The pelvic contents of the male.
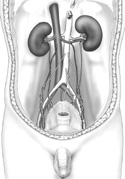
Find the ureters as they descend from the kidneys on the posterior abdominal wall. They cross over the pelvic brim and empty into the lateral sides of the urinary bladder (Figure 4-9).
From a superior to inferior view of the whole cadaver, the urinary bladder is the most anterior of the male pelvic viscera.
Moving posterior locate and identify the sigmoid colon and the rectum.
On the lateral side of the pelvic cavity, is the deep inguinal ring with the testicular artery, vein and the ductus deferens passing through it. Follow the ductus deferens medially until the left and right ducts enlarge and merge with the ducts of the seminal vesicles.
If the peritoneum has been sufficiently removed, you may be able to lift the urinary bladder and see the seminal vesicles projecting laterally from this juncture.
Now identify the abdominal aorta as it splits into a right and left common iliac artery. Follow the common iliac artery until it splits into an internal and external iliac artery. Likewise, identify the internal and external iliac veins, joining to form the common iliac vein, which joins with its partner on the other side to form the inferior vena cava.