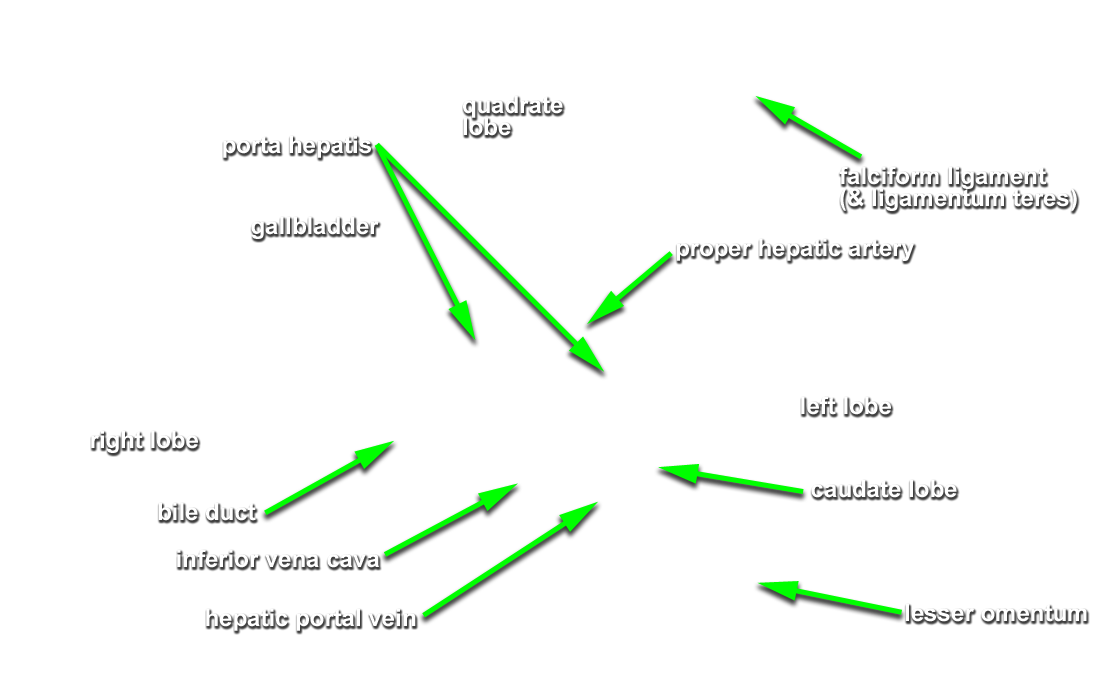
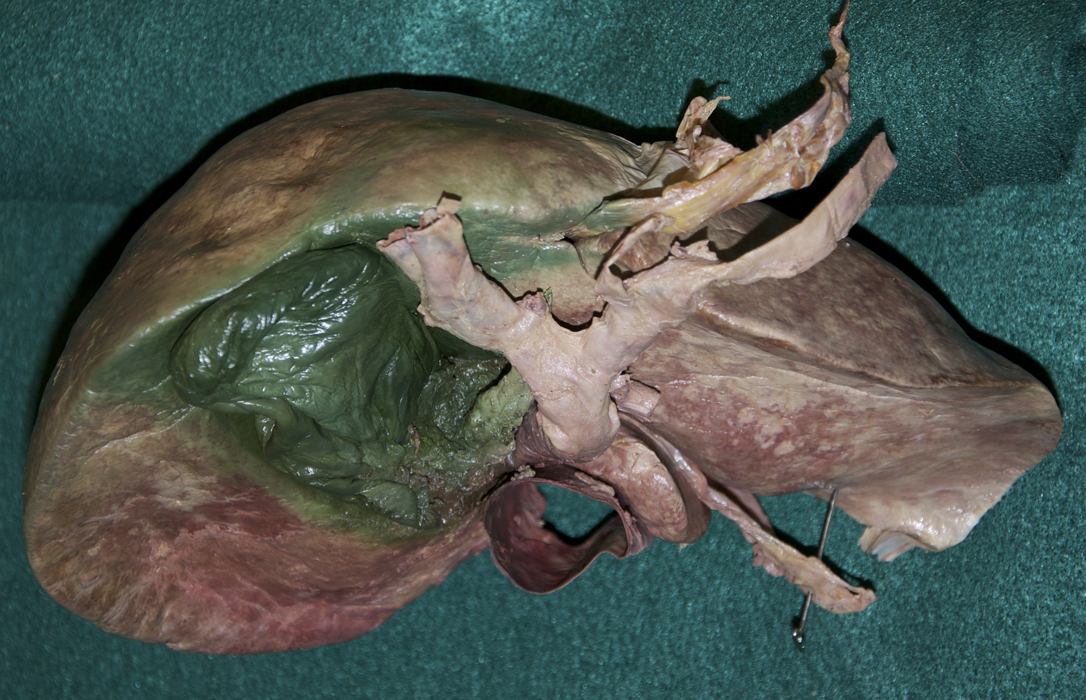
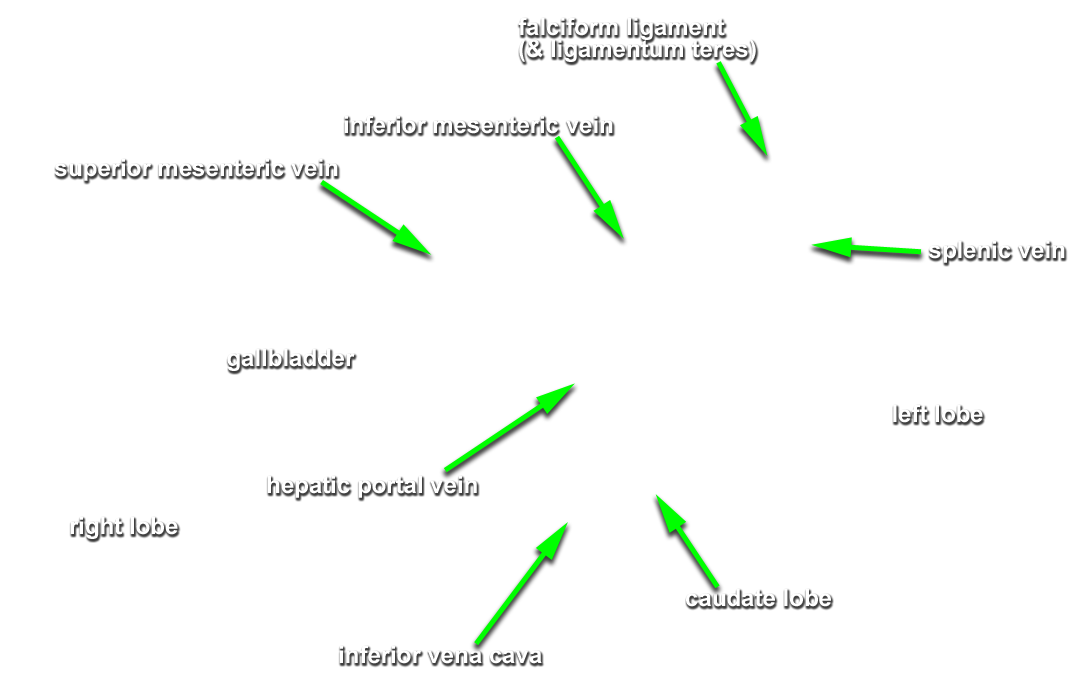
Partially mobilize the liver and examine its visceral (posteriorinferior) surface. (G 4.51A;N 277;Gl 15.22)
- Use your fingers to free the liver from the diaphragm by tearing the coronary ligament.
- Use bone shears to remove the right costal cartilages 6-10. Use a scalpel to remove the anterior right aspect of the diaphragm as far posterior as the inferior vena cava. (G 4.22A;N 268;Gl 13.6)
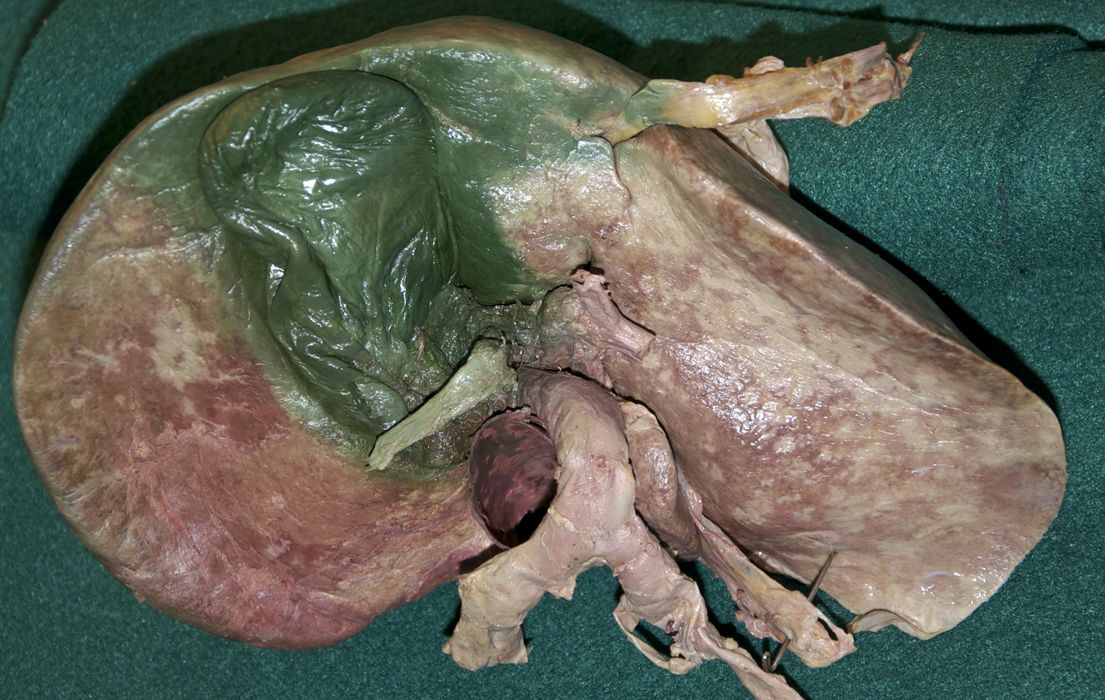
- Identify the right and left lobes of the liver (G 4.50;N 277;Gl 15.22)
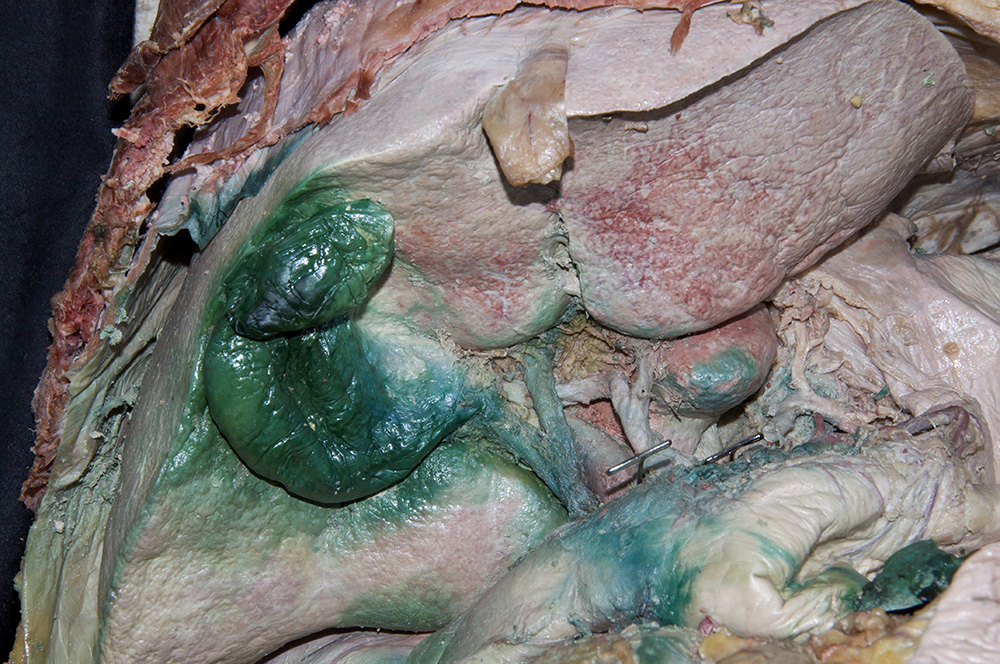
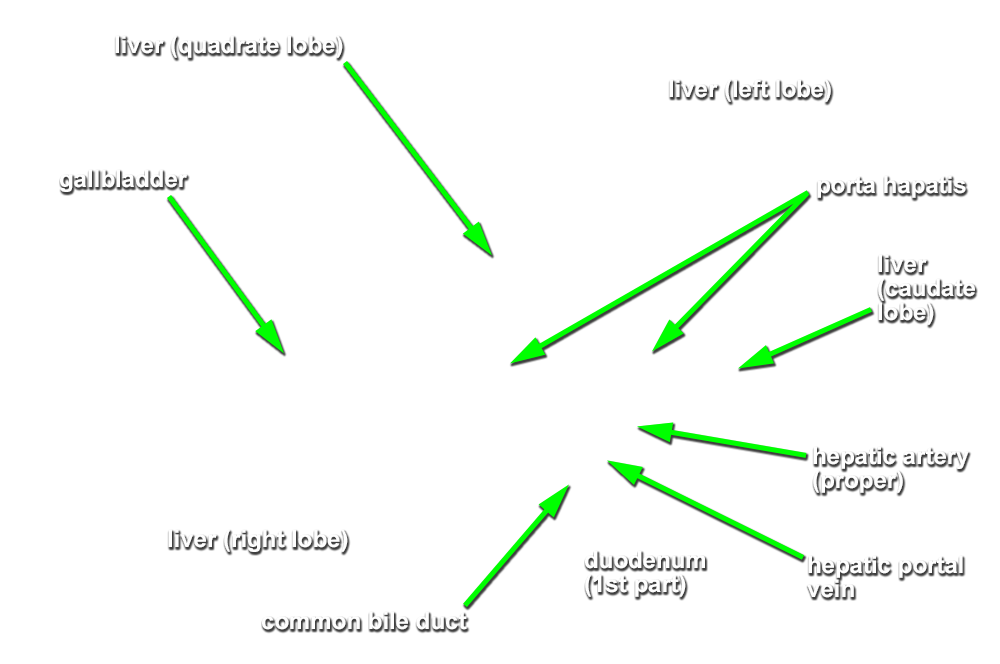
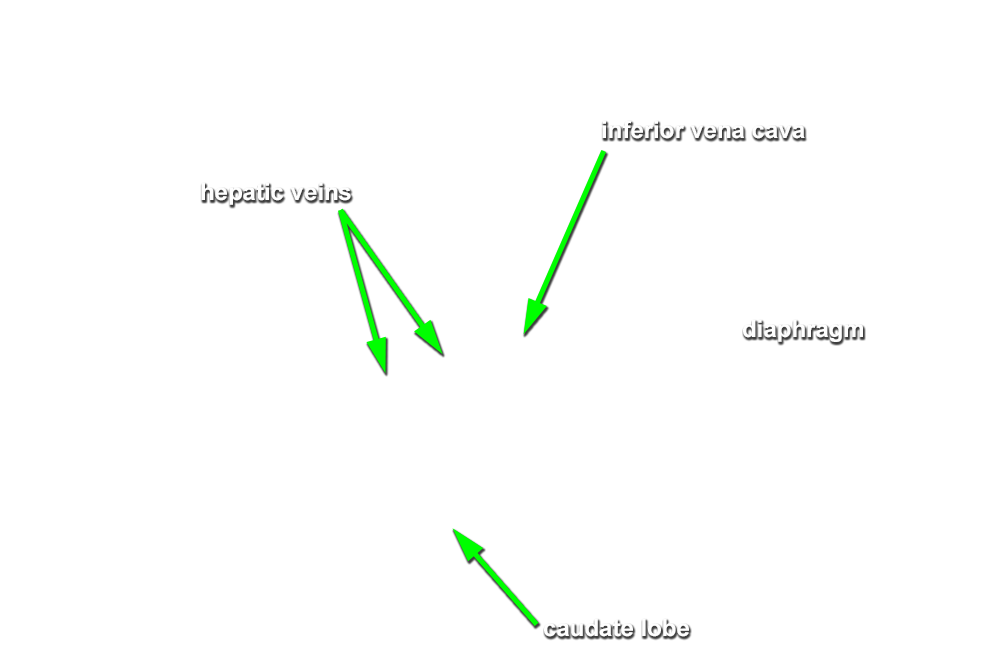
- Use your fingers to elevate the inferior margin of the liver and identify the inferior vena cava, fossa for the gall bladder, porta hepatis, caudate lobe, quadrate lobe, fissure for ligamentum teres and fissure for ligamentum venosum. (G 4.57A;N 277;Gl 15.22C) Observe (from the thoracic side) the hepatic veins draining into the inferior vena cava near the diaphragm.
Important Relationships
- The inferior vena cava passes posterior to the liver and is positioned lateral to the caudate lobe.
- The gallbladder is positioned lateral to the quadrate lobe of the liver.