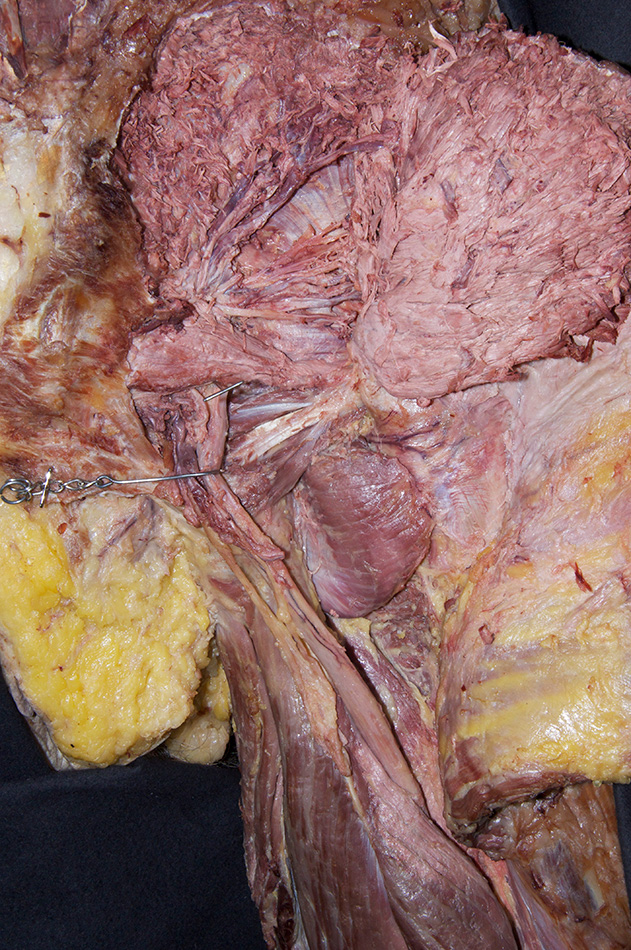
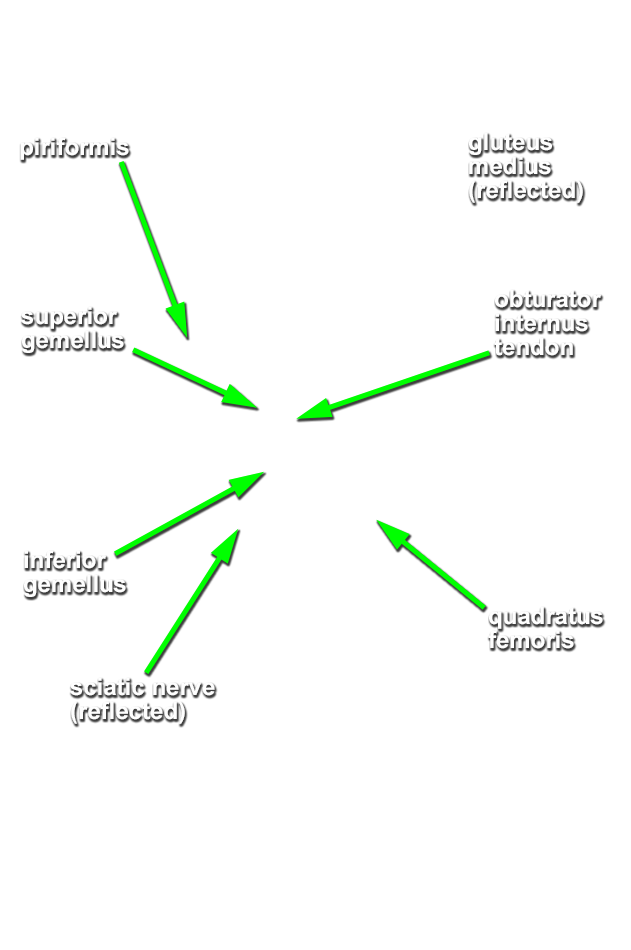
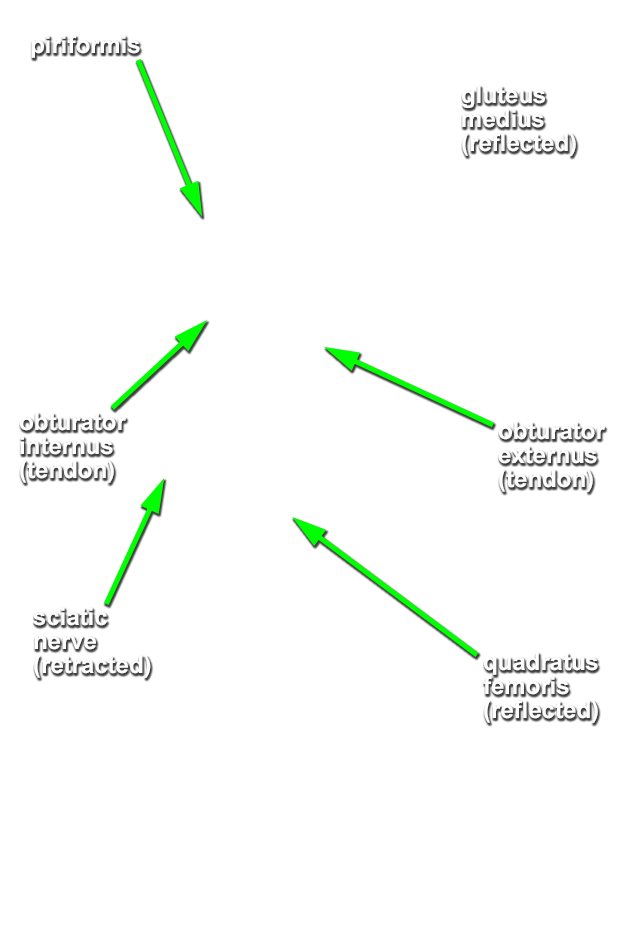
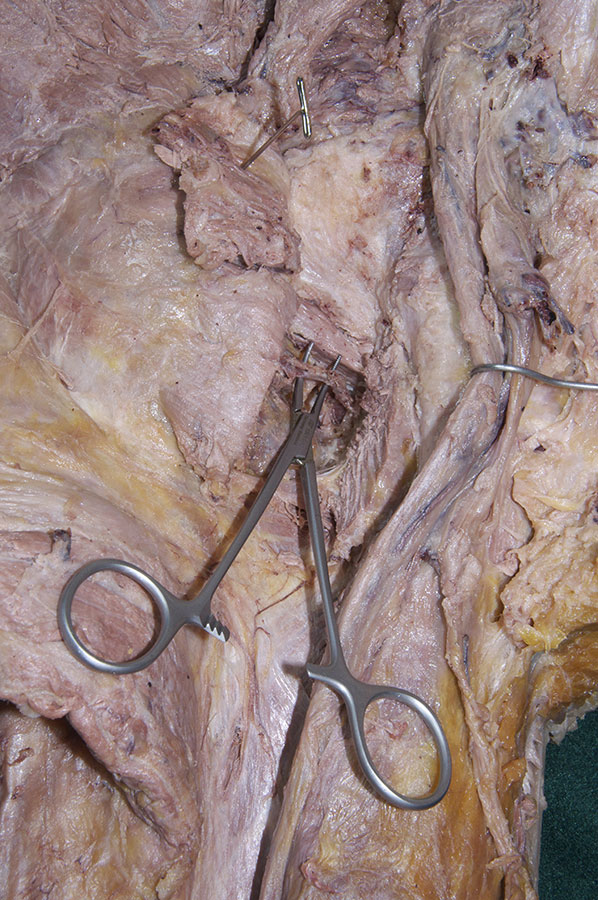
Identify the obturator internus tendon and, superior gemellus, inferior gemellus and quadratus femoris muscles. (G 6.32A;N 482;Gl 31.14B)
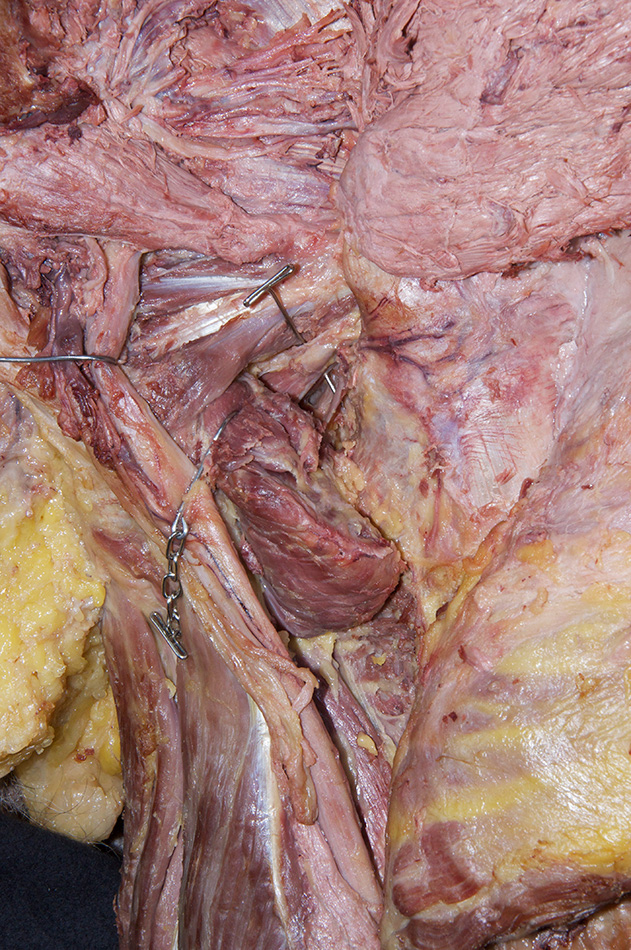
- Identify the obturator internus tendon and the adjacent superior and inferior gemelli muscles. It may be difficult to distinguish the gemelli muscles and the tendon of the obturator internus muscle as they emerge inferior to the piriformis muscle. It may be helpful to medially rotate the femur by rotating the cadaver's foot. This will remove the slack from these structures.
- Identify the quadratus femoris muscle inferior to the obturator internus tendon and inferior gemellus muscle.
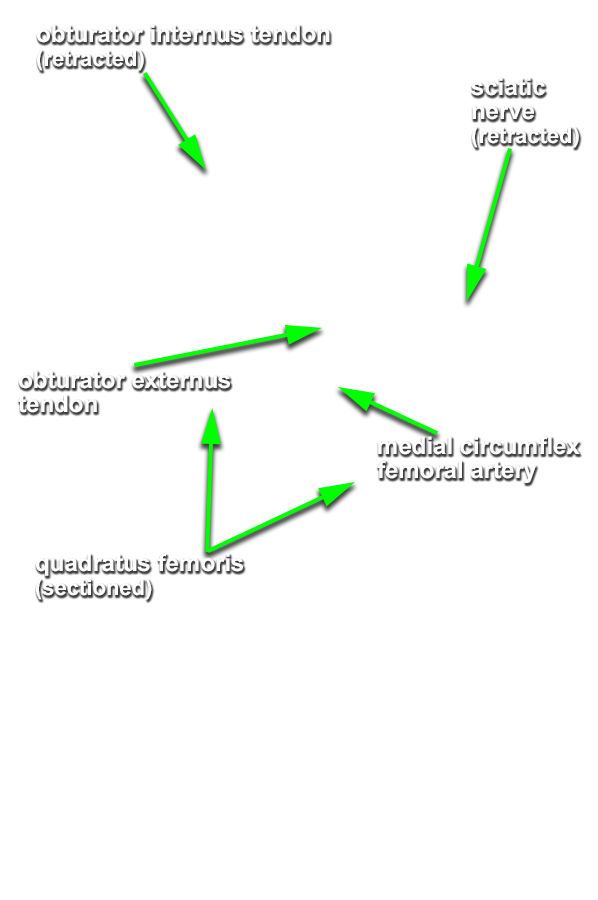
- Reflect the quadratus femoris muscle and identify the tendon of the obturator externus muscle. The vessels deep to the quadratus femoris muscle are branches of the medial circumflex femoral artery and vein.
Important Relationships
- The piriformis muscle is positioned superior to the tendon of the obturator internus (and gemelli muscles).
- The sacrotuberous ligament passes posterior (superficial) to the sacrospinous ligament.
- The obturator internus muscle passes inferior to the sacrospinous ligament.
- The obturator internus muscle passes anterior (deep) to the sacrotuberous ligament.
- The tendon of the obturator internus (and gemelli muscles) is positioned superior to the quadratus femoris muscle.
- The tendon of the obturator internus muscle passes posterior to the femur (neck).
- The obturator externus muscle passes posterior to the femur (neck).
- At its distal attachment, the tendon of the obturator externus muscle is positioned directly inferior to the tendon of the obturator internus.
- The sciatic nerve passes posterior to the obturator internus tendon, and gemelli and quadratus femoris muscles.