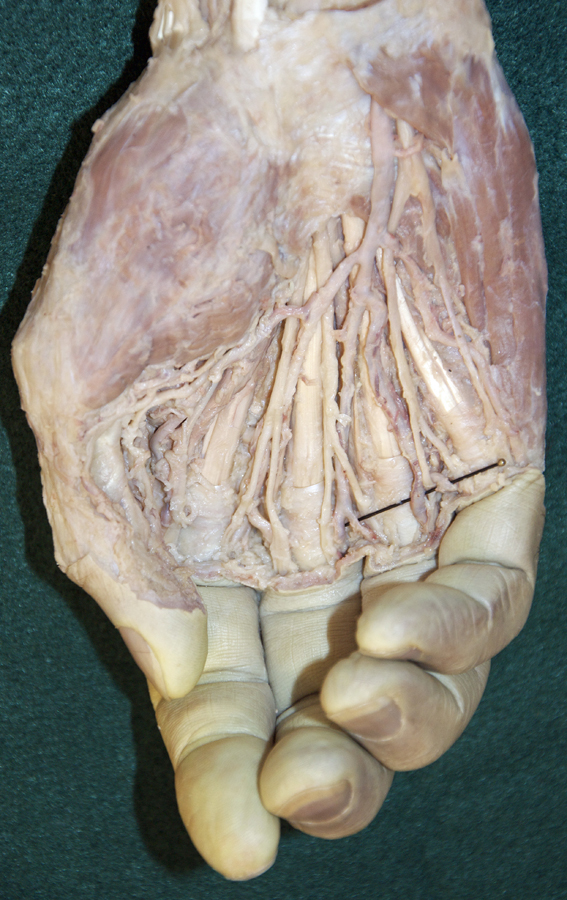
(ON THE RIGHT SIDE ONLY) Clean and identify the superficial nerves, arteries and muscles of the hand. (G 2.74A;N 447;Gl 28.44A) THE DEEP PALMAR DISSECTION (STEP 8) WILL BE DONE ON THE LEFT SIDE ONLY
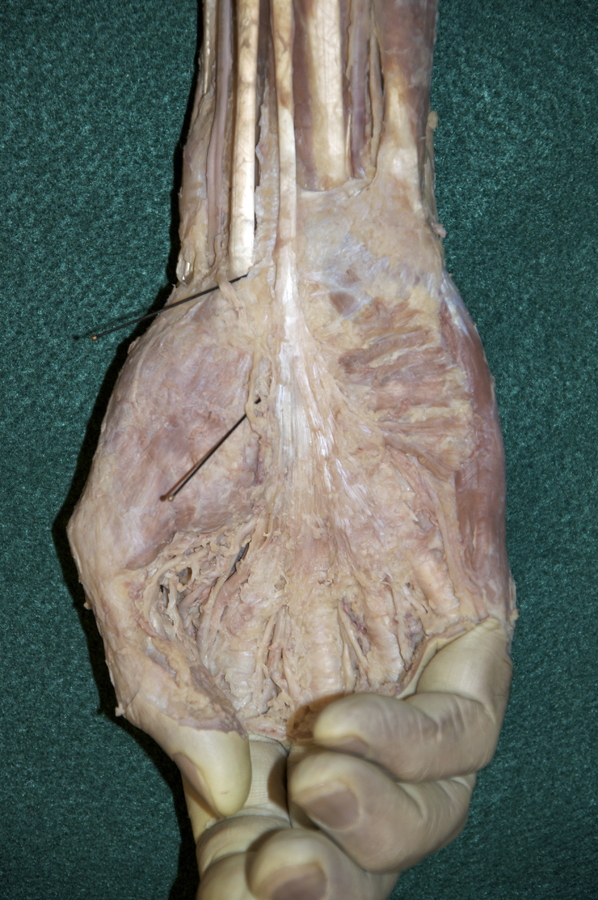
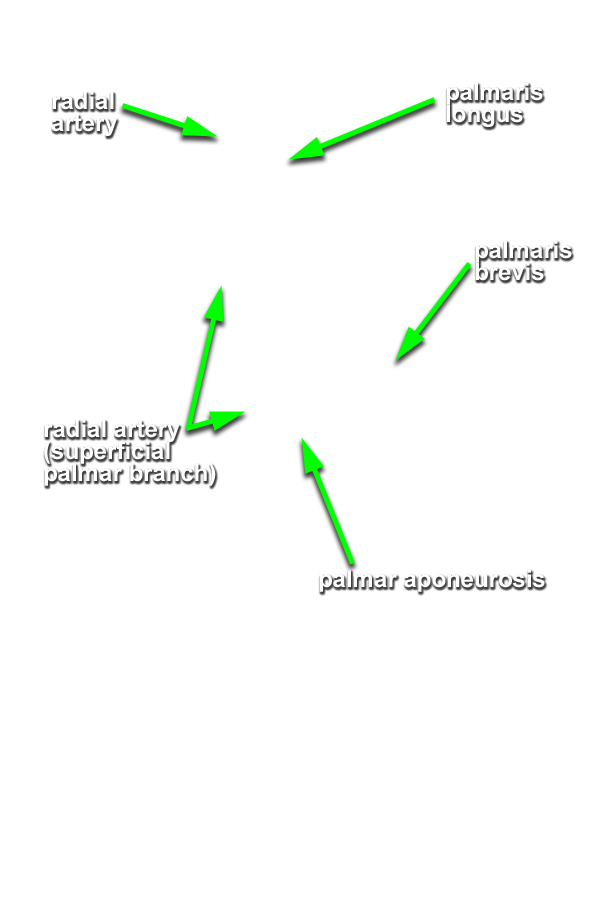
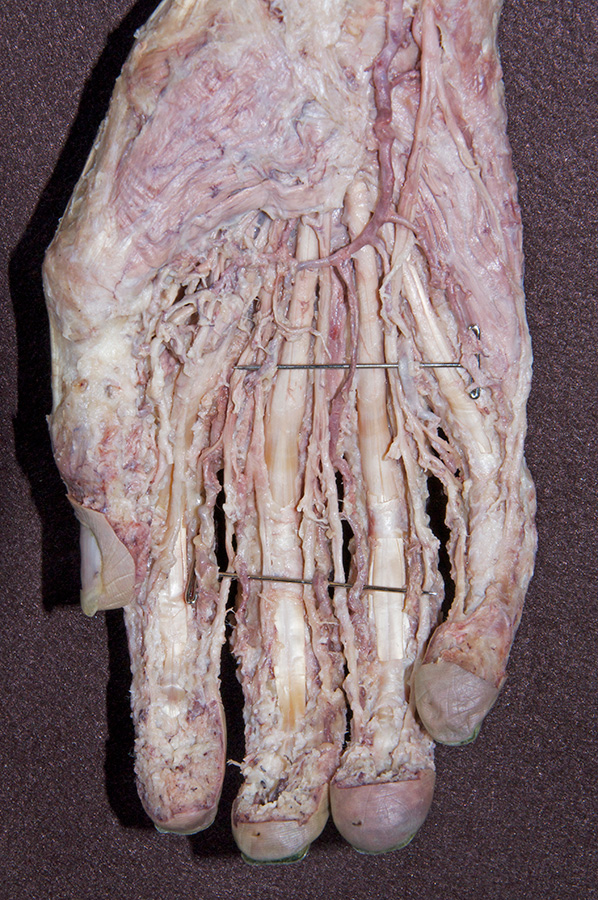
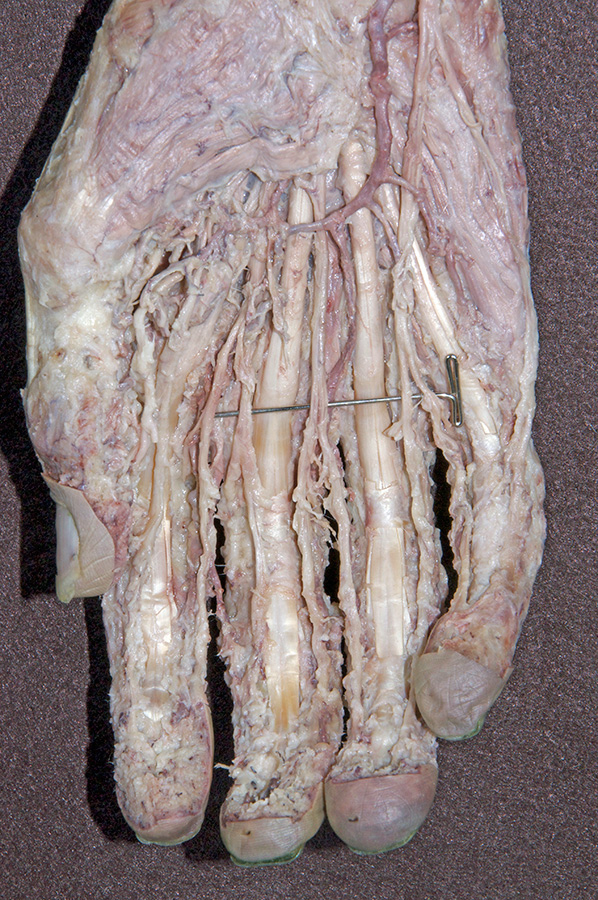
- Use the scissor technique to locate the palmar digital arteries and nerves near the web spaces between the digits. Be sure to blunt dissect parallel to the course of the arteries and nerves. (G 2.74A;N 453;Gl 28.42B) Once you locate a nerve or artery, then start tracing (cleaning) the nerve (and/or artery) in the proximal direction. Use your scissors to remove the palmar aponeurosis as you clean the nerves and vessels. Be patient! This will be one of the more challenging dissections you will complete. Trace and completely clean the superficial arteries and nerves. You may completely remove the palmar aponeurosis and the palmaris brevis muscle.
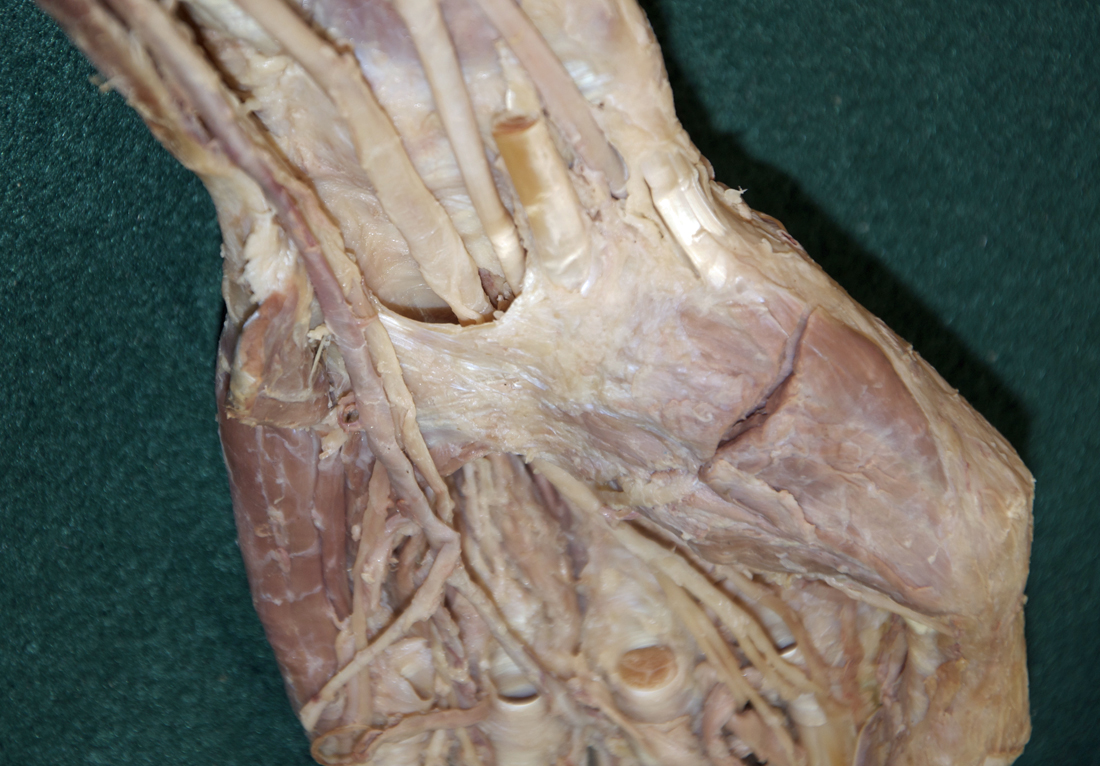
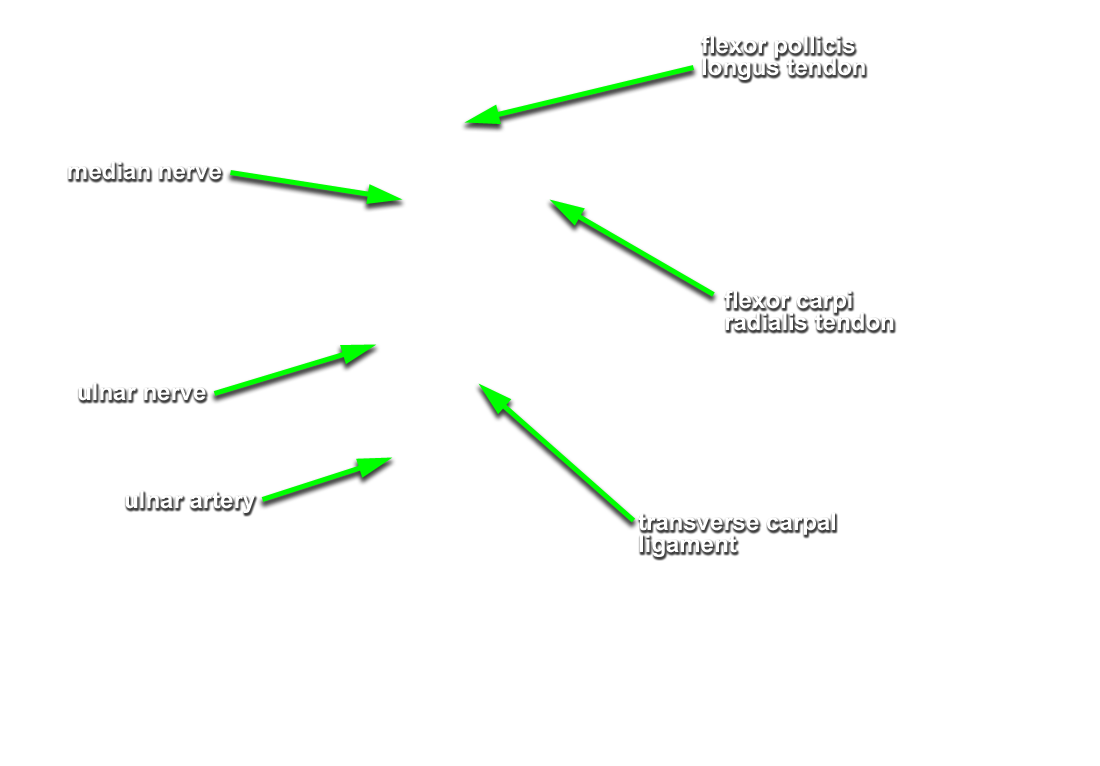
- Identify the transverse carpal ligament (G 2.74B;N 453;Gl 28.42B) This is the deep portion of the flexor retinaculum. It is immediately anterior to the carpal tunnel.
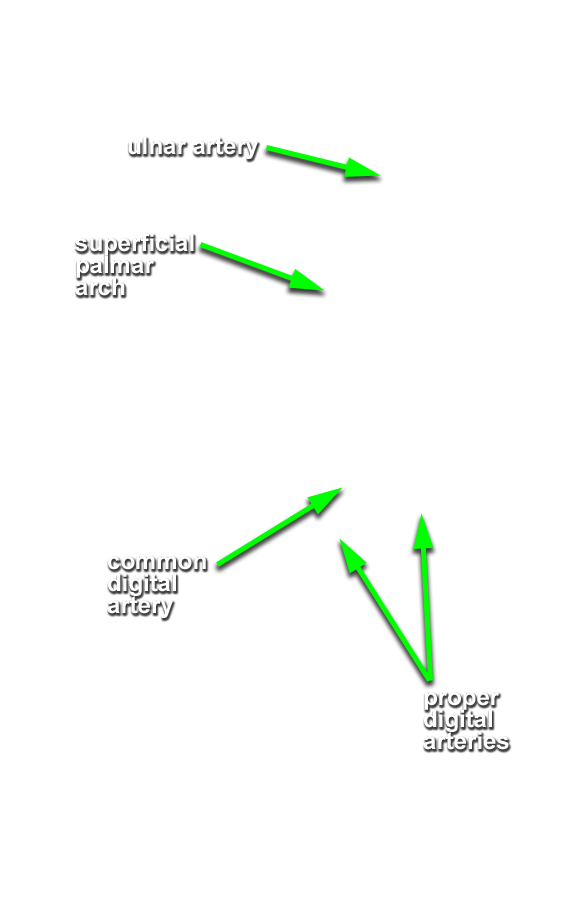
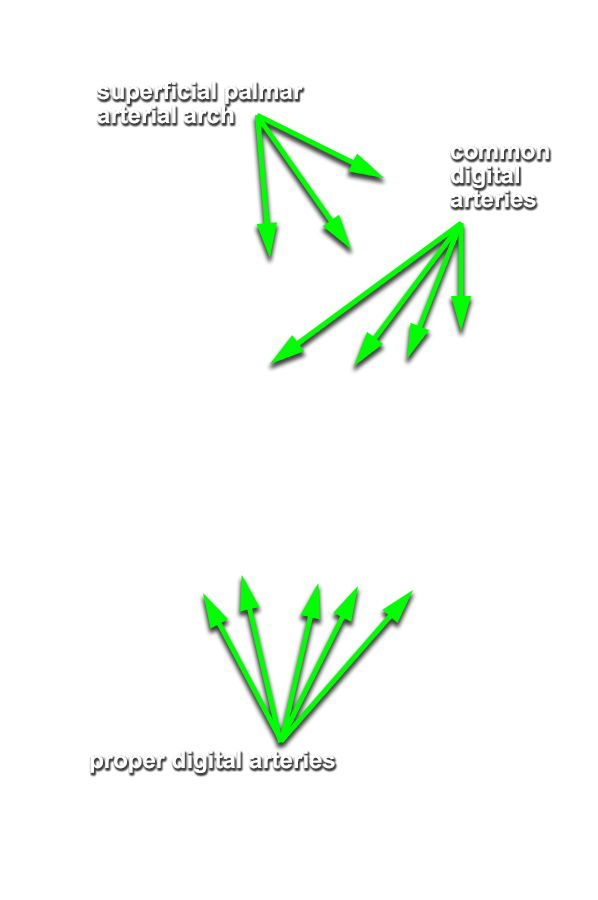
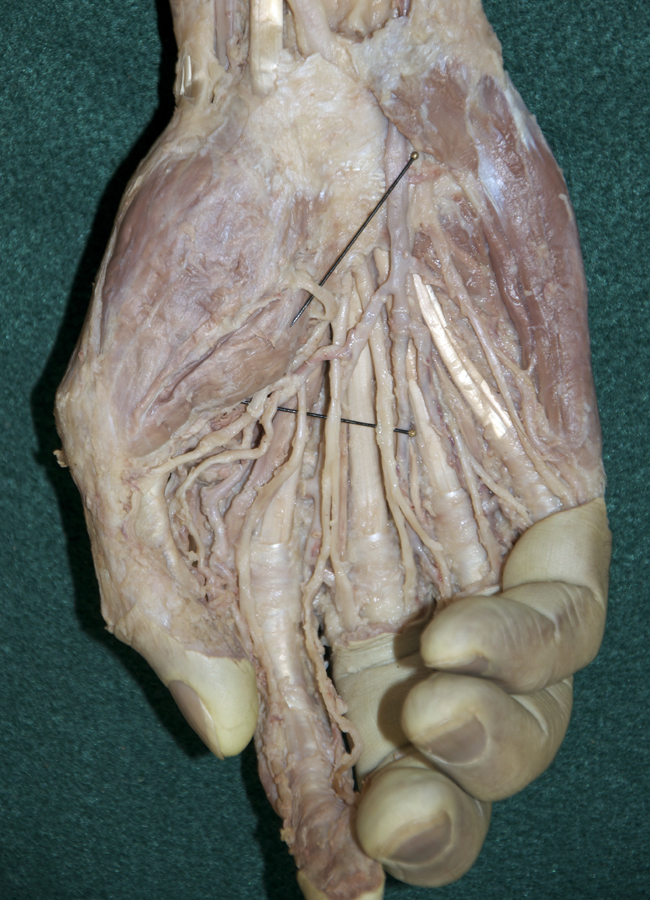
- Identify the superficial palmar arterial arch and the common and proper digital arteries. Attempt to identify the anastomosis between the superficial palmar arterial arch and the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery.
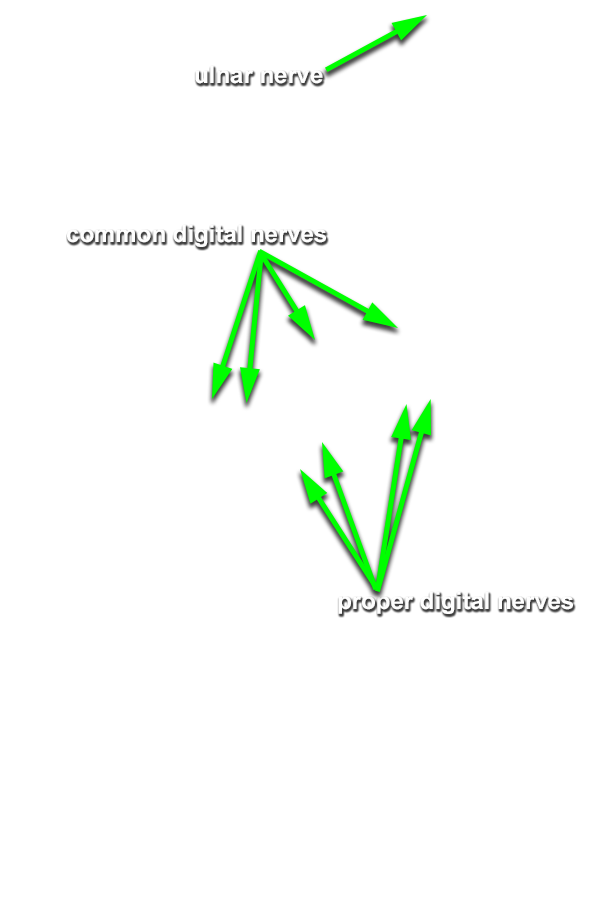
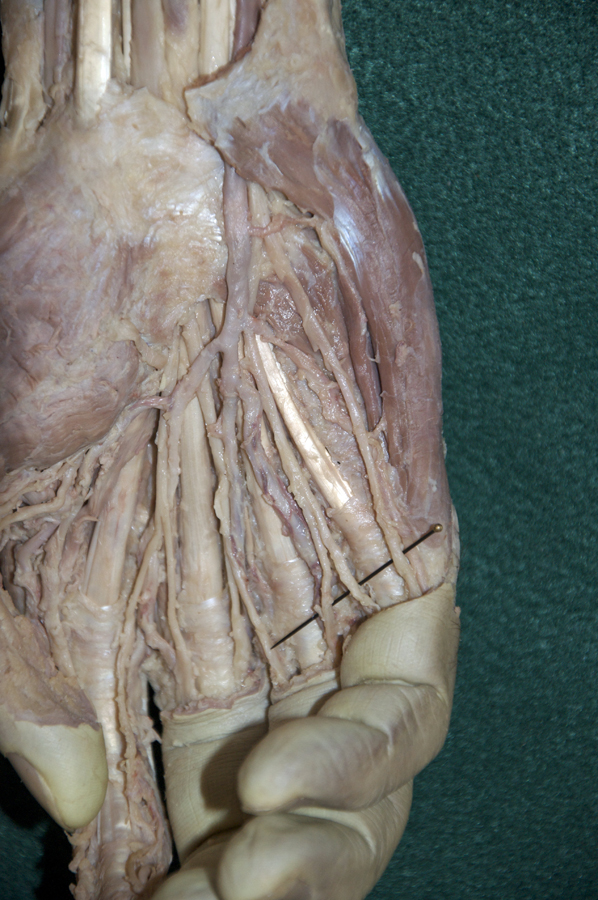
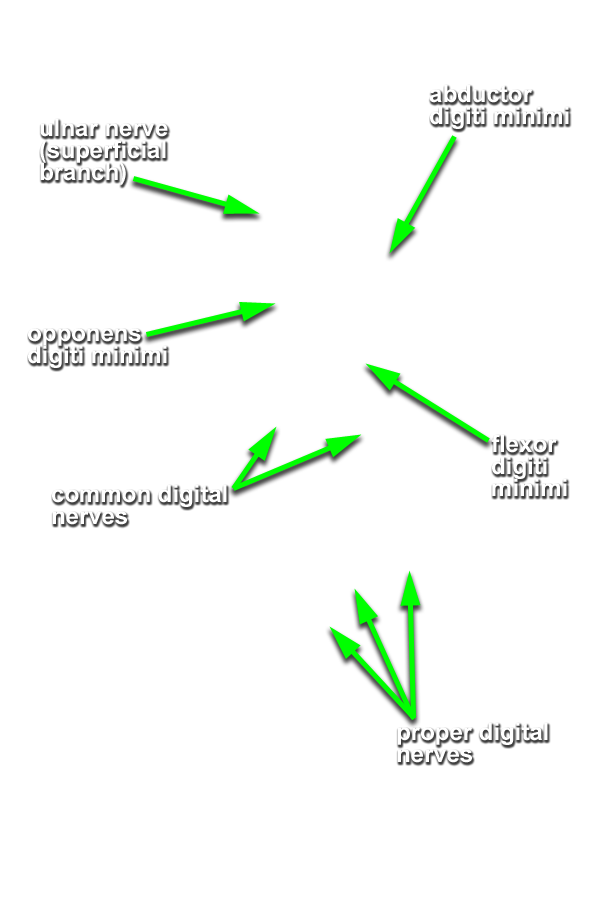
- Identify the ulnar nerve adjacent to the pisiform bone. (G 2.74A;N 453;Gl 28.44A) Identify the common and proper digital nerves (branches of the ulnar nerve).
- Identify and clean the three hypothenar ( abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis and opponens digiti minimi) muscles. (G 2.74B;N 449;Gl 27.25) It may be impossible to separate the flexor digiti minimi brevis and opponens digiti minimi muscles.
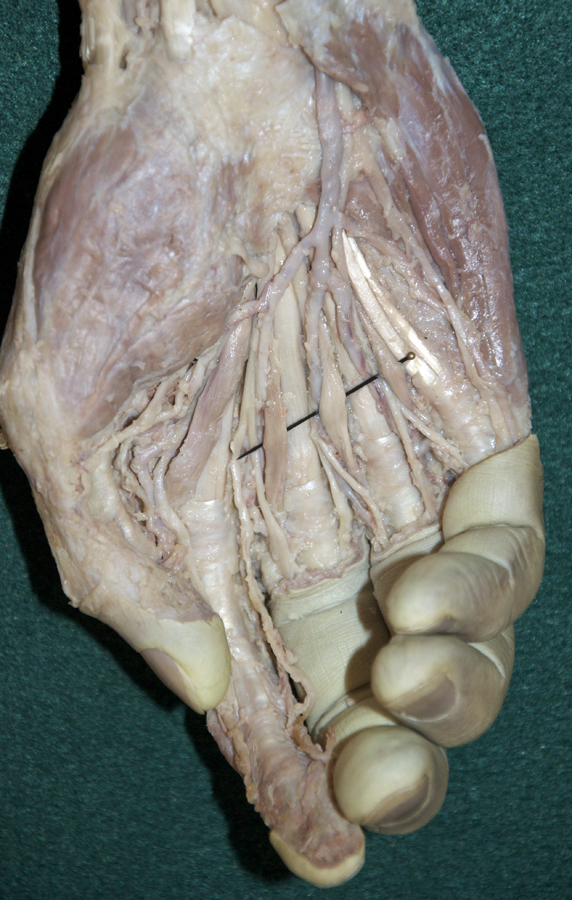
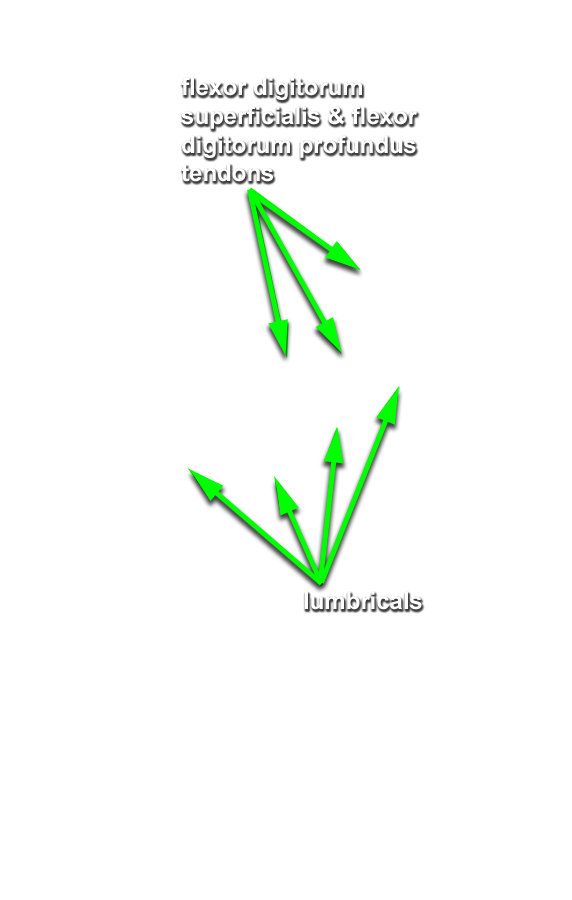
- Identify and clean the four lumbrical muscles. (G 2.74B;N 449;Gl 27.27A) Trace the 1st lumbrical to its distal attachment to the extensor expansion. (G 2.87B;N 451;Gl 27.23)
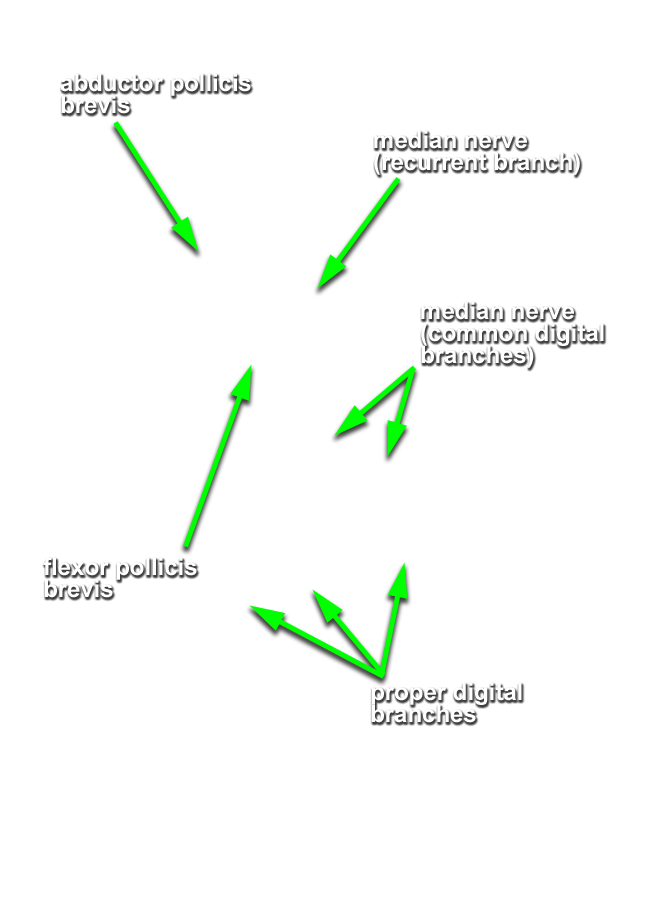
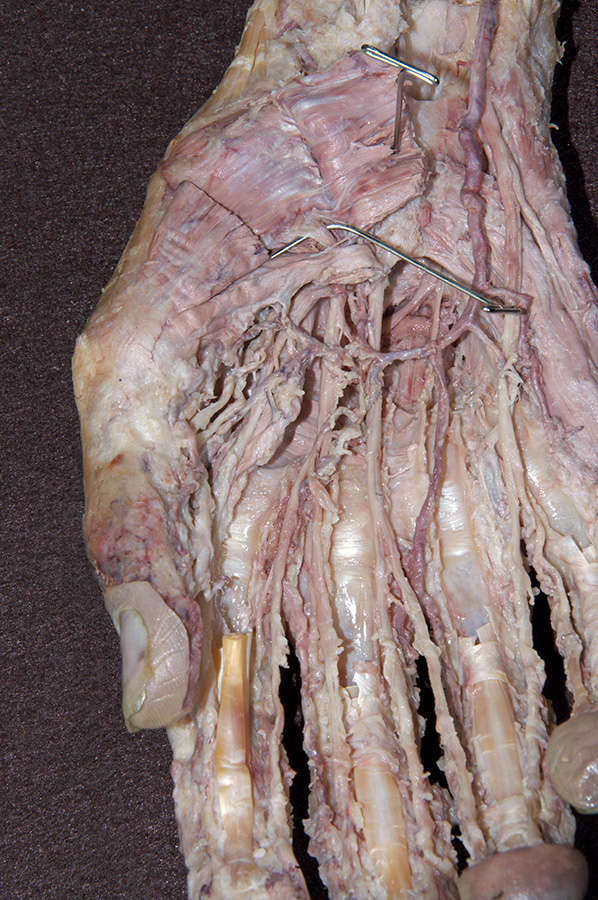
- Identify the branches of the median nerve ( common and proper digital, and recurrent) immediately distal to the transverse carpal ligament. (G 2.74B;N 453;Gl 28.44A)
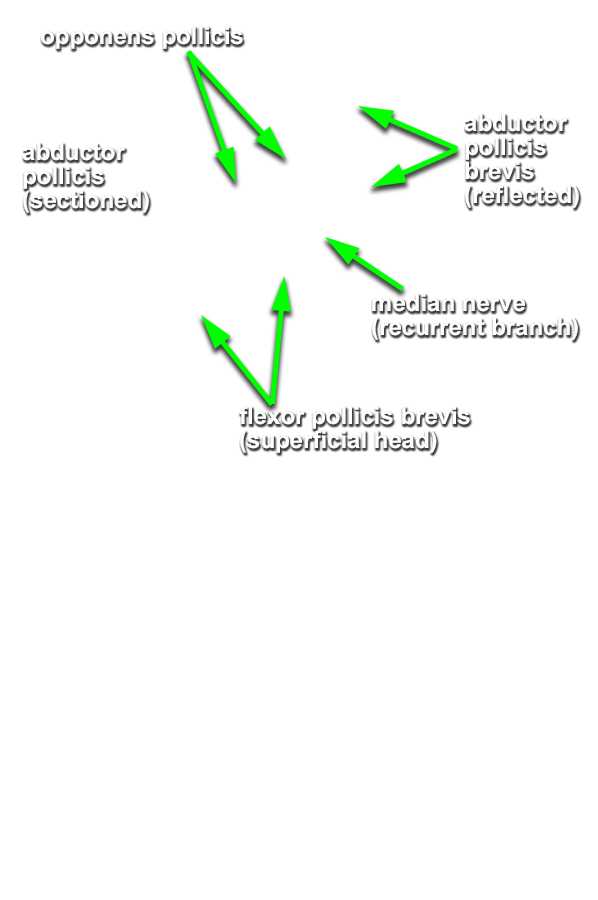
- Identify and clean the three thenar muscles ( flexor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis (this muscle group is identified incorrectly in the VH Dissector)). (G 2.74A;N 452;Gl 27.18) Blunt dissect the abductor pollicis brevis muscle from the opponens pollicis muscle. Expose the opponens pollicis muscle by transecting the abductor pollicis brevis muscle approximately 1 cm distal to where the recurrent branch of the median nerve enters this muscle .
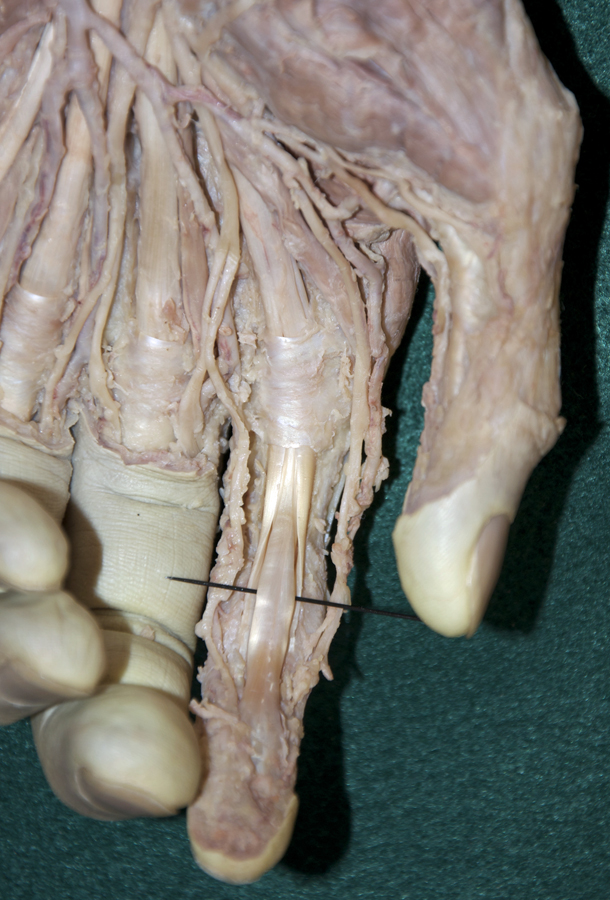
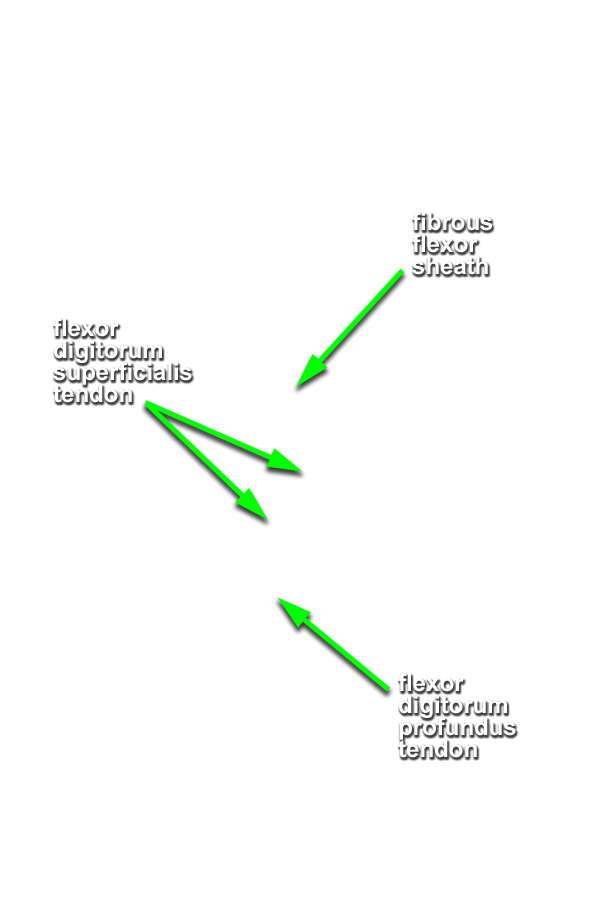
- Trace the tendon of the flexor pollicis longus muscle to its attachment to the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb. (G 2.77;N 452;Gl 27.18D) Identify its fibrous digital sheath. Leave the sheath intact.
- On the second digit, trace the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus to their distal attachments (middle phalanges and bases of distal phalanges). Open the digital synovial sheath. (G 2.78;N 451;Gl 27.18D)
Important Relationships
- The ulnar nerve and artery pass directly lateral to the pisiform bone.
- The ulnar nerve and artery pass superficial (anterior) the flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament).
- Near their distal sites of attachment, the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle are positioned directly anterior (superficial) to the tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus.