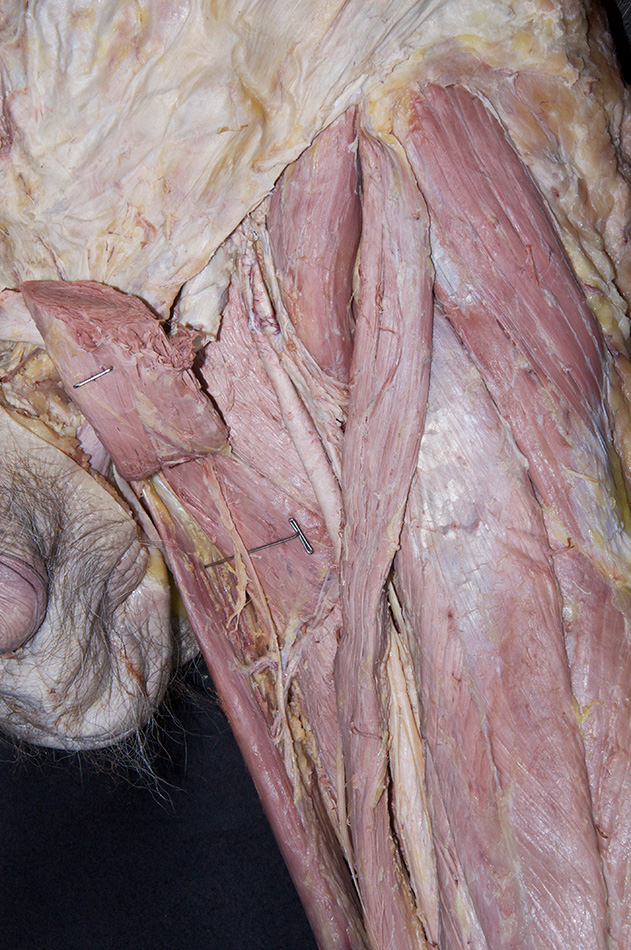
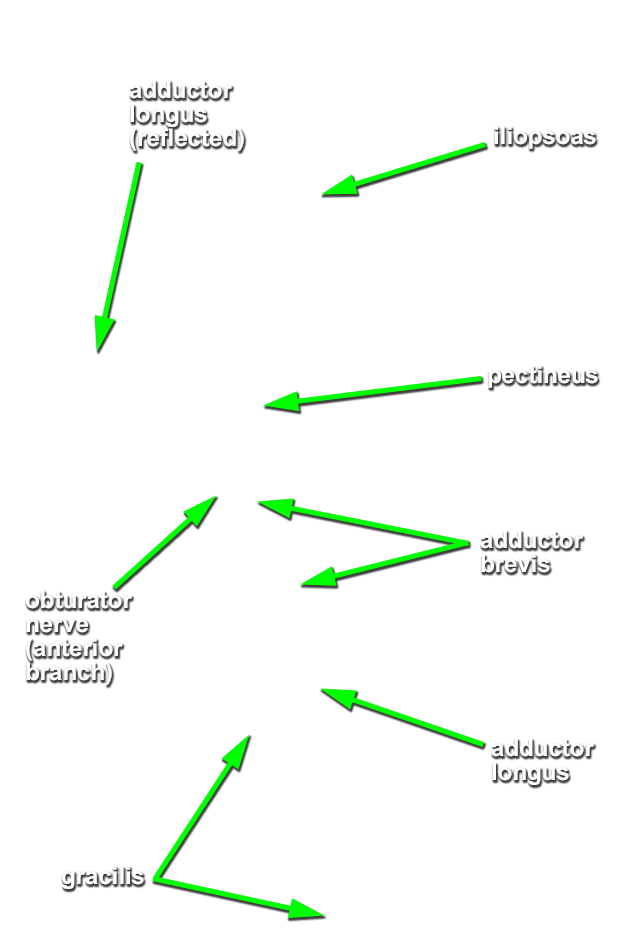
Return to the adductor longus and pectineus muscles.
- Separate these muscles from each other. Attempt to identify the first perforating branch of the profunda femoral artery that typically passes between the pectineus and the adductor longus muscles.
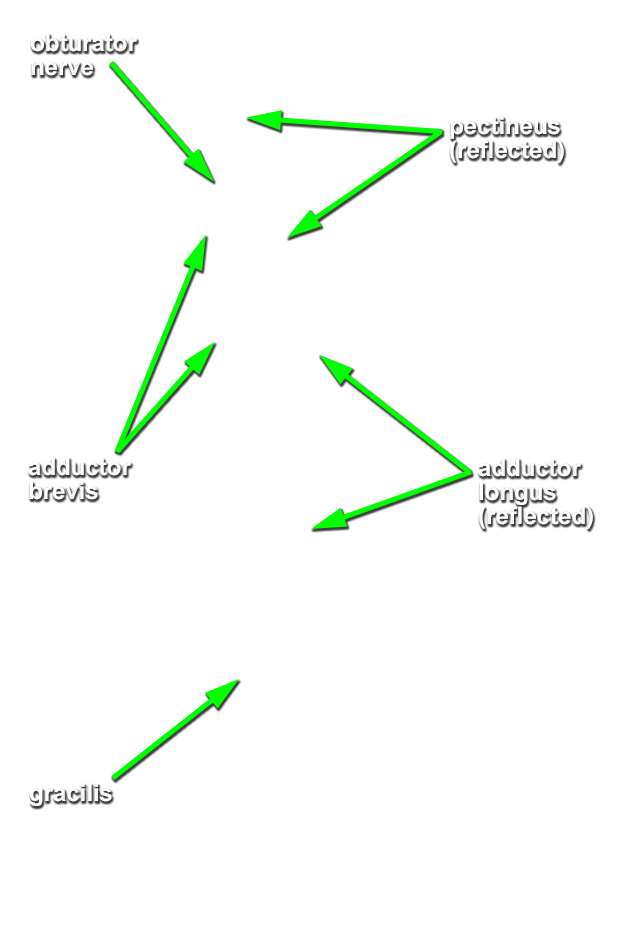
- Identify the anterior branches of the obturator nerve (G 6.25;N 488;Gl 34.34B) entering the gracilis muscle. Trace these nerve branches in the superior-lateral direction. They will pass between the adductor longus and the (deeper) adductor brevis muscles.
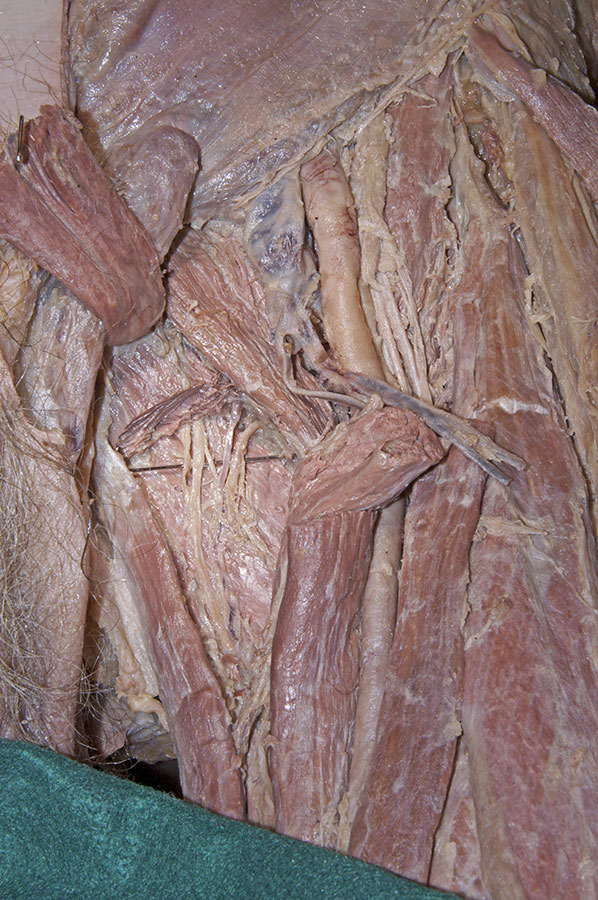
- Transect the adductor longus muscle midway between its proximal and distal attachments. Reflect both parts of the adductor longus to expose the adductor brevis muscle. (G 6.21B;N 488;Gl 31.11D)
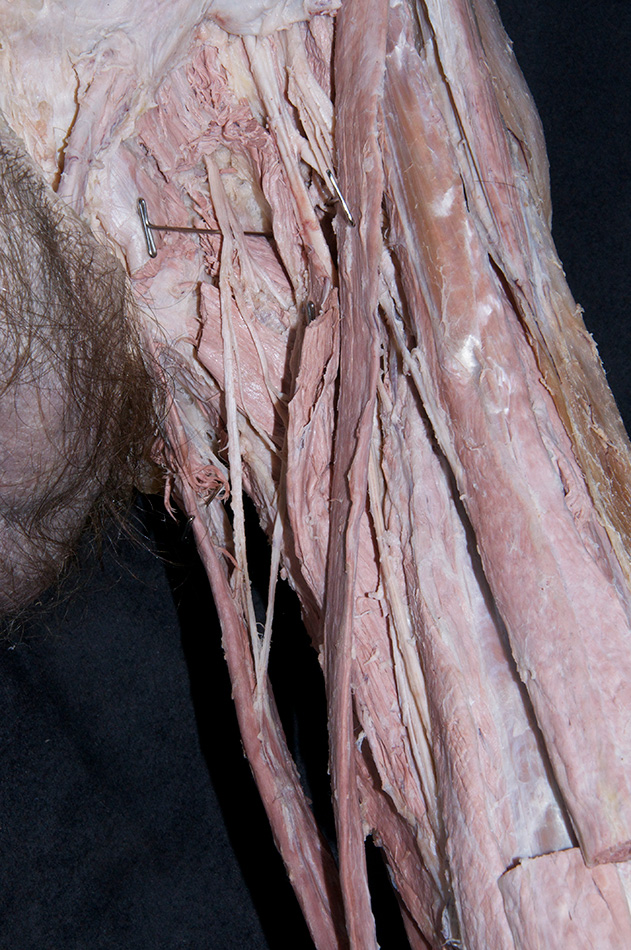
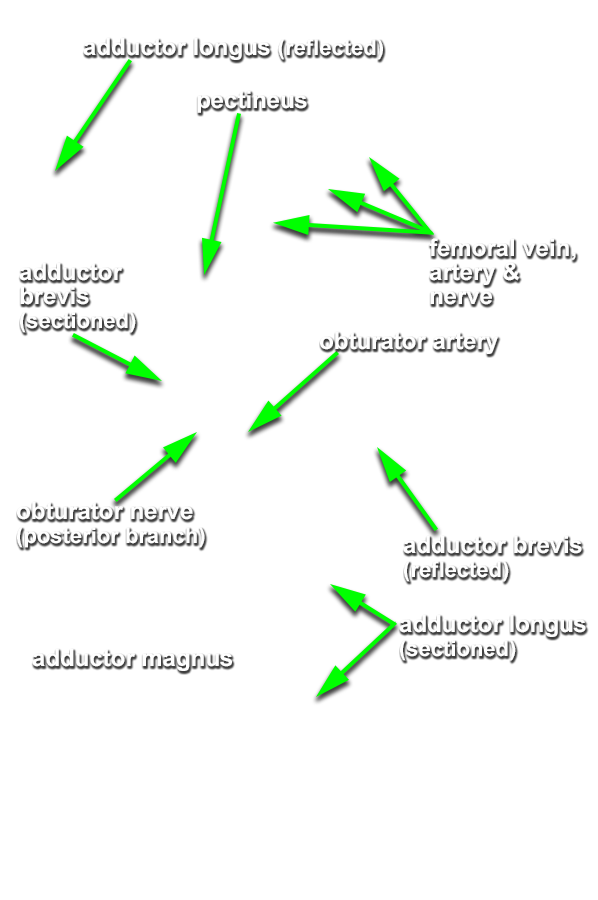
- Return to the obturator nerve branches. Trace the branches across the anterior surface of the adductor brevis. The branches disappear under the pectineus muscle. At this point they join the posterior branches of the obturator nerve (N 488;Gl 34.15). Blunt dissect and trace the posterior branches as they pass posterior to the adductor brevis muscle. As you trace the branches, you will separate the adductor brevis from the deepest muscle of the medial compartment, the adductor magnus. Attempt to identify the obturator artery.
Important Relationships
s
- The obturator nerve passes directly inferior to the superior pubic ramus.
- The adductor brevis muscle is positioned posterior to the adductor longus and anterior to the adductor magnus muscle.