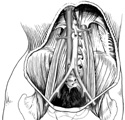
Posterior abdominal muscles and blood vessels.
Identification of these structures will be easiest on a cadaver after the G.I. system has been removed.
Posterior and inferior to the kidneys against the vertebral column, locate the long psoas major. This muscle begins inferior to the diaphragm, descends through the pelvis and joins the iliacus muscle filling the iliac fossa. The two muscles form the iliopsoas.
Lateral to the psoas, find the quadratus lumborum muscle. Farther lateral, identify the tendinous part of the transversus abdominis muscle.
Identify at least one of the four paired
lumbar arteries
 arising superior to the bifurcation of the aorta, inferior to the renal arteries. Coming off the sides of the aorta, these small arteries soon disappear beneath the psoas muscle on their way to supply the posterior abdominal wall. (Figure 3-27)
arising superior to the bifurcation of the aorta, inferior to the renal arteries. Coming off the sides of the aorta, these small arteries soon disappear beneath the psoas muscle on their way to supply the posterior abdominal wall. (Figure 3-27)