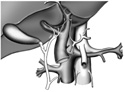
Origins of left gastric, splenic, and superior mesenteric arteries.
Trace the common hepatic artery back to the celiac trunk identifying two more celiac branches:
Directly inferior (1/2 inch) to the celiac trunk identify the superior mesenteric artery arising from the abdominal aorta. This artery is distributed to most of the small intestine. Find the superior mesenteric vein with the superior mesenteric artery.
You can now find the inferior vena cava as it lies to the right and slightly posterior to the abdominal aorta.
Large transversely running renal veins can be seen emptying into the inferior vena cava near the level of origin of the superior mesenteric vein. Notice the left renal vein is somewhat more superior to the right renal vein. Trace these veins to the kidneys.
Posterior to these veins, find the renal arteries running from the abdominal aorta to the kidneys.
Moving inferior to the renal arteries, on the abdominal aorta, find the gonadal arteries. In older individuals, these can be very small and easily lost. The much larger gonadal veins reflect the common development of the urinary and reproductive systems. The left gonadal vein empties into the left renal vein; the right gonadal vein empties into the inferior vena cava. (Figure 3-24)
Just superior to where the abdominal aorta bifurcates into the common iliac arteries find the small inferior mesenteric artery. The inferior mesenteric artery runs to the lower left abdominal quadrant and supplies the descending and sigmoid colon, as well as the rectum.
Return to the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta. Again locate the first branches after the aortic split, the right and left common iliac arteries. If you follow a common iliac inferiorly you will see it split into a medially branching internal iliac, which supplies most of the pelvic viscera. The other, more lateral branch is the external iliac that will eventually become the femoral artery and supply the lower extremity with arterial blood.
Now see if you can find the bifurcation of the inferior vena cava into right and left common iliac veins, each of which then splits into an internal and external iliac vein. (Figure 3-25)