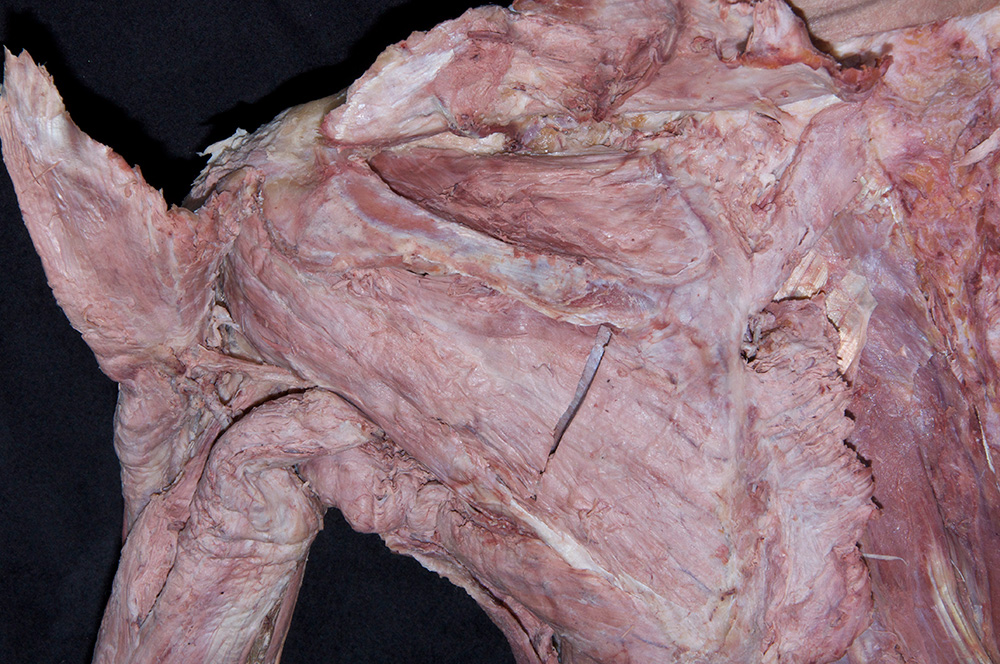
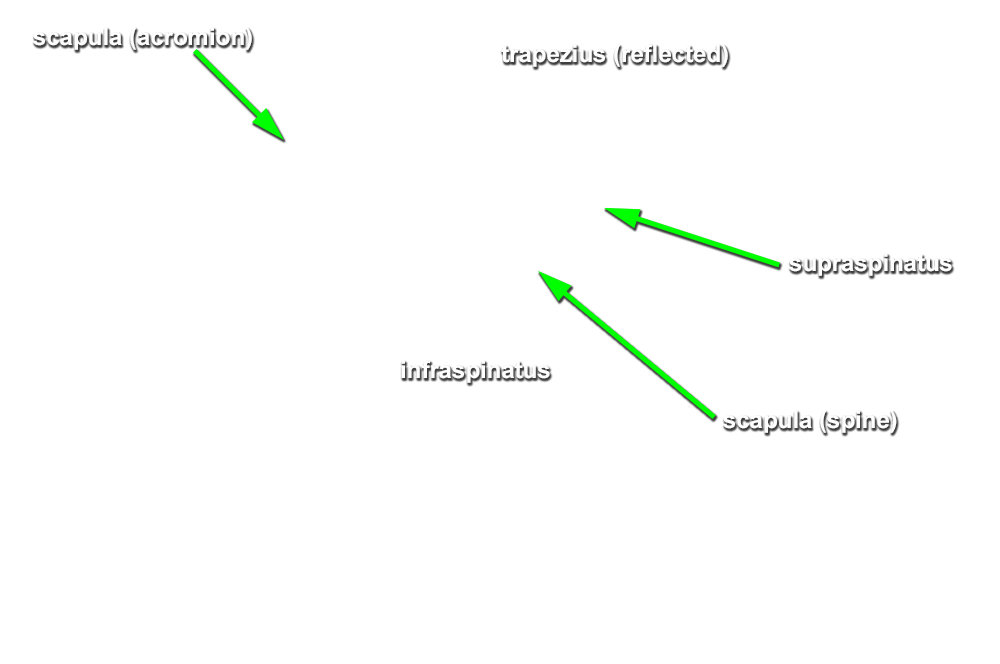
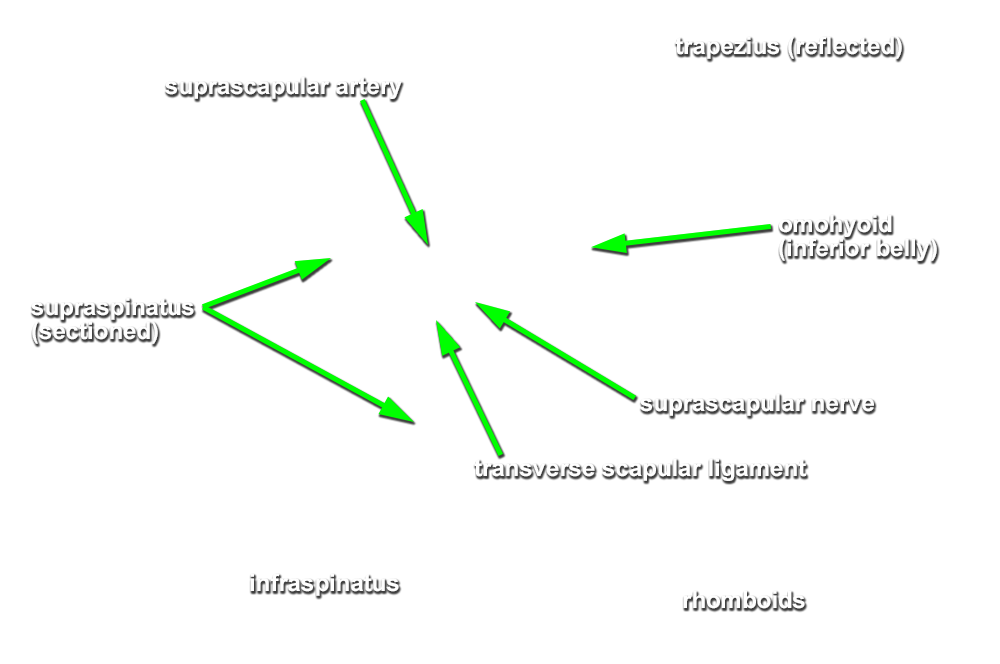
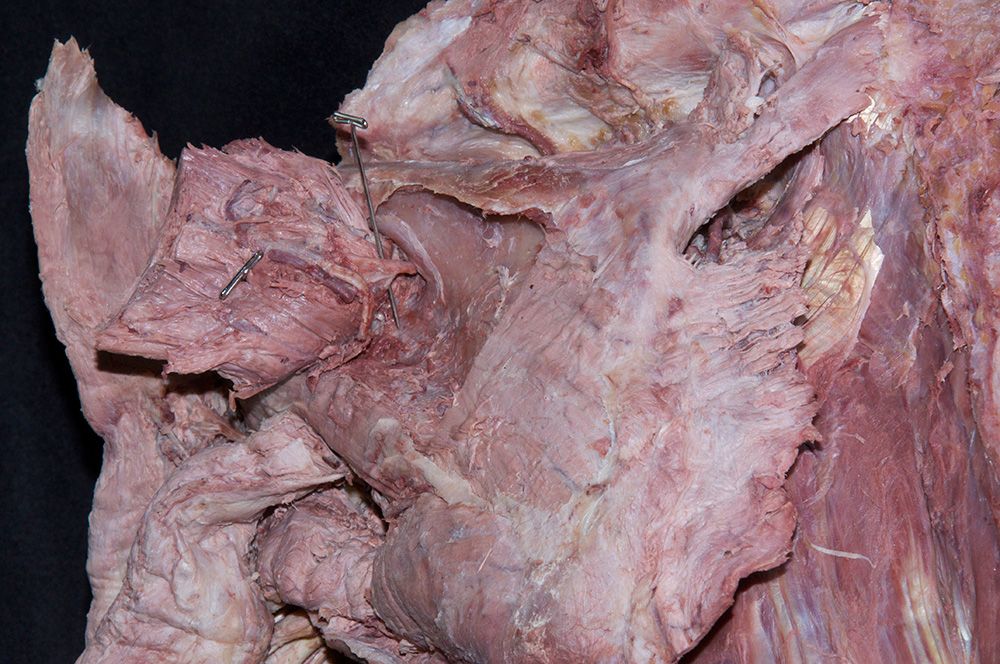
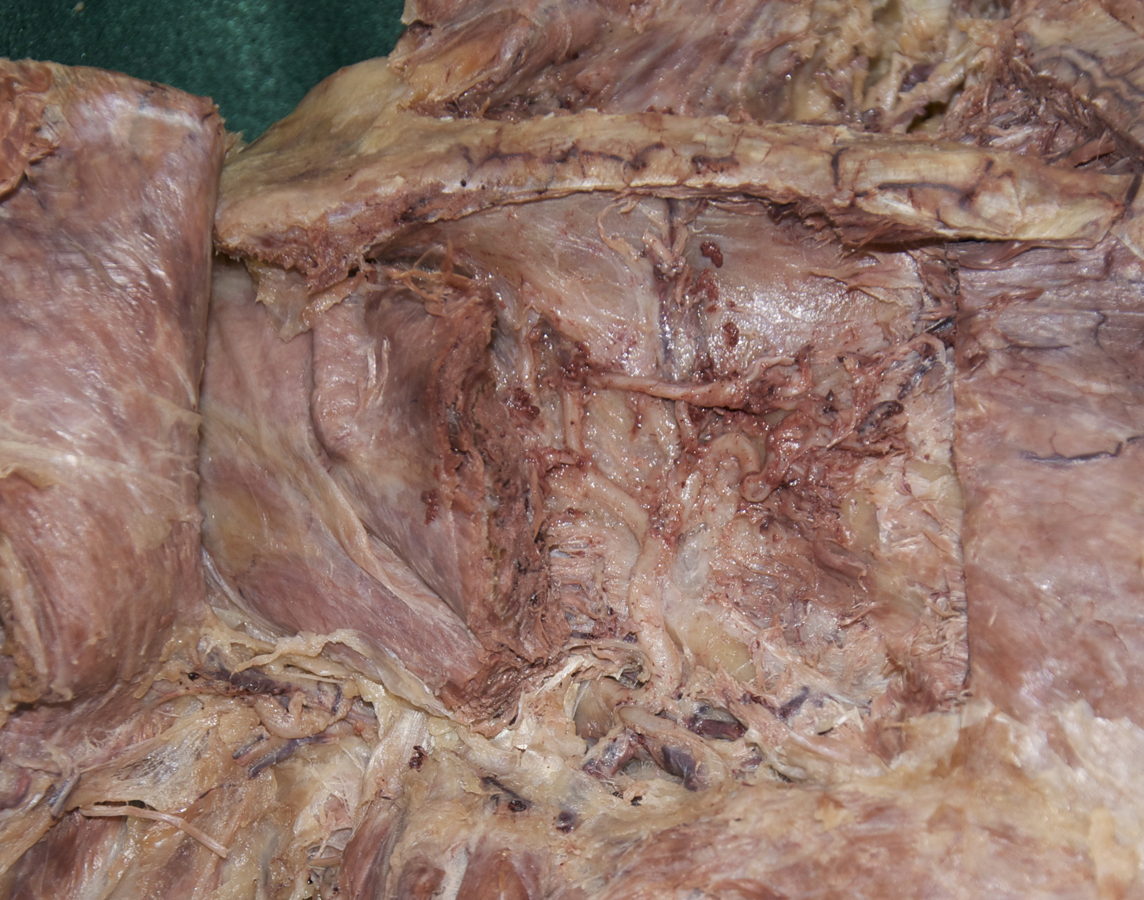
- Reflect the trapezius muscle in the superior direction and identify the supraspinatus muscle. (G 2.43A;N 409;Gl 25.21B)
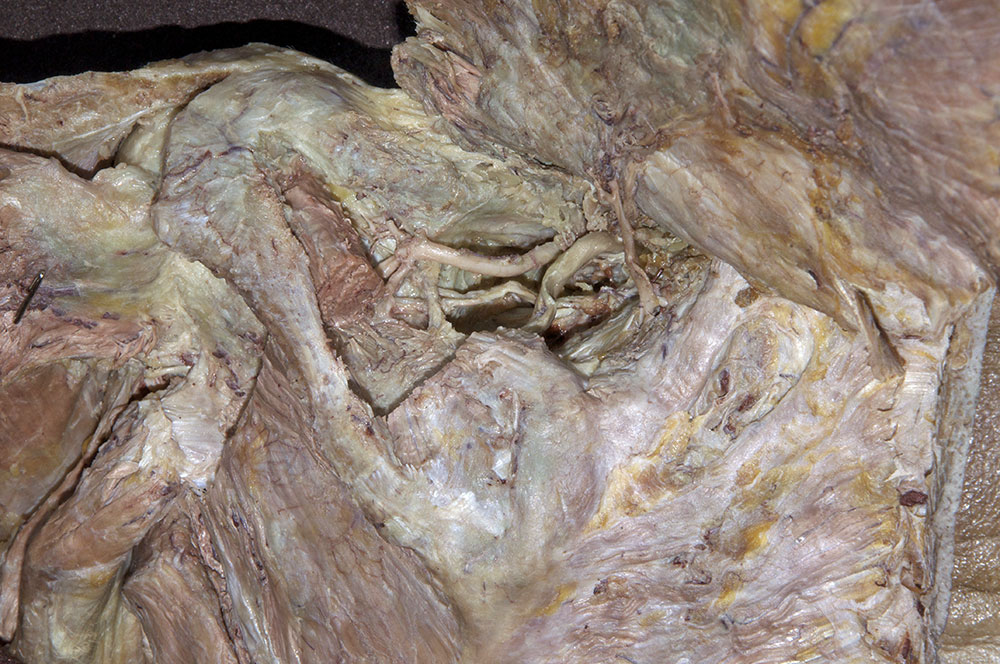
- Reflect the supraspinatus muscle and identify the superior transverse scapular ligament. (G 2.43A;N 413;Gl 28.29) The ligament is always ossified and will feel like a sharp ridge of bone.
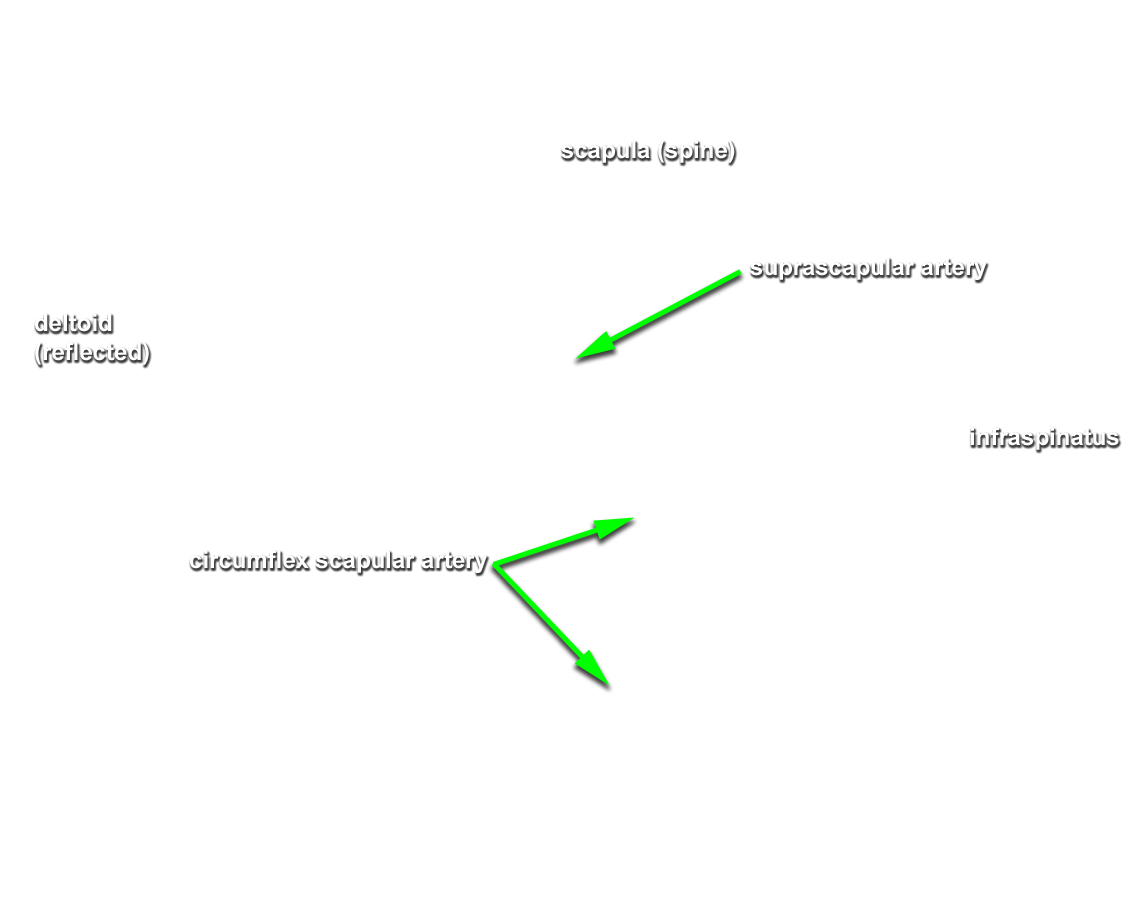
- Identify the suprascapular artery passing superior to the superior transverse scapular ligament.
- Identify the suprascapular nerve passing inferior to the ligament. Trace the suprascapular nerve and artery to where they enter the supraspinatus muscle.
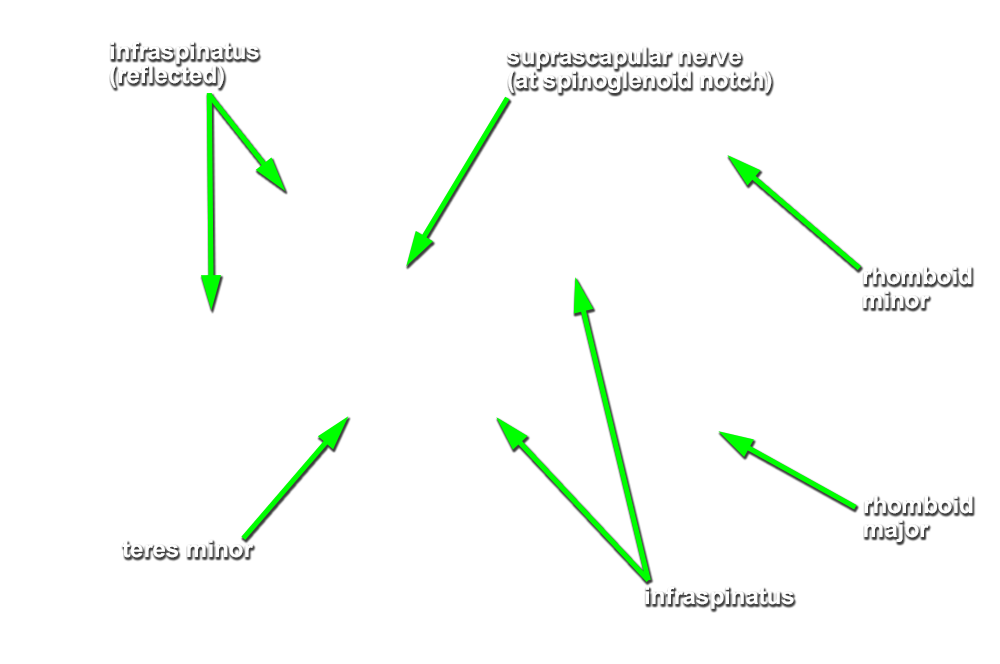
- Identify the infraspinatus muscle. Reflect the muscle laterally to expose the suprascapular nerve and artery where they pass lateral to the spinoglenoid notch. Attempt to identify the anastomosis (along the lateral border of the scapula) between the suprascapular and circumflex scapular arteries. (G 2.43C;N 414;Gl 28.3)
Important Relationship
- The supraspinatus muscle (tendon) passes superior to the head of the humerus (glenohumeral joint).
- The suprascapular artery passes directly superior to the transverse scapular ligament.
- The suprascapular nerve passes directly inferior to the transverse scapular ligament.
- The suprascapular artery and nerve pass directly lateral to the spine of the scapula (spinoglenoid notch).