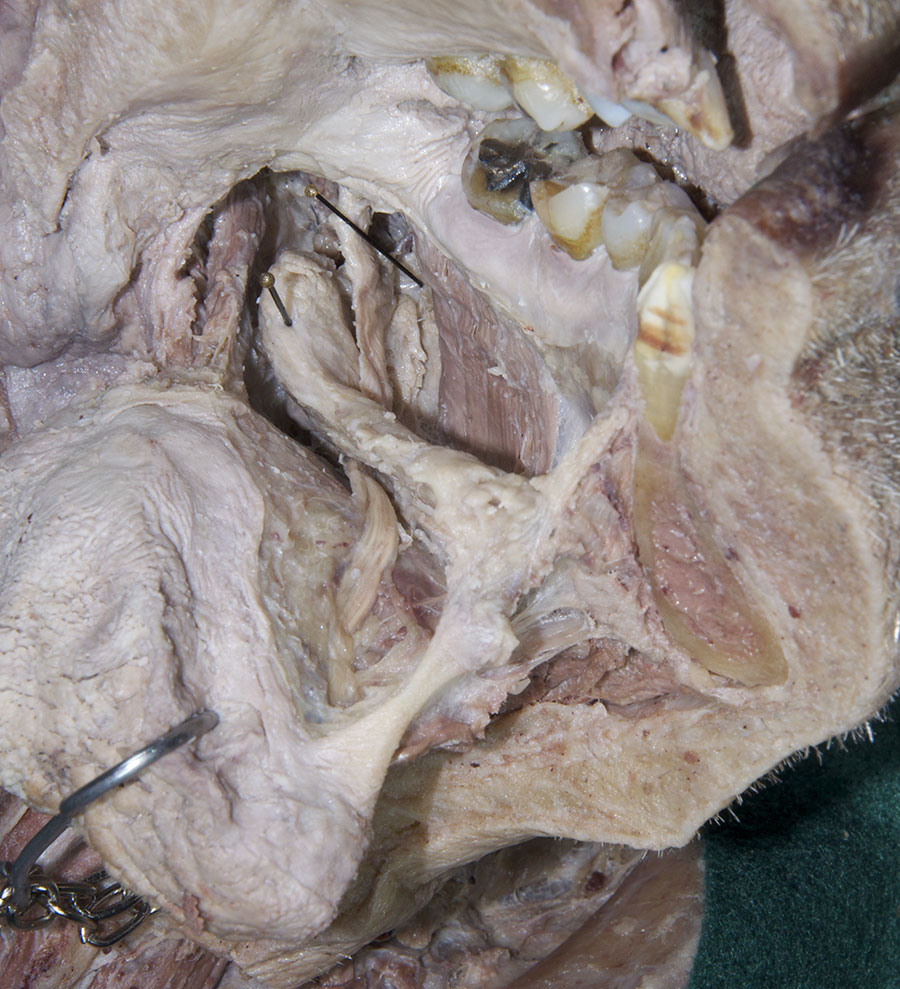
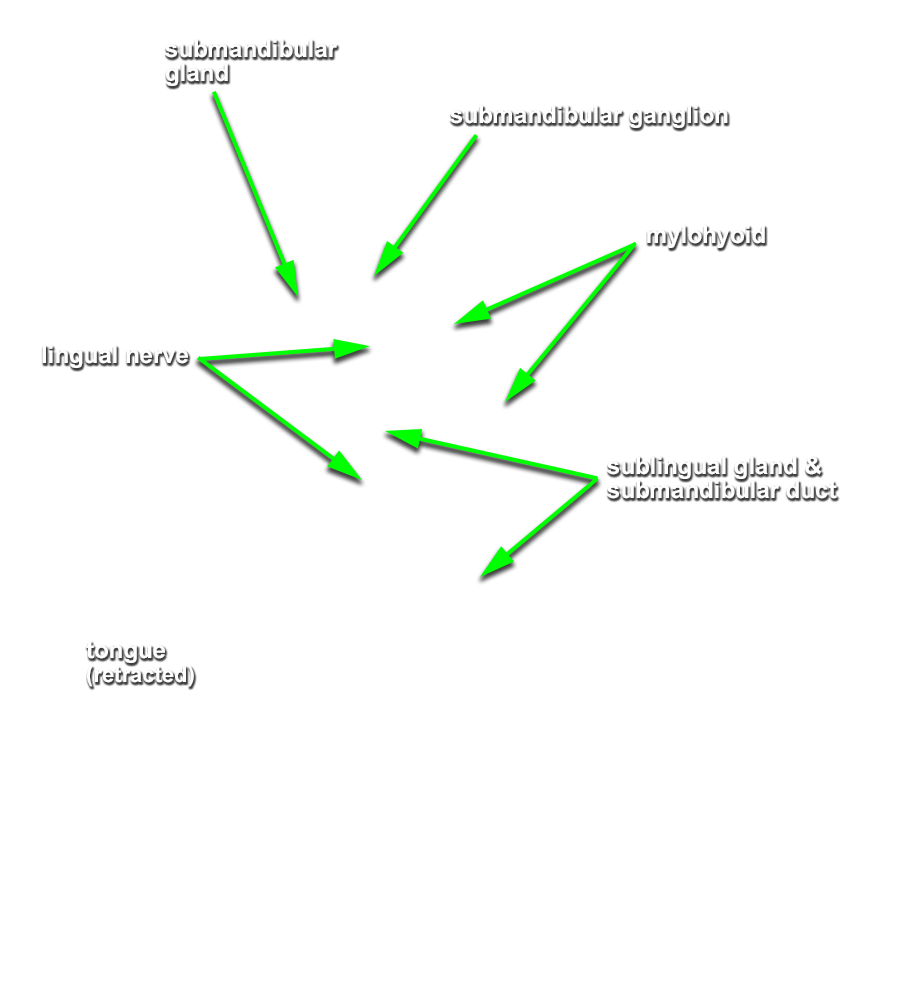
(ON THE LEFT SIDE ONLY) Carefully strip the mucosa from the sublingual fold and posterior-lateral aspect of the oral cavity. Identify and clean the
sublingual gland,
submandibular duct and
lingual nerve. (G 8.19B;N 53;Gl 38.27C)
Important Relationship
- The sublingual artery is positioned inferior to the submandibular duct.
- The sublingual gland is positioned superior to the mylohyoid muscle and lateral to the genioglossus muscle.
- The lingual nerve passes medial to the mandible and lateral to the medial pterygoid and styloglossus muscles.
- The lingual nerve passes inferior to the superior constrictor and pterygomandibular raphe.
- The lingual nerve passes lateral, inferior and medial to the submandibular duct.