
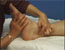
Sidelying
Ask the patient to wear shorts or roll up long pants and remove shoes and socks.
Medial to the foot being examined.
Please lie on your side. May I touch the inside of your ankle and the bottom of your big toe? (or point to the areas). Please bend and straighten your big toe (or demonstrate).
Guide or ask the patient to lie on his/her side. With the patient relaxed and with permission, place your fingers on the posterior aspect of the medial ankle, posterior to the tibialis posterior tendon, the flexor digitorum longus tendon, and the posterior tibial artery and vein. This muscle is palpable just anterior to the calcaneal tendon (Achilles tendon).
Ask the patient to flex and then relax the hallux. This action allows the alternate tensing and relaxation of the flexor hallucis longus muscle and tendon.
If location of the tendon is difficult, guide the patient to invert the foot to locate the tibialis posterior tendon first.
The distal tendon of this muscle is palpable as it inserts onto the plantar aspect of the distal phalanx of the hallux. The tendon is tensed as the patient attempts to flex the hallux. Palpation is enhanced with stabilization of the medial and lateral sides of the distal phalanx while flexion is attempted but full flexion is prevented. Prevention of full joint motion allows room for palpation of the tendon.
If location of the tendon is difficult, guide the patient to invert the foot to locate the tibialis posterior tendon first.
The distal tendon of this muscle is palpable as it inserts onto the plantar aspect of the distal phalanx of the hallux. The tendon is tensed as the patient attempts to flex the hallux. Palpation is enhanced with stabilization of the medial and lateral sides of the distal phalanx while flexion is attempted but full flexion is prevented. Prevention of full joint motion allows room for palpation of the tendon.
VH - Leg and foot skeleton with Achilles tendon, gastrocnemius and soleus muscles and tendonñ add posterior tibialis, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus and peroneus longus and brevis muscles and tendons on one side