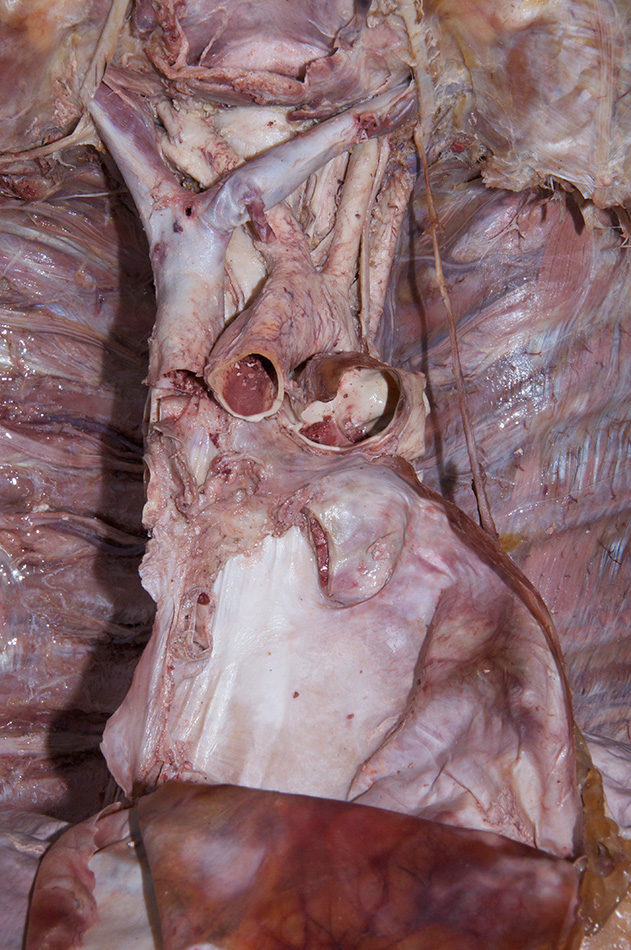
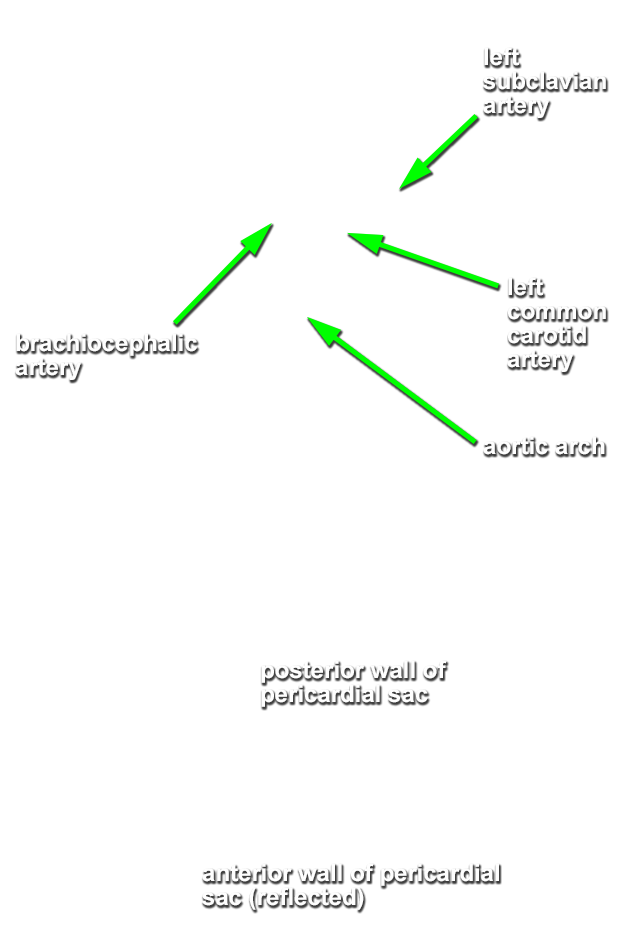
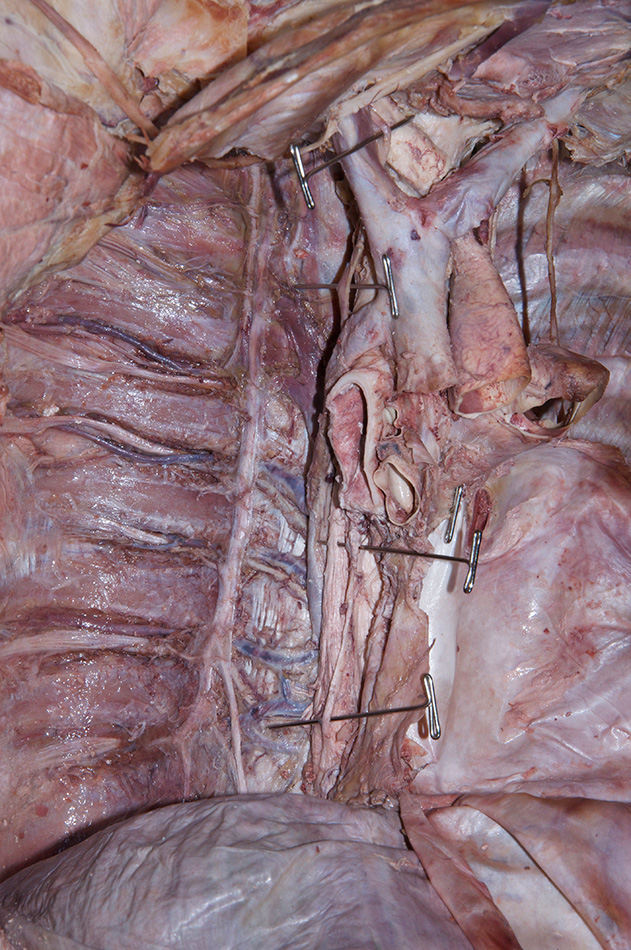
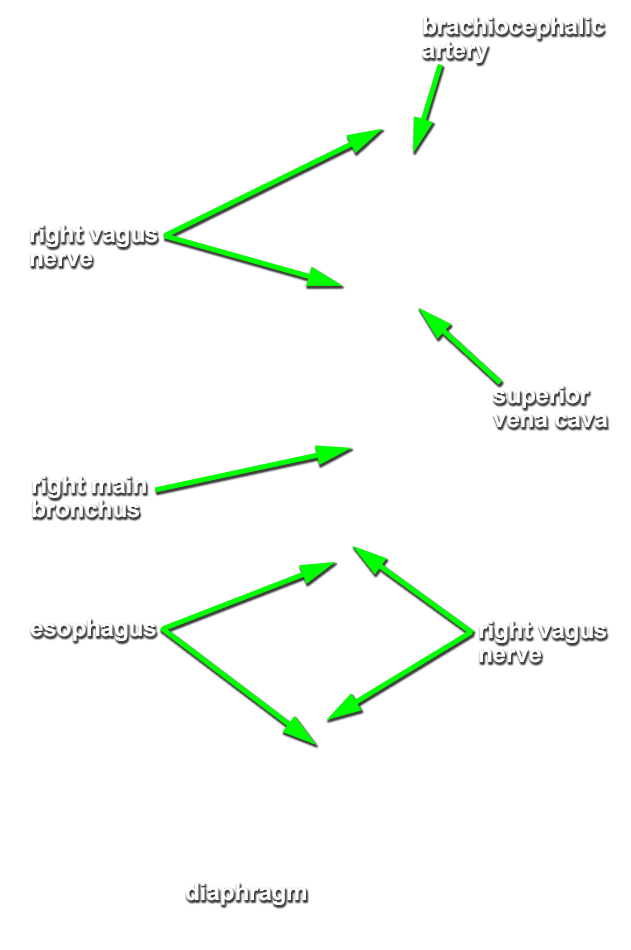
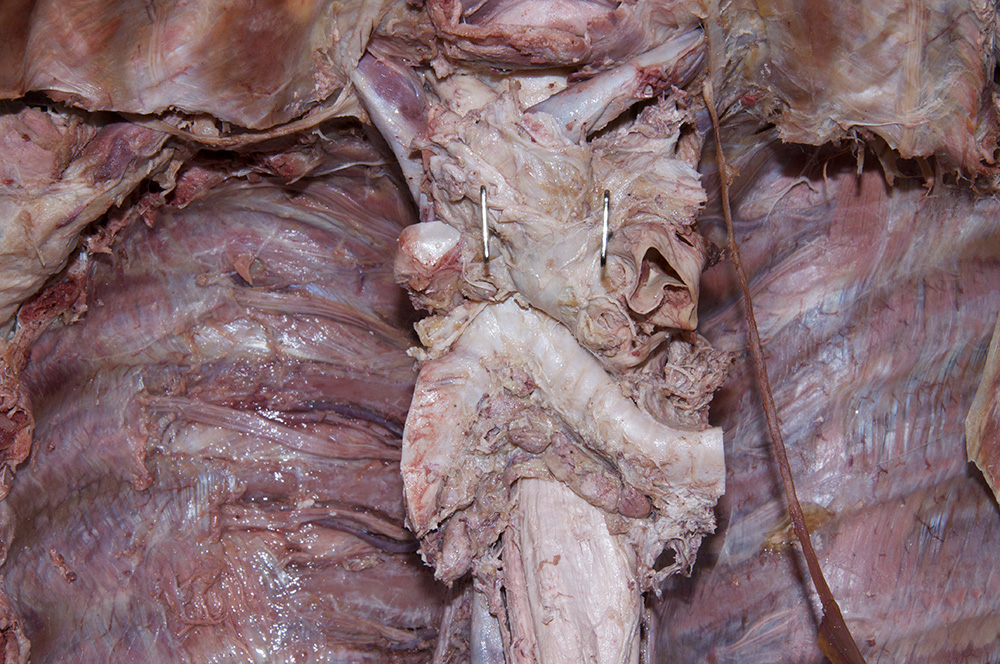
Return to the superior mediastinum. (G 3.60B;N 203;Gl 10.6B)
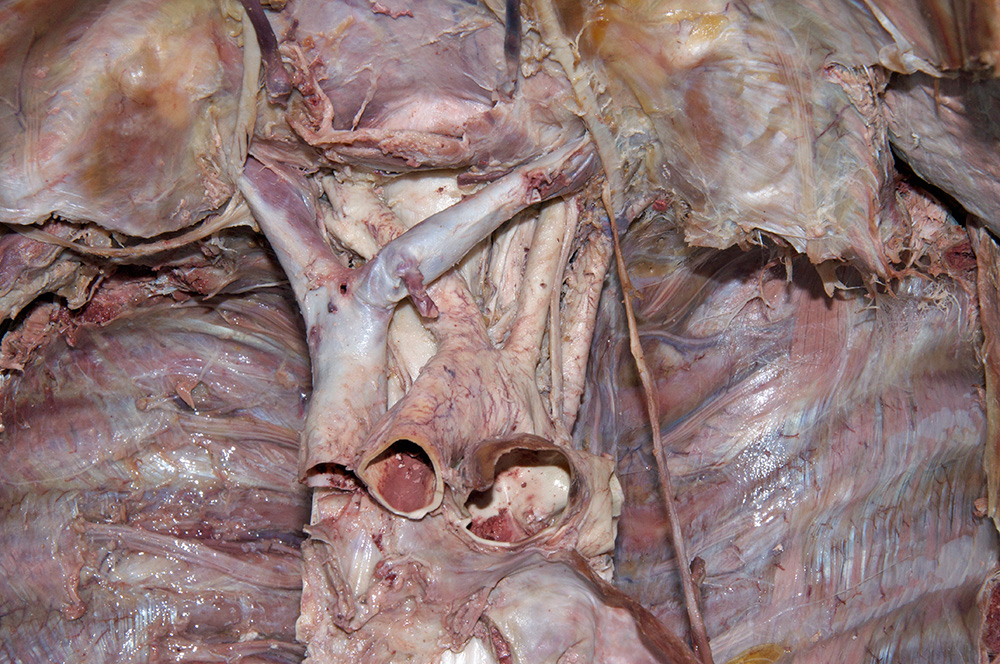
- Look for some fatty tissue immediately posterior to the manubium of the sternum. This is most likely the remnant of the thymus. Identify the
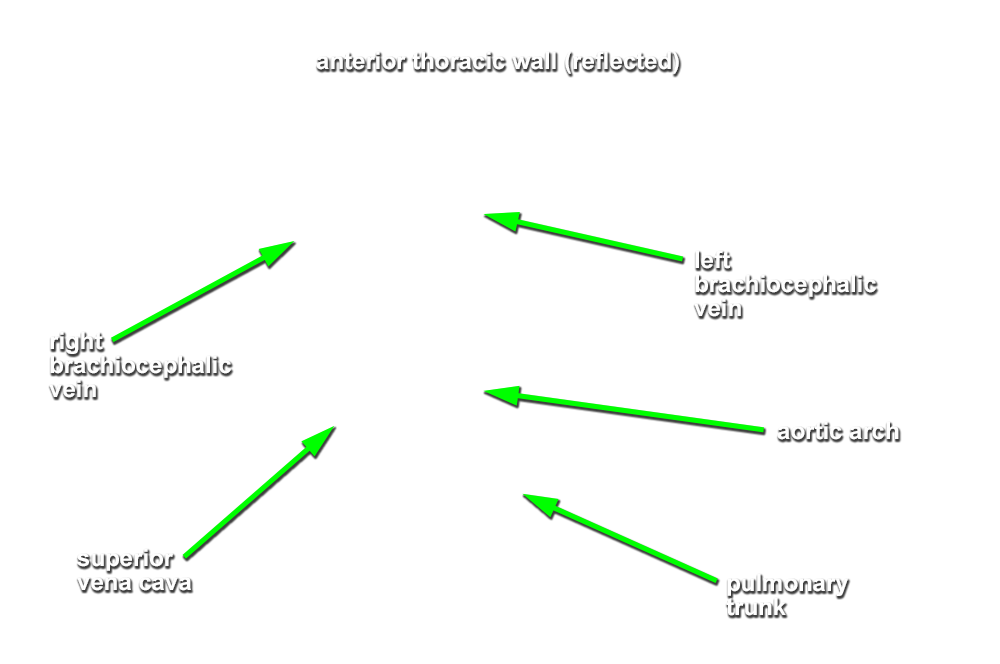
right and
left brachiocephalic veins. Look for the
left superior intercostal vein draining into the left brachiocephalic vein. Identify the origins of the
brachiocephalic,
left common carotid and
left subclavian arteries. Identify the
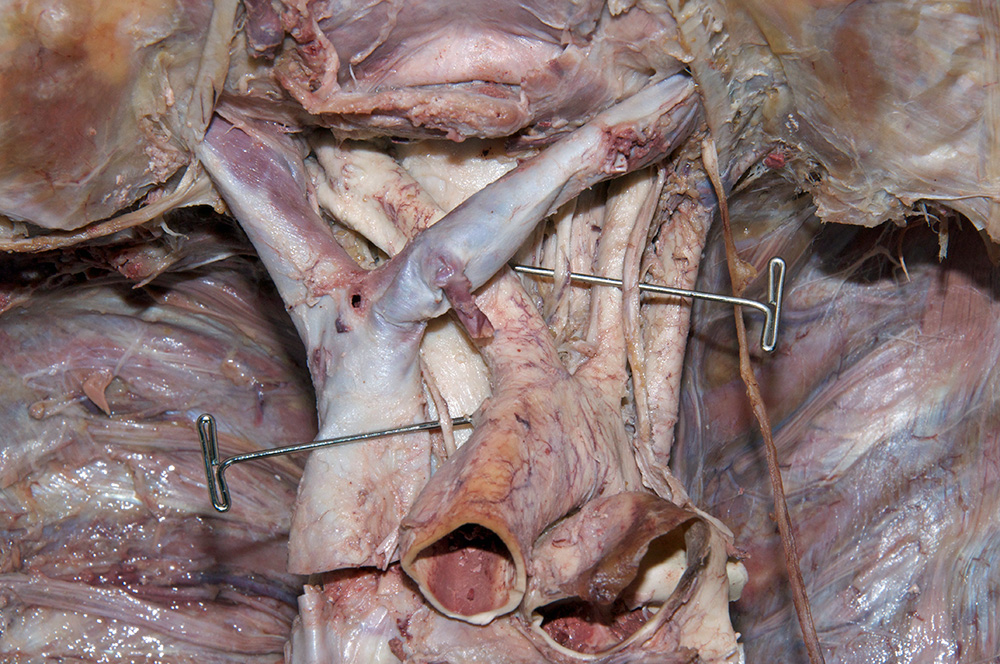
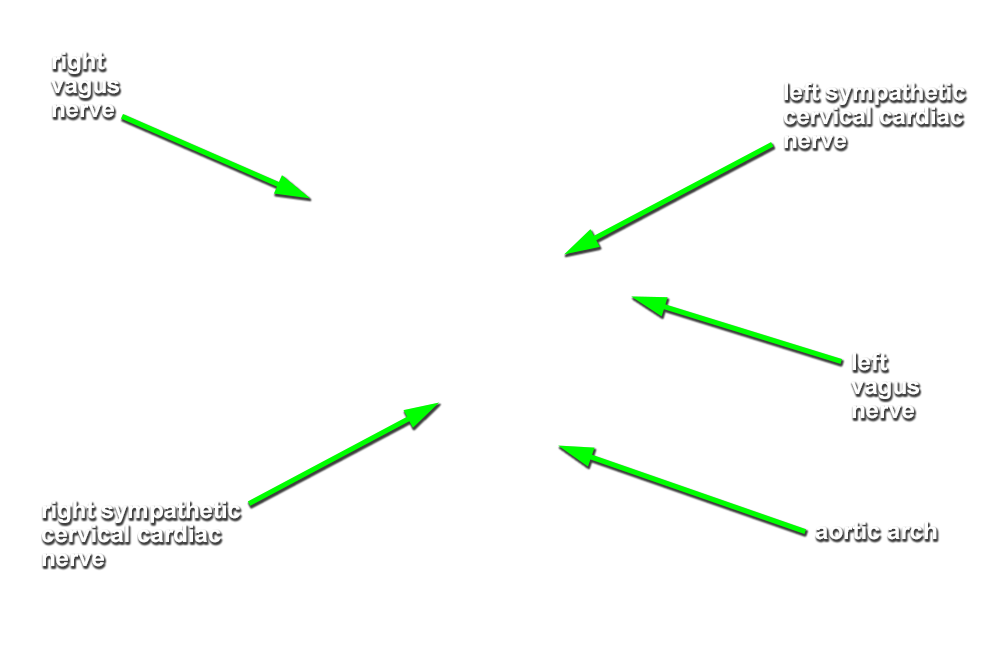
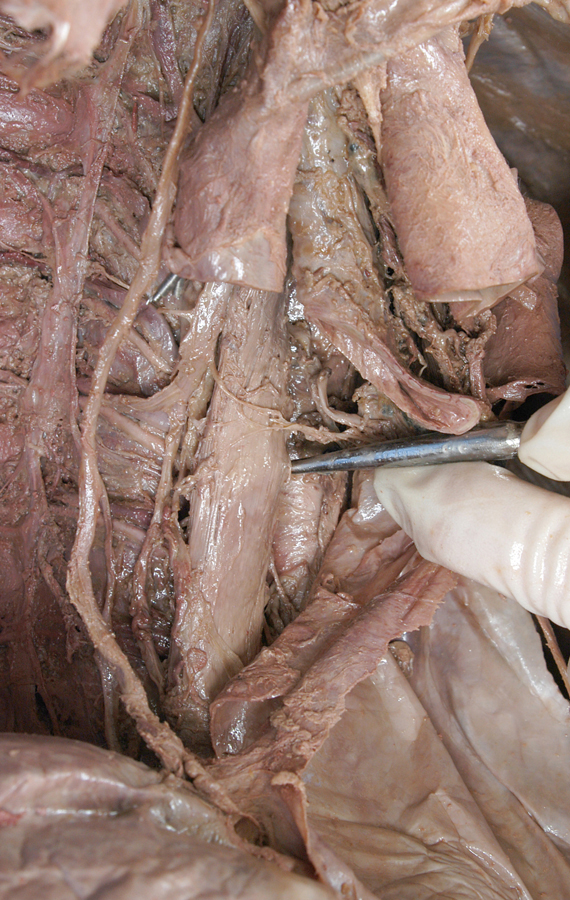
right vagus nerve. (G 3.61;N 227;Gl 9.3A) The right vagus nerve passes anterior to the subclavian artery and then posterior to the right main bronchus. Attempt to identify the sympathetic cervical cardiac nerves contributing to the cardiac and pulmonary plexuses.
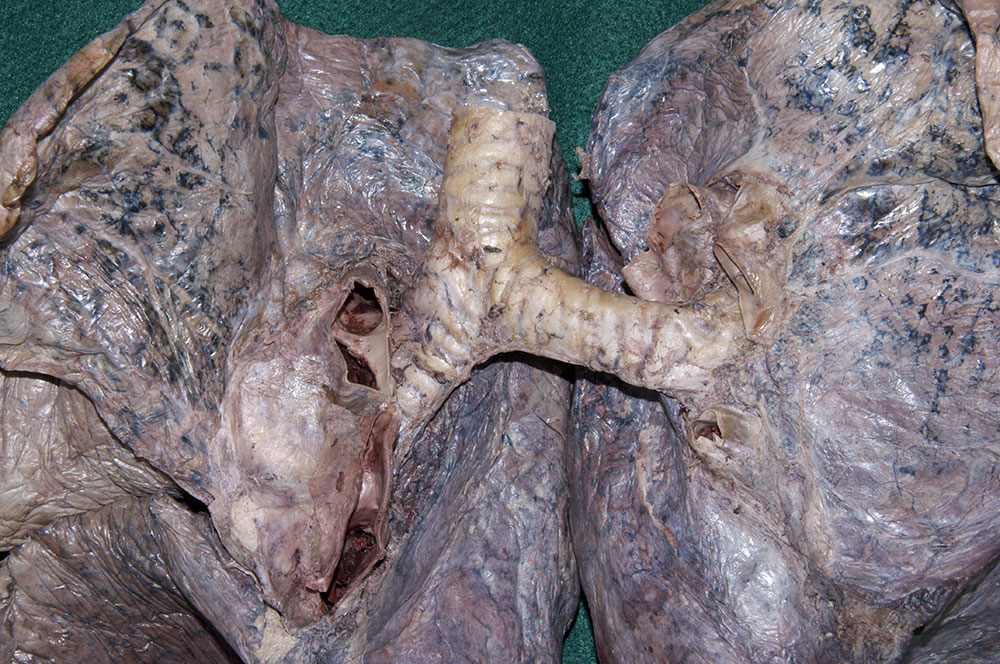
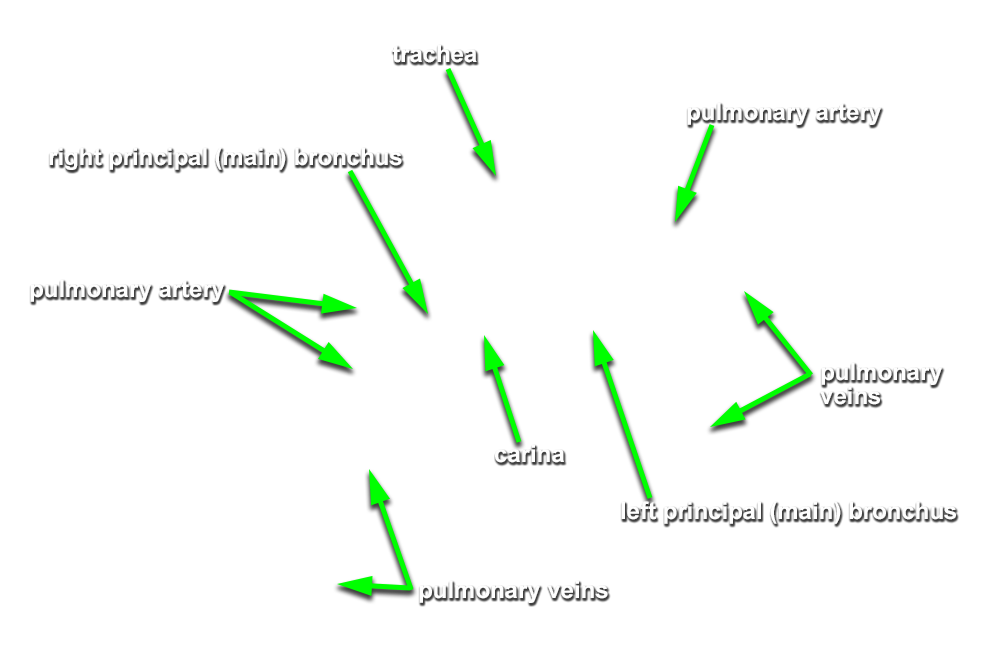
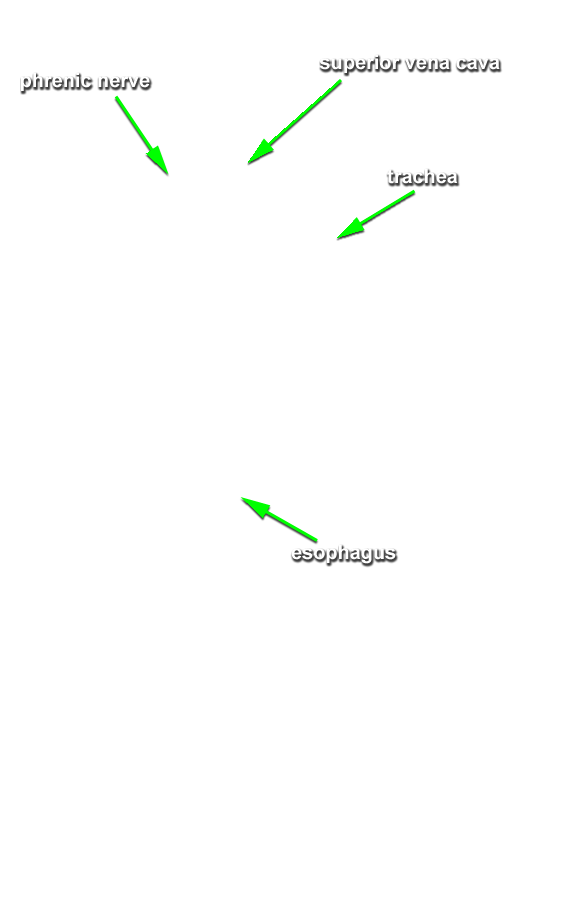
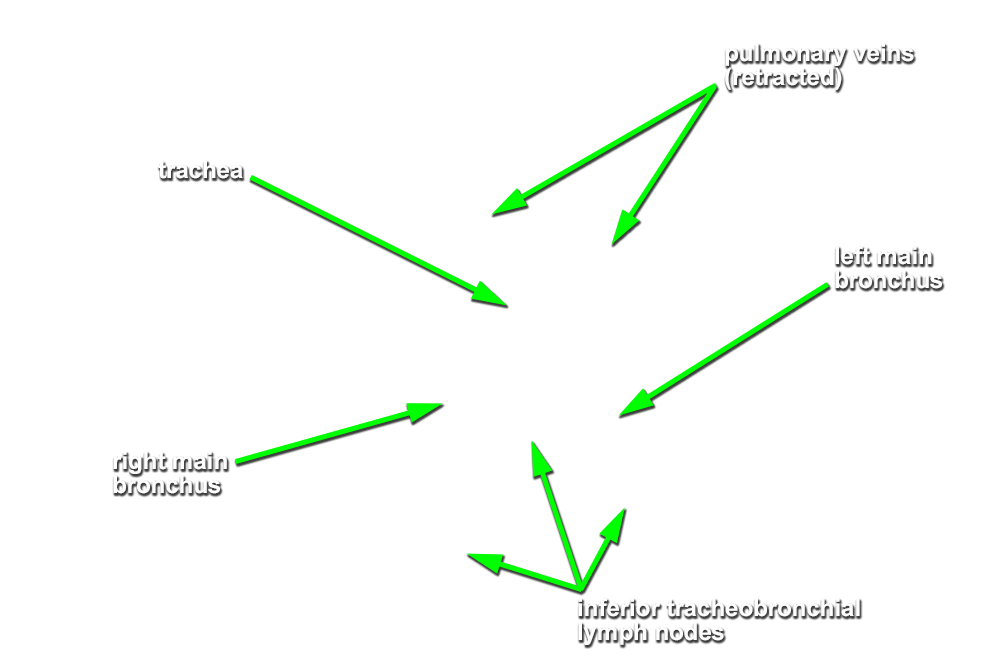
- Identify the
trachea and
esophagus. Trace the trachea to its bifurcation into the
right and
left main bronchi. Identify the
superior and
inferior tracheobronchial lymph nodes at the bifurcation. (G 3.63;N 205;Gl 9.31A) Attempt to identify one or more
bronchial arteries. (G 3.63;N 239;Gl 10.25) Examine the cut (from the removal of the lung) edge of the bronchus. Identify the small lumen of a vessel. This is a bronchial artery. Attempt to trace it back to its origin from the aorta (or posterior intercostal artery).
Important Relationships
- The
esophagus is positioned
posterior to the trachea.
- The
esophagus passes
posterior to the left main bronchus.
- The
descending (thoracic) aorta passes
posterior to the left main bronchus.
- At the hilum of the left lung, the
pulmonary artery is positioned
superior to the main bronchus.
- At the hilum of the left lung, the
pulmonary veins are positioned
anterior and
inferior to the main bronchus.
- At the hilum of the right lung, the
pulmonary artery is positioned
anterior to the main bronchus.
- At the hilum of the right lung, the
pulmonary veins are positioned
anterior and
inferior to the main bronchus.
- At the hilum of the right lung, the
pulmonary veins are positioned
anterior and
inferior to the pulmonary arteries.