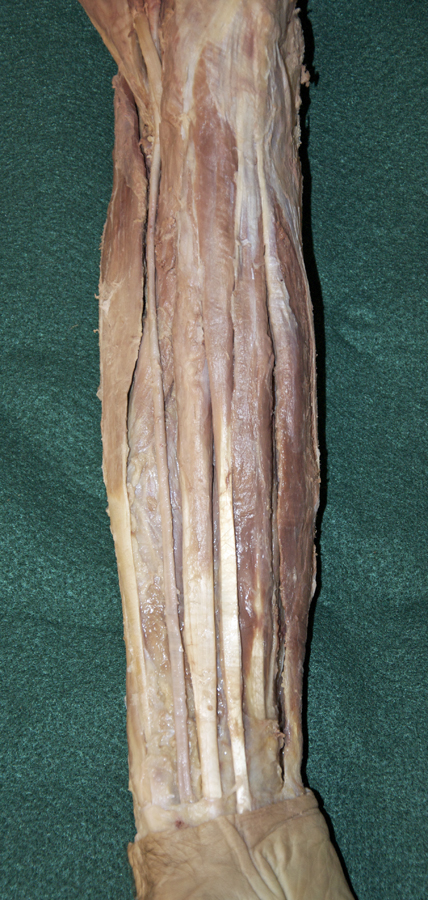
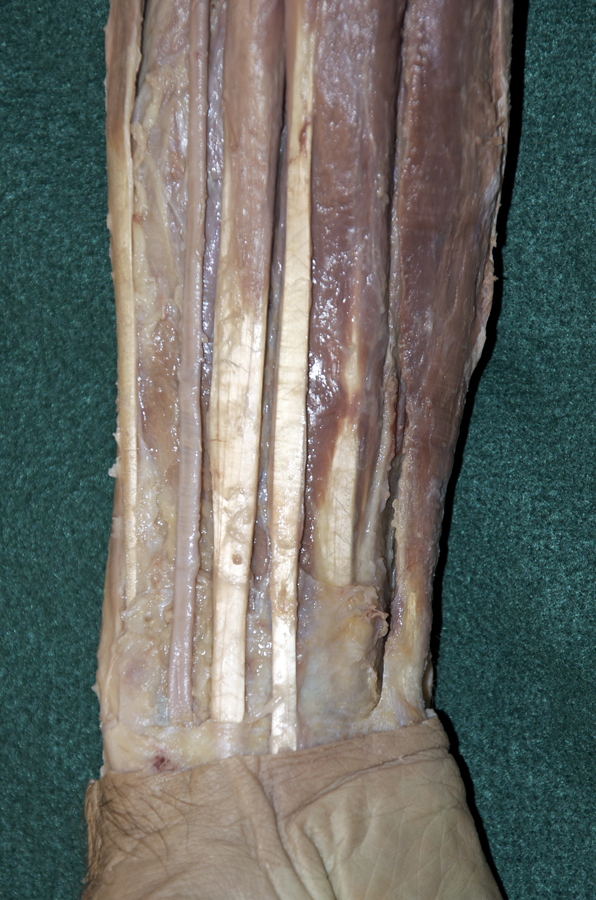
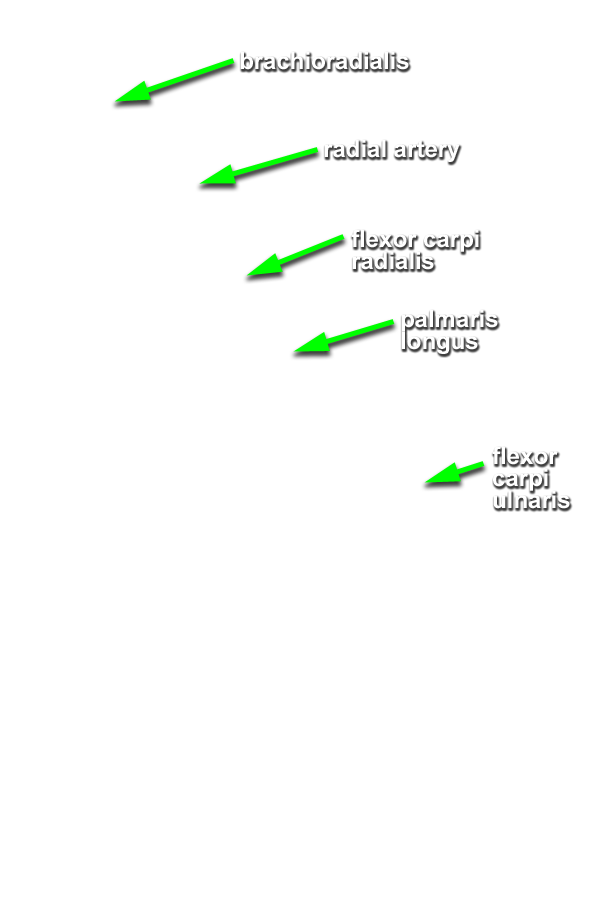
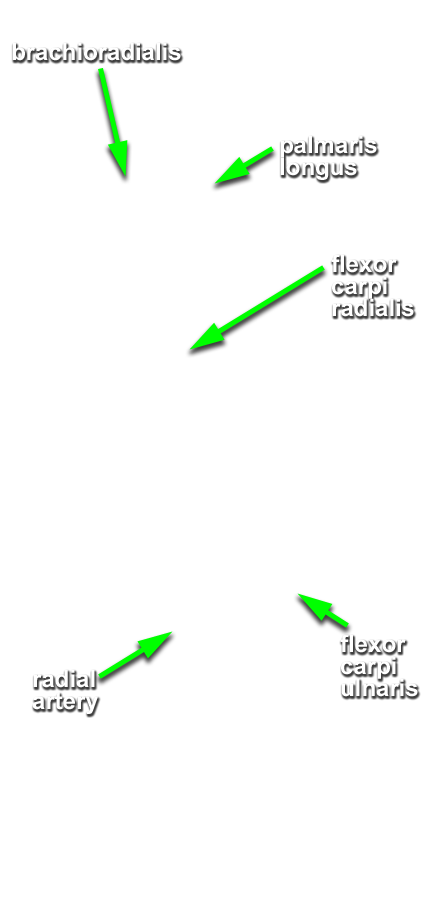
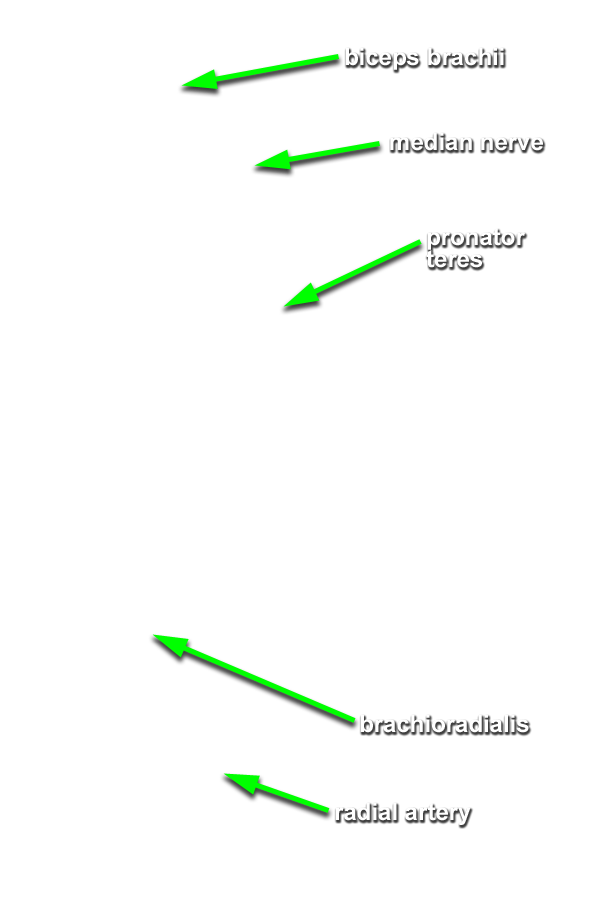
(ON BOTH SIDES) Expose and identify the superficial muscles of the anterior compartment of the forearm. (G 2.63B;N 432;Gl 26.10A)
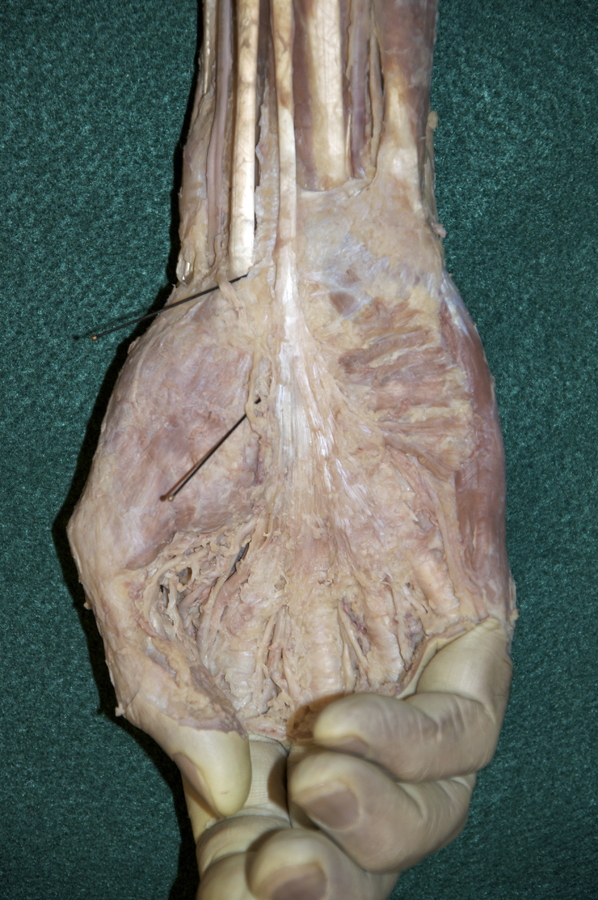
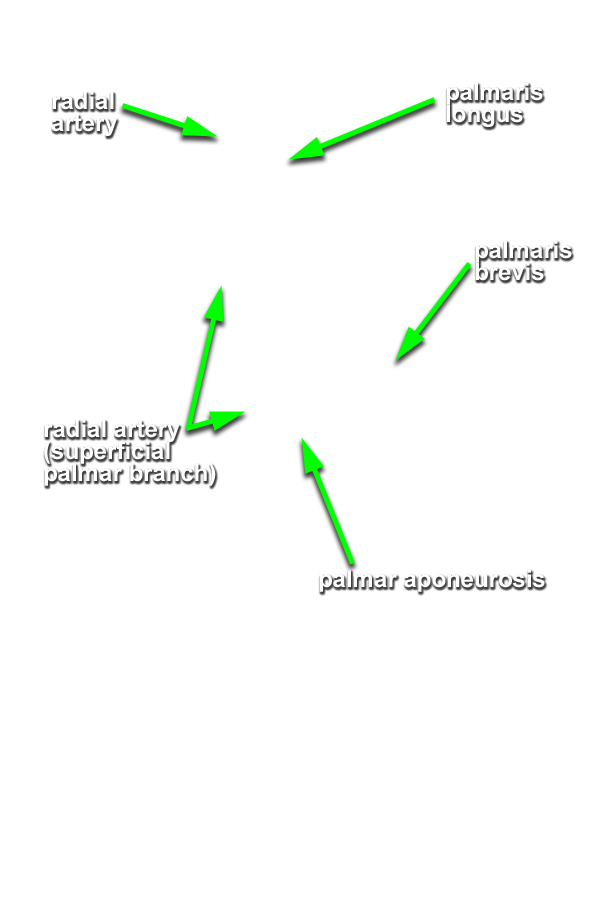
- Start at the reflected bicipital aponeurosis and blunt dissect under the deep fascia of the anterior compartment of the forearm. Remove the deep fascia to the level of the flexor retinaculum (pisiform bone). The flexor retinaculum has a superficial component that is continuous with the palmar aponeurosis and a deep component, the transverse carpal ligament.
- Identify and clean the tendon and belly of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle (attaches to the pisiform bone).
- Identify and clean the tendon and belly of the palmaris longus muscle. Your cadaver may not have a palmaris longus muscle (the Visible Human Male does not).
- Identify and clean the tendon and belly of flexor carpi radialis muscle.
- Identify and clean the radial artery between the brachioradialis and flexor carpi radialis muscles. Attempt to identify the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery. This branch arises near the flexor retinaculum and disappears into the palmar aponeurosis. Attempt to preserve this branch as you continue the dissection.
- Identify and clean the pronator teres muscle.
Important Relationship
- Near the wrist, the radial artery is positioned lateral to the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle.