Standing or sitting
Ask the patient to remove shoes and socks to allow direct palpation on the skin.
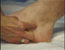
Medial to the patientís foot.
Please stand (or sit). May I touch the inside of your foot? (or demonstrate).
Guide the patient to stand (or sit). Ask the patient to relax the arch of the foot or
stand on one foot while the arch is relaxed. If given permission, place your thumb on
the medial aspect of the navicular bone. If the patient had excessive pronation, the
tuberosity of the navicular bone will be prominent distal to the head of the talus,
which will bulge medially and be displaced downward.
With the prominence of the navicular bone and the medial bulge and downward displacement of the talus, the muscles on the medial foot, the tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus will be stretched and can be painful as they attempt to maintain the position of the sustentaculum tali, which is the bony structure supporting the talus.
With the prominence of the navicular bone and the medial bulge and downward displacement of the talus, the muscles on the medial foot, the tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus will be stretched and can be painful as they attempt to maintain the position of the sustentaculum tali, which is the bony structure supporting the talus.
VH - Tibia, fibula and foot skeleton showing the medial side ñ add the tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus on one side