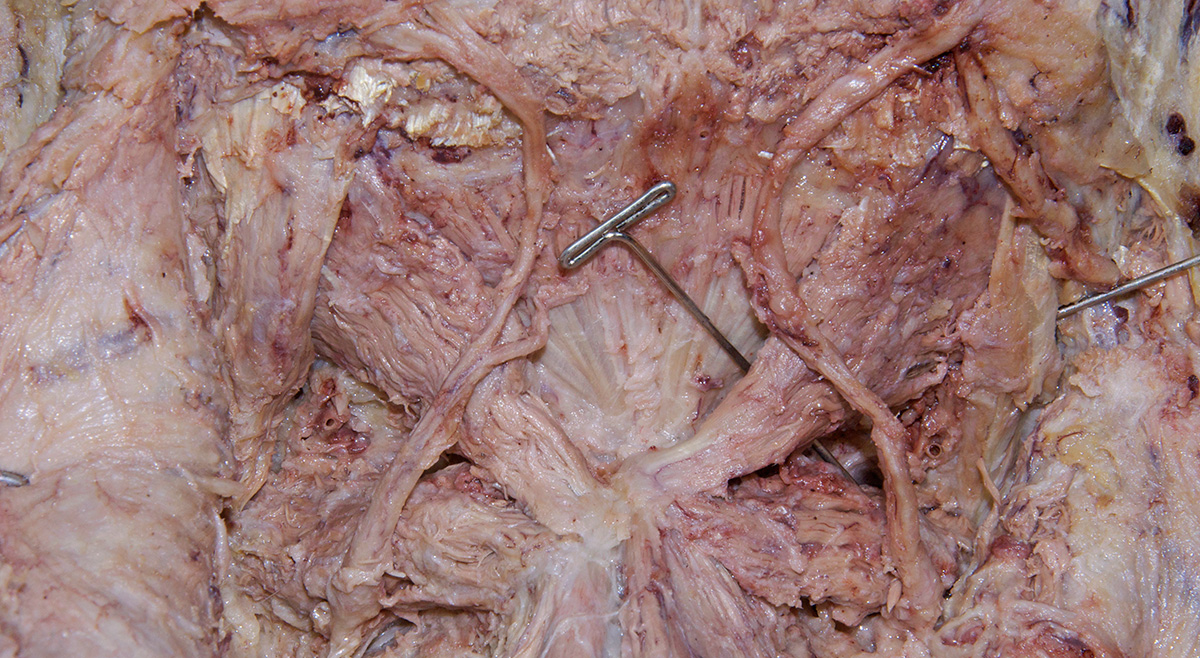
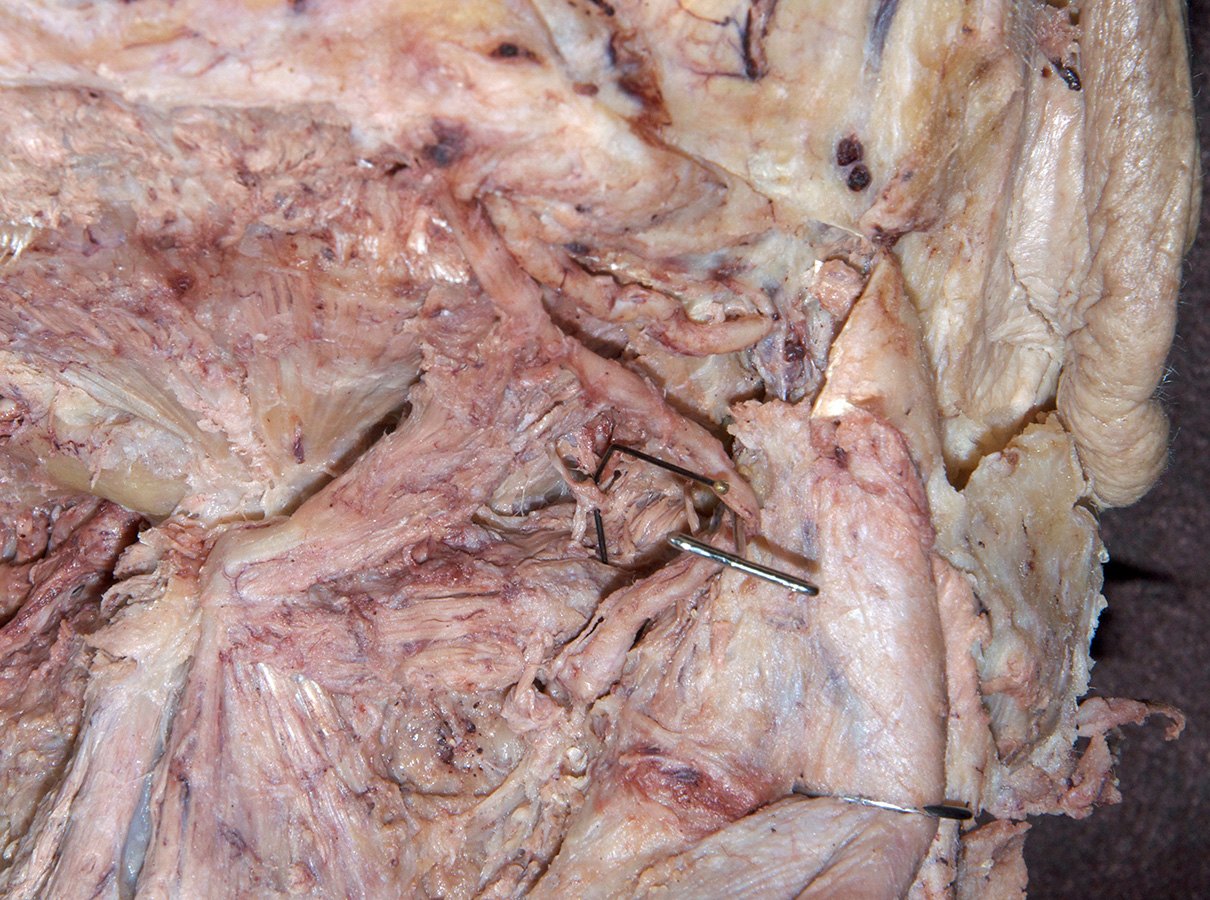
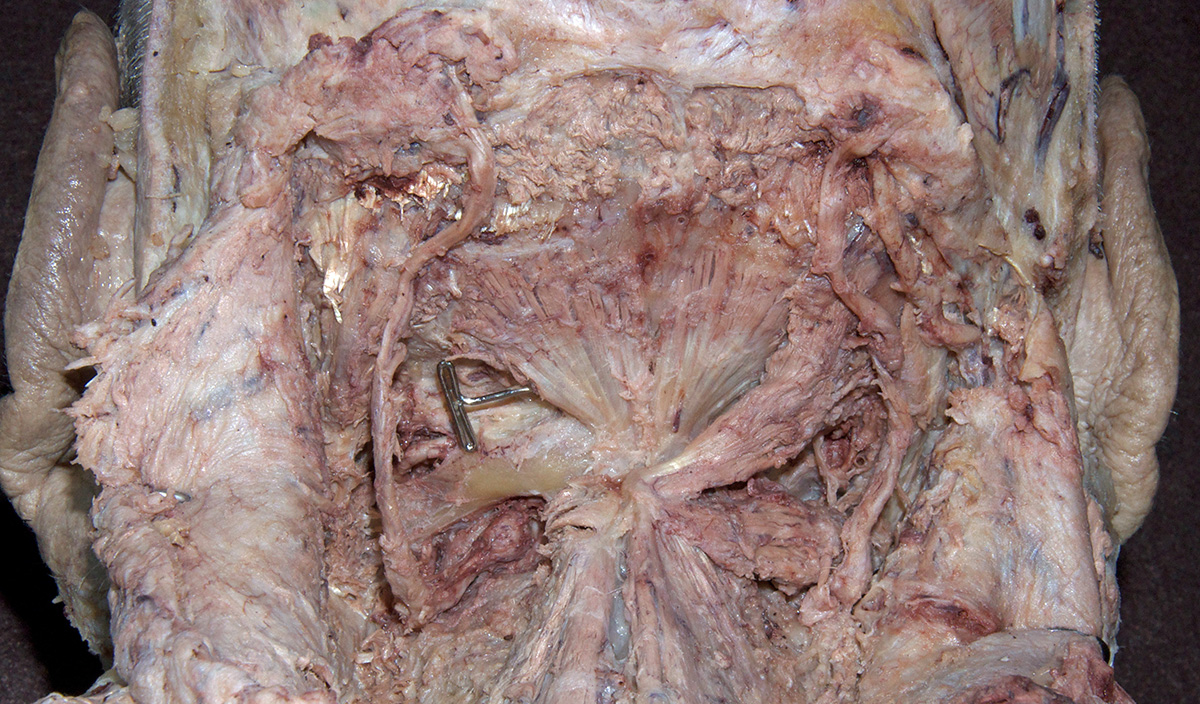
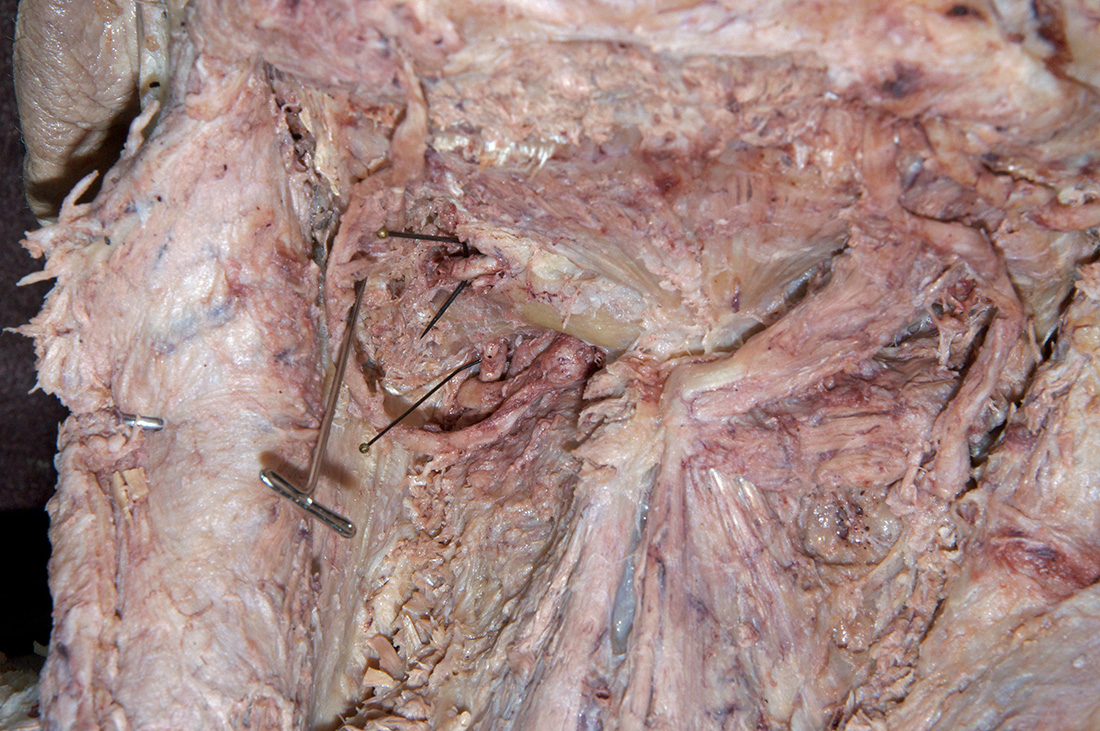
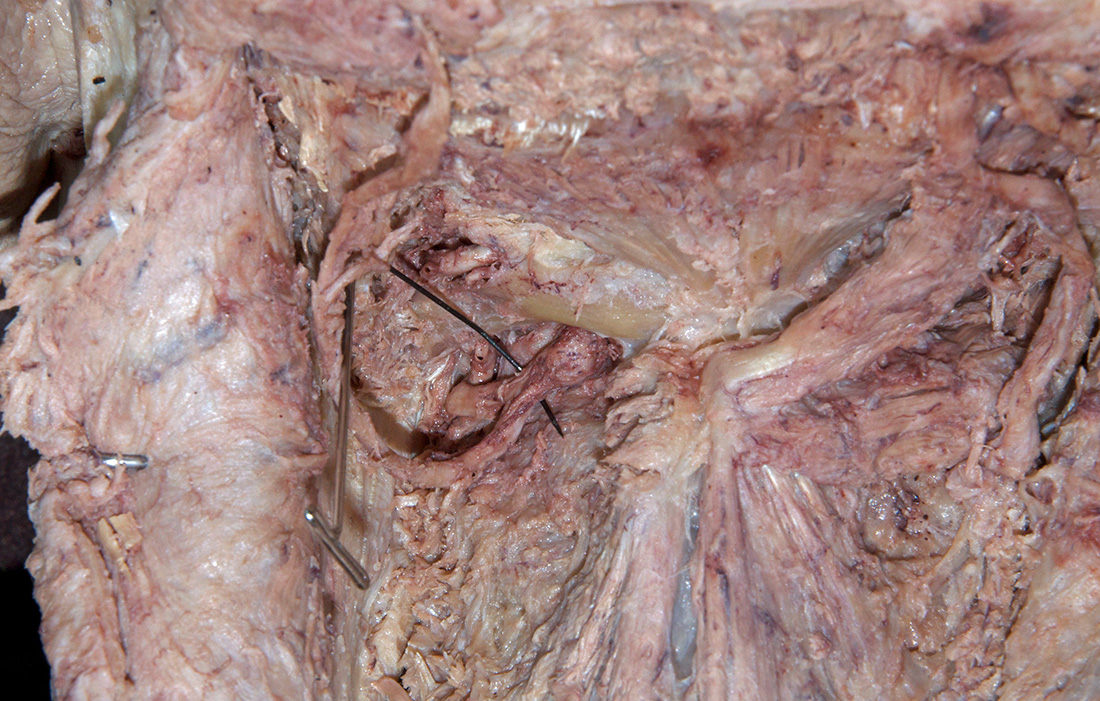
Identify the structures of the suboccipital triangle. (G 4.39;N 172;Gl 4.17)
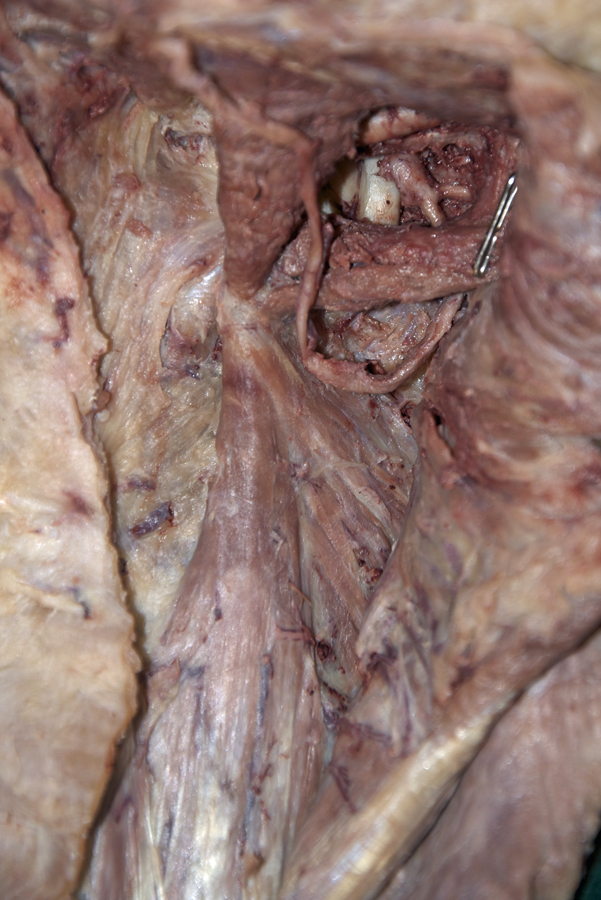
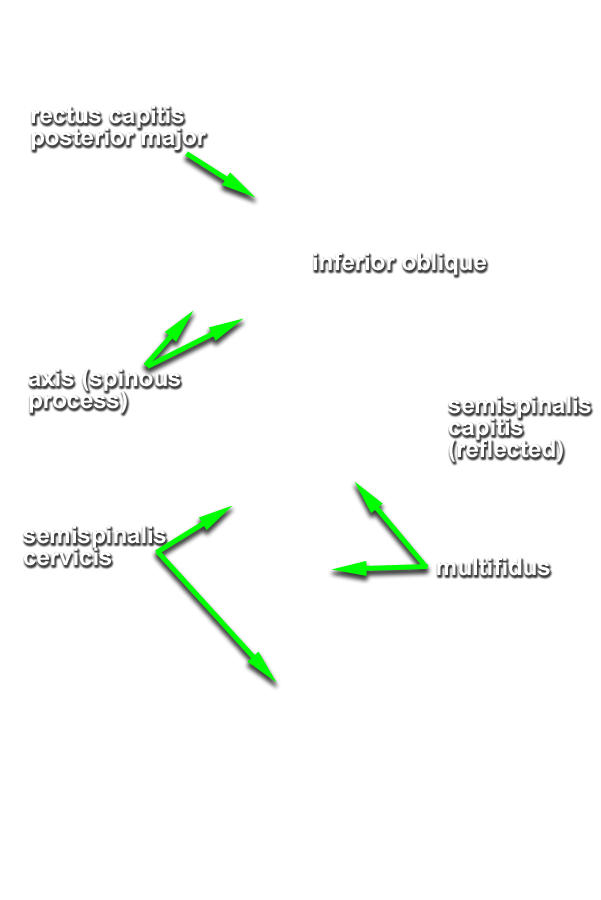
- Start by identifying (palpation) the bifid spinous process of the axis.
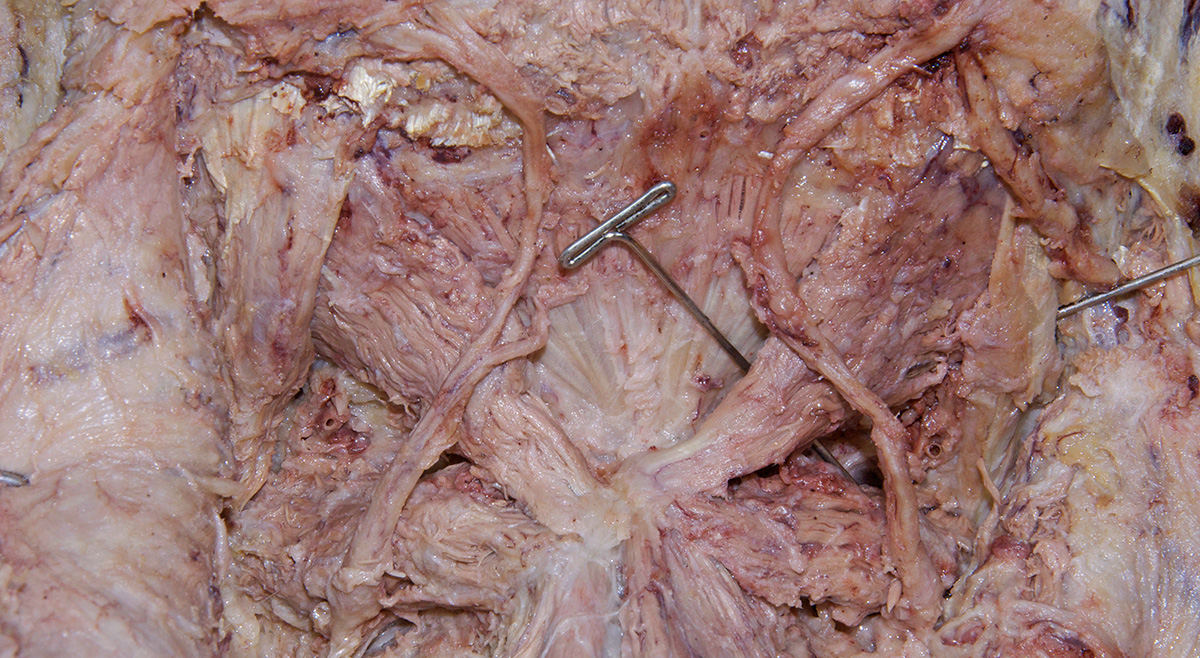
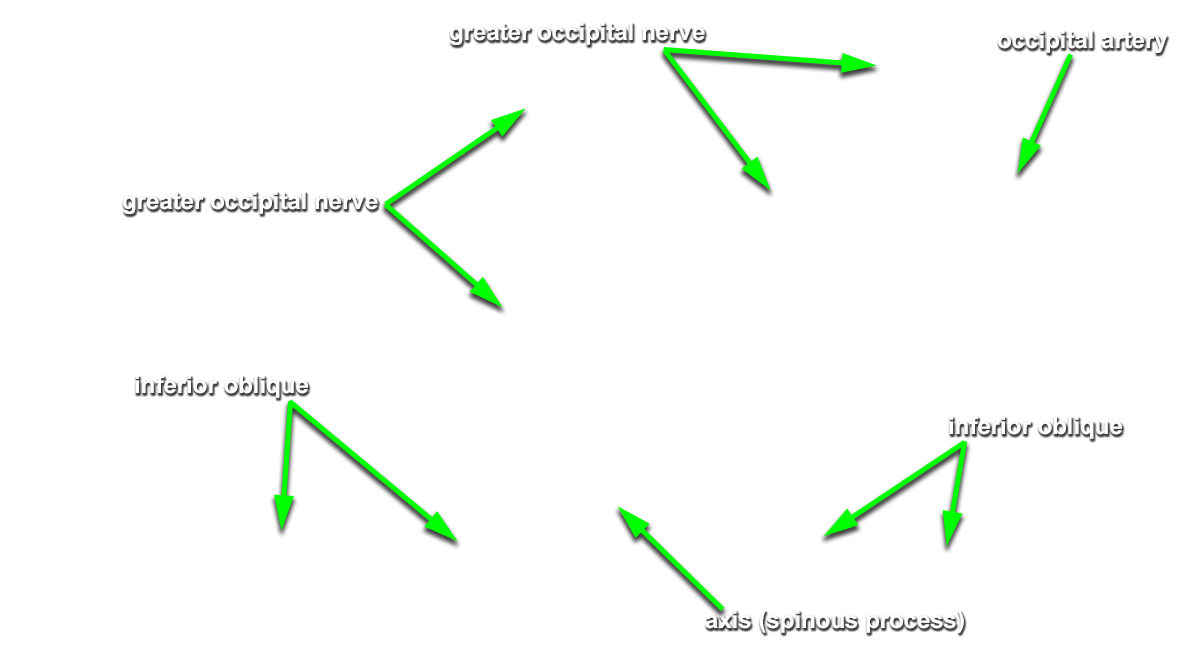
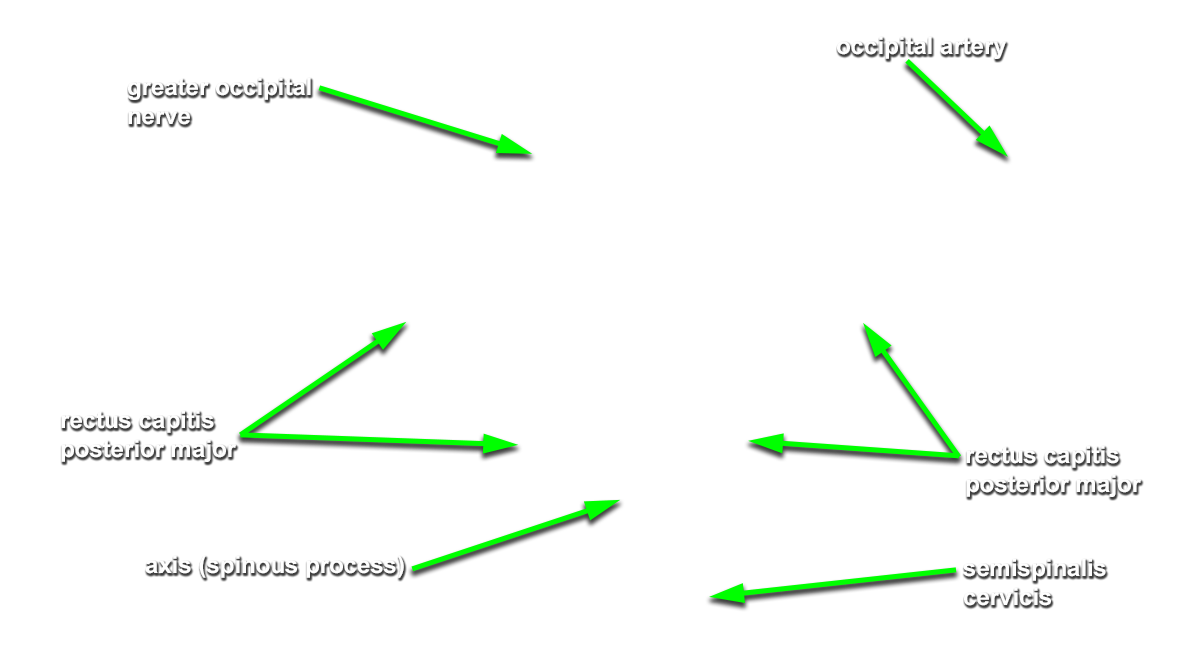
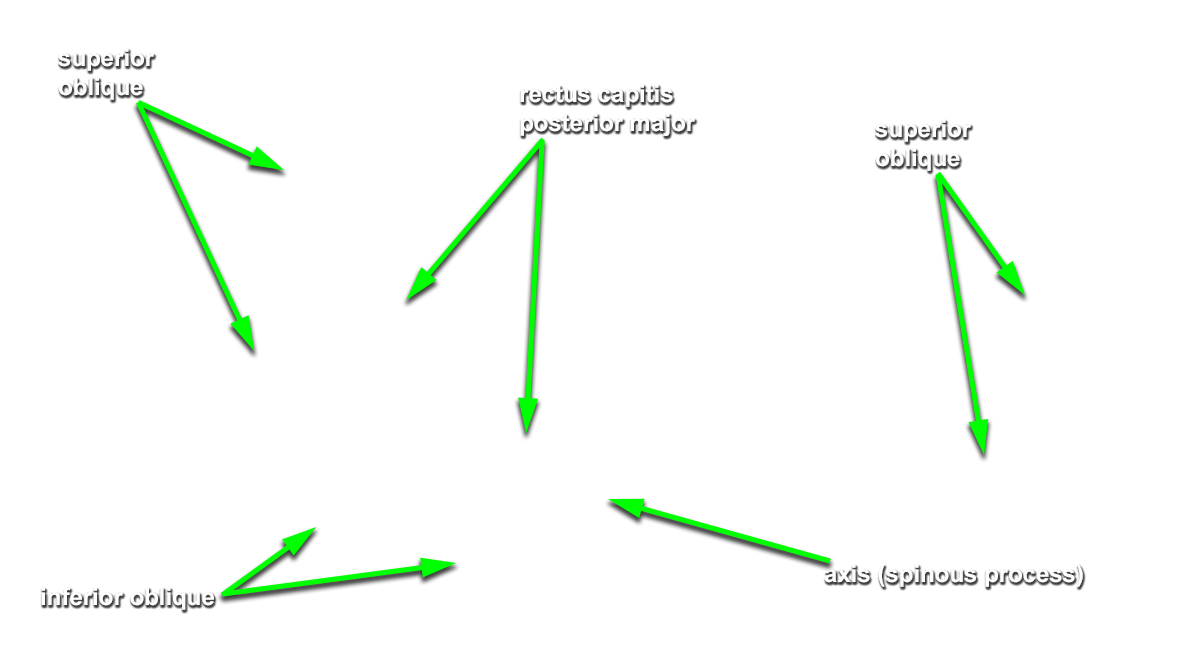
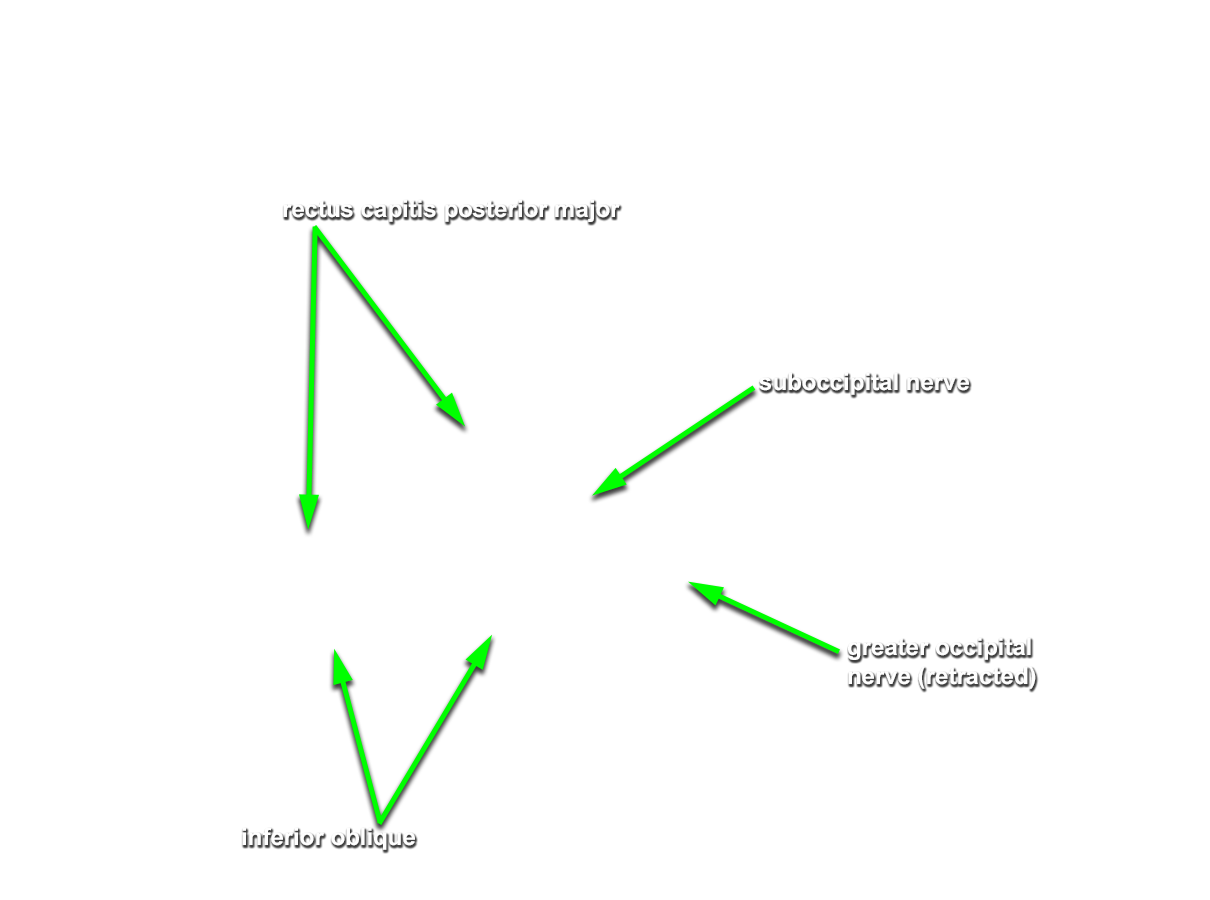
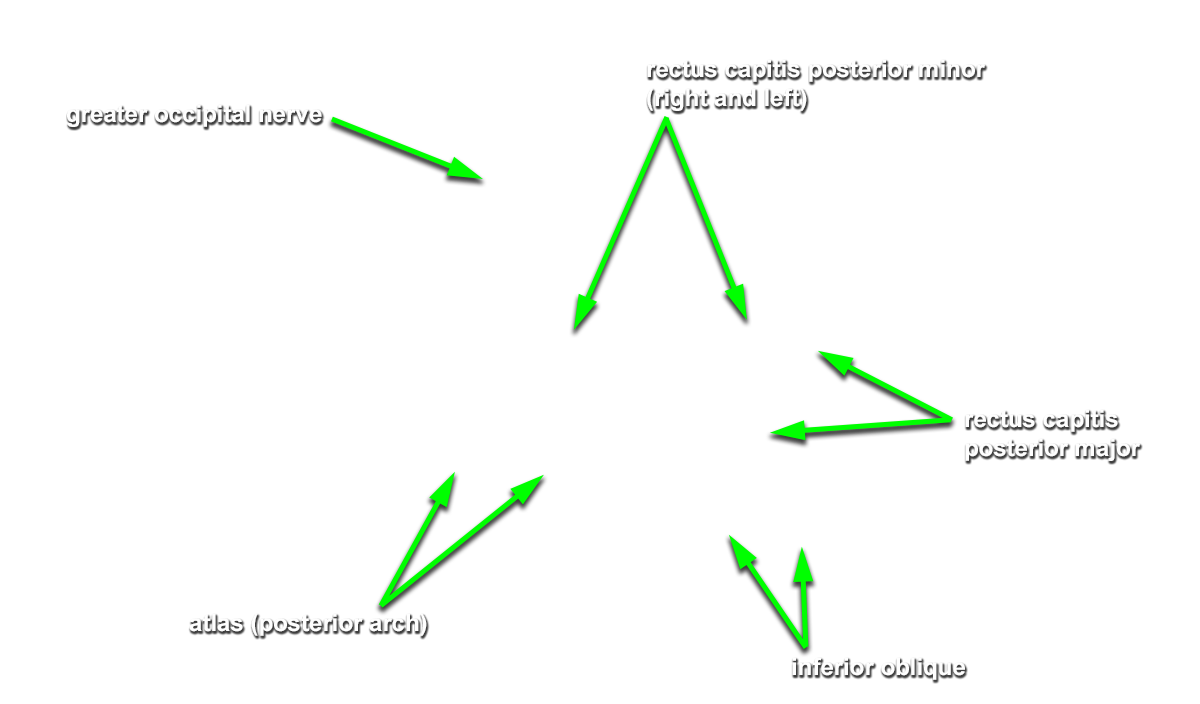
Identify the semispinalis cervicis muscle attaching to the spinous process of the axis. Use the spinous process of the axis and the greater occipital nerve to identify the inferior oblique muscle. The greater occipital nerve passes posterior and then inferior to this muscle. - Identify the rectus capitis posterior major muscle. This muscle also attaches to the spinous process of the axis.
- Identify the superior oblique muscle. Attempt to identify the suboccipital nerve in the suboccipital triangle.
- Identify the
rectus capitis posterior minor muscle and
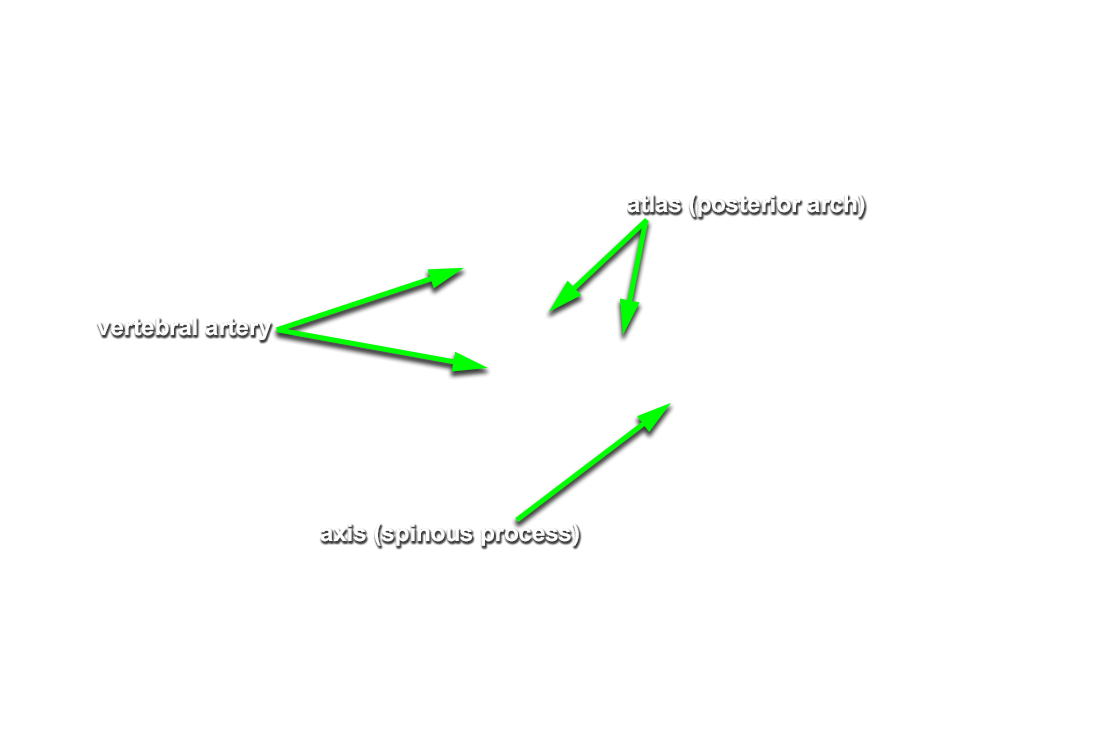
posterior arch of the atlas. Identify the
vertebral artery along the superior surface of the posterior arch of the atlas.
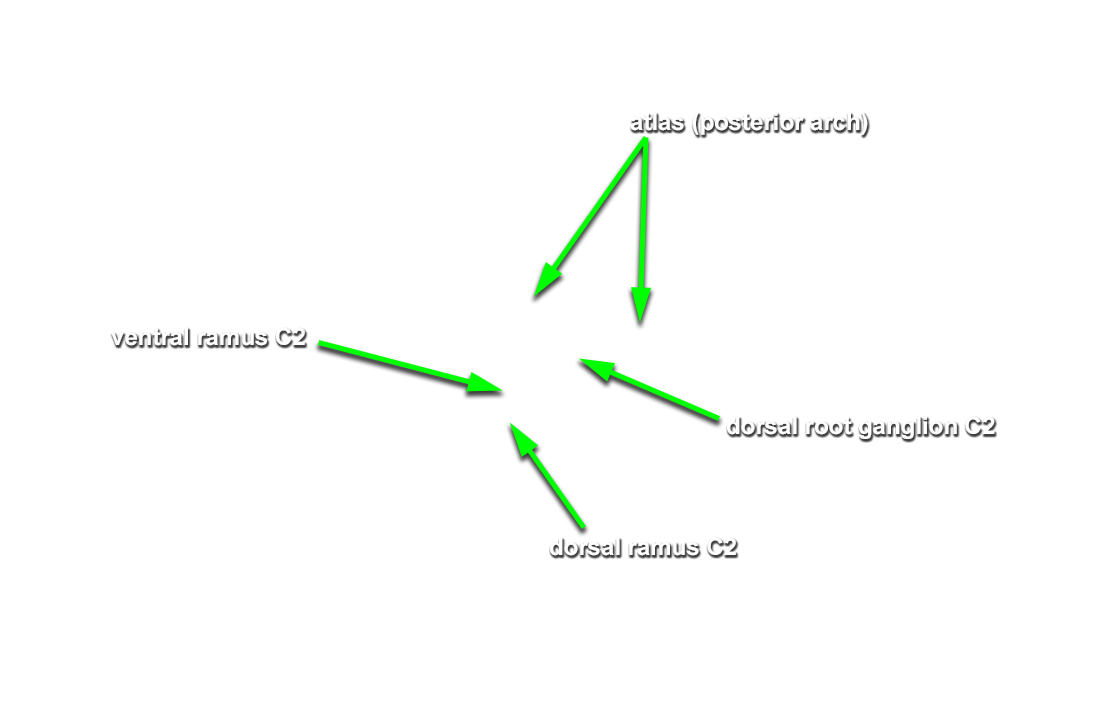
(G Table 4.5 Posterior View;N 172;Gl 4.17) Trace the greater occipital nerve in the proximal direction to identify the
C2 dorsal root ganglion.
Important Relationship
- The greater occipital nerve passes inferior and posterior to the inferior oblique muscle.