Identify the internal surface features and muscles associated with the nasal pharynx, oral pharynx and palate.
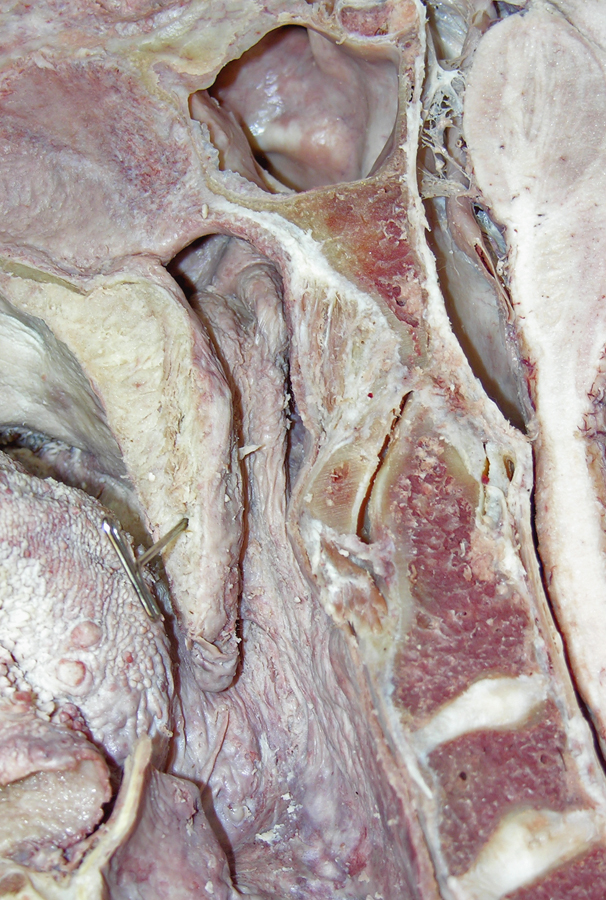
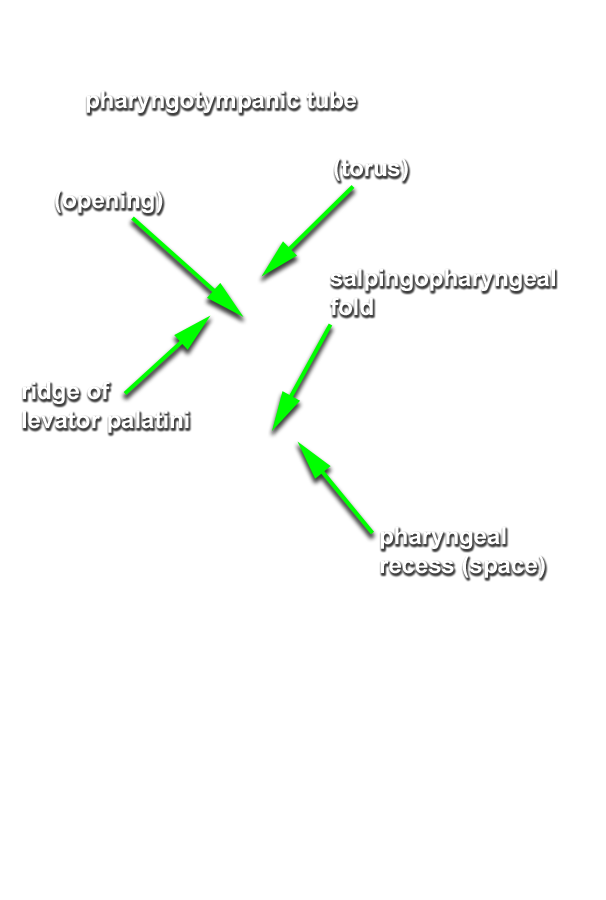
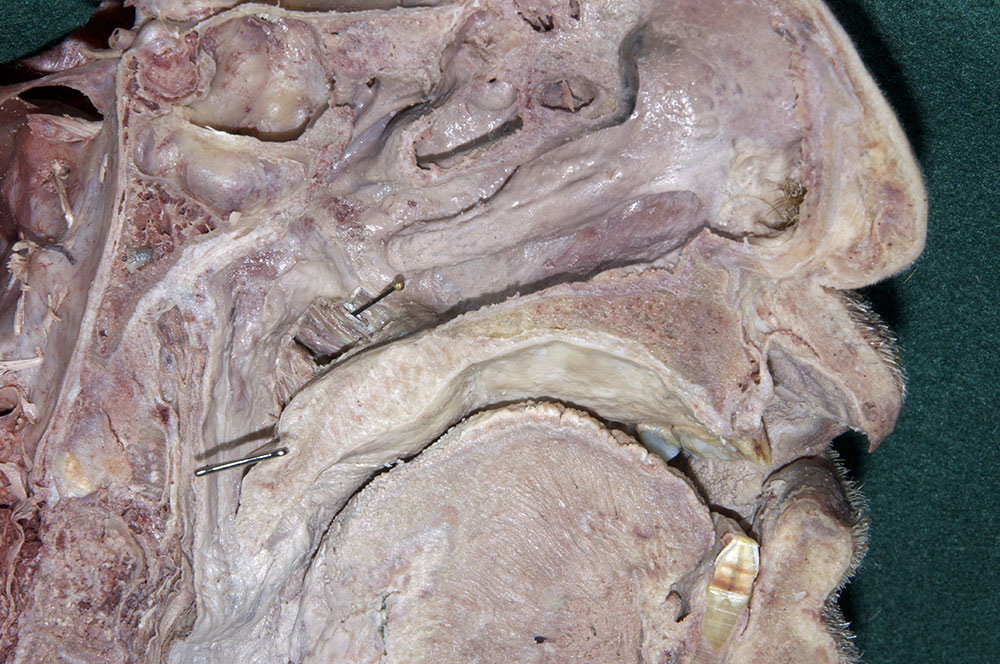
- (ON BOTH SIDES) Identify the opening and torus of the pharyngotympanic tube, ridge of the levator veli palatini, salpingopharyngeal fold and pharyngeal recess. (G 8.27A;N 64;Gl 38.28)
-
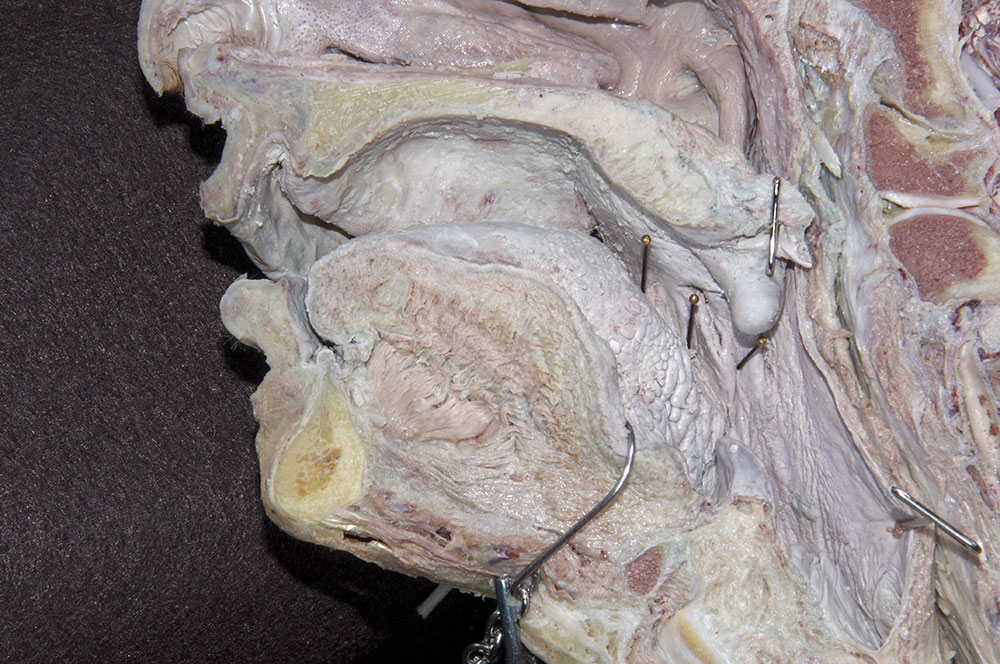
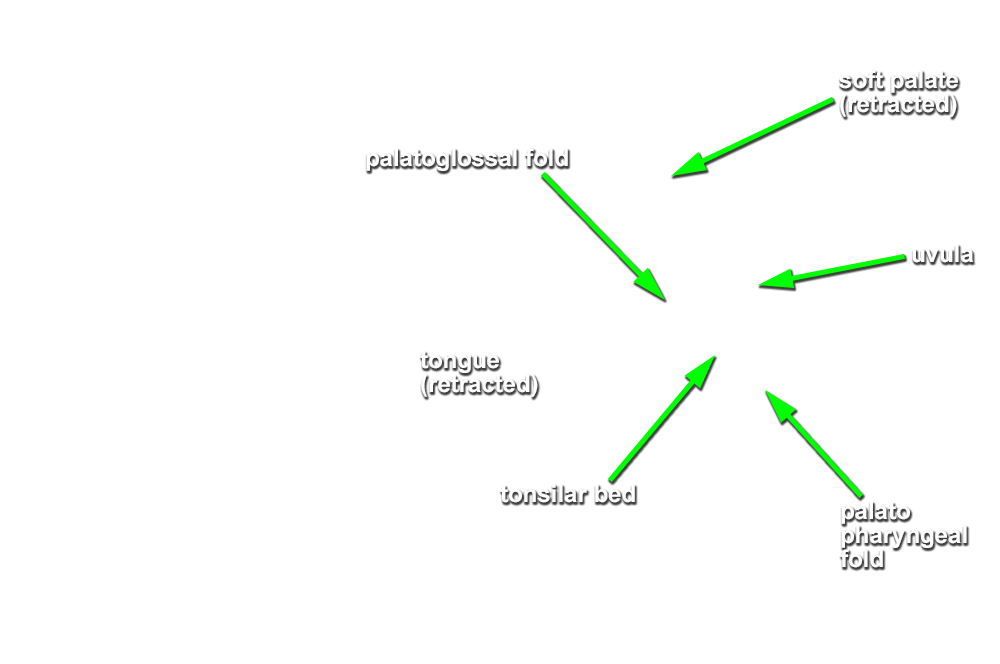
(ON BOTH SIDES) Identify the
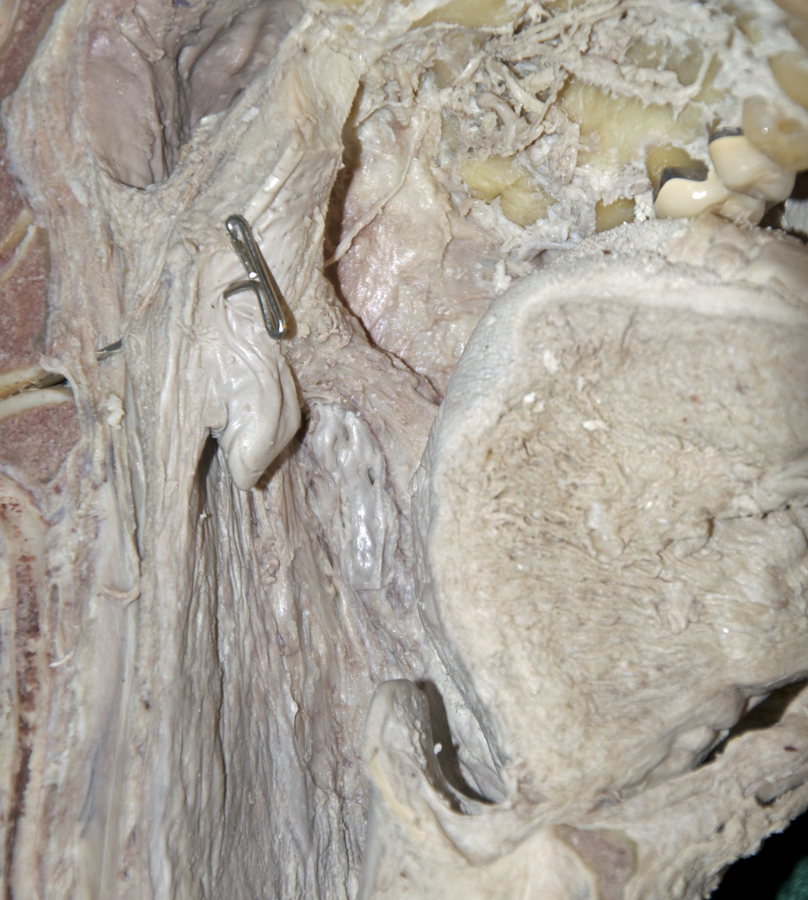
oropharyngeal isthmus,
hard palate,
soft palate (in cross section but not identified) and
uvula,
palatoglossal arch (fold),
tonsilar bed (fossa) and
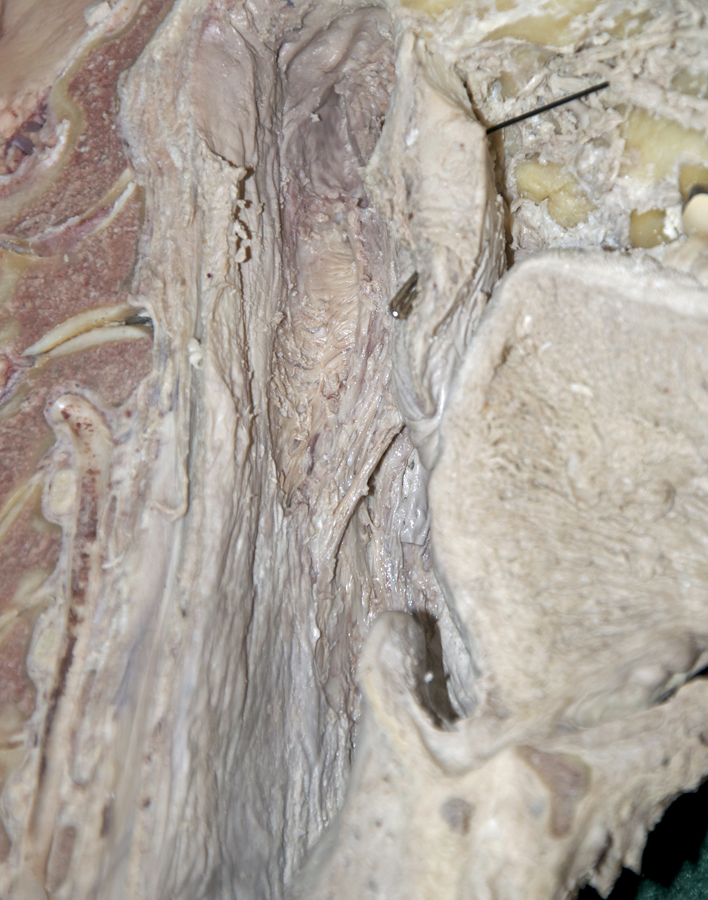
palatopharyngeal arch (fold). (G 8.27A;N 64;Gl 38.28)
Important Relationship
- The tonsilar bed is positioned anterior to the palatopharyngeal arch and posterior to the palatoglossal arch.
-
(ON THE SIDE WITHOUT THE NASAL SEPTUM) Carefully strip the mucosa from the ridge of the levator veli palatini and identify the
levator veli palatini muscle. (G 8.27B;N 65;Gl 38.31B) Use small scissors to blunt dissect slightly anterior and lateral to the levator palatini and expose and identify the
tensor veli palatini muscle. The superior constrictor passes between the tensor veli palatini and the levator veli palatini muscles. Attempt to trace the tendon of the tensor veli palatini to the hamulus of the medial pterygoid plate
.
Important Relationship
- The tensor veli palatini muscle is positioned anterior-lateral to the levator veli palatini muscle.
- The tensor veli palatini muscle (tendon) passes inferior to the sphenoid bone (hamulus of the medial pterygoid plate).
-
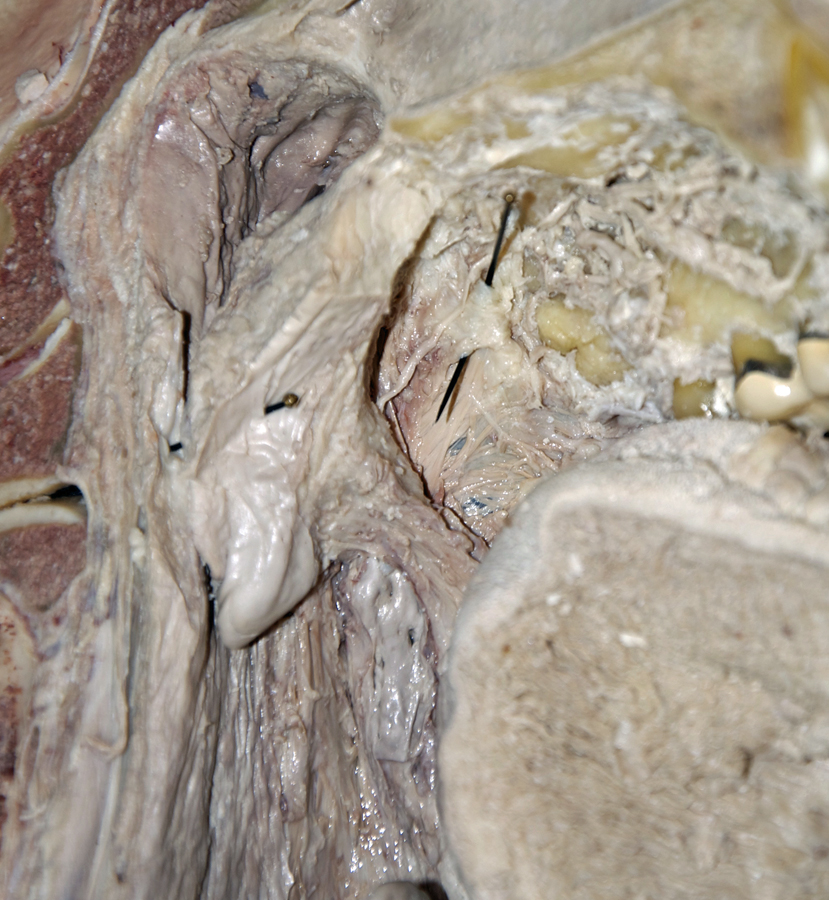
(ON THE LEFT SIDE ONLY) Carefully strip the mucosa from the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal folds and identify the
palatoglossal and
palatopharyngeal muscles. (G 8.27B;N 64;Gl 38.28)
Important Relationship
- The palatoglossal fold (muscle) is positioned directly anterior to the tonsilar bed.
- The palatopharyngeal fold (muscle) is positioned directly posterior to the tonsilar fold.
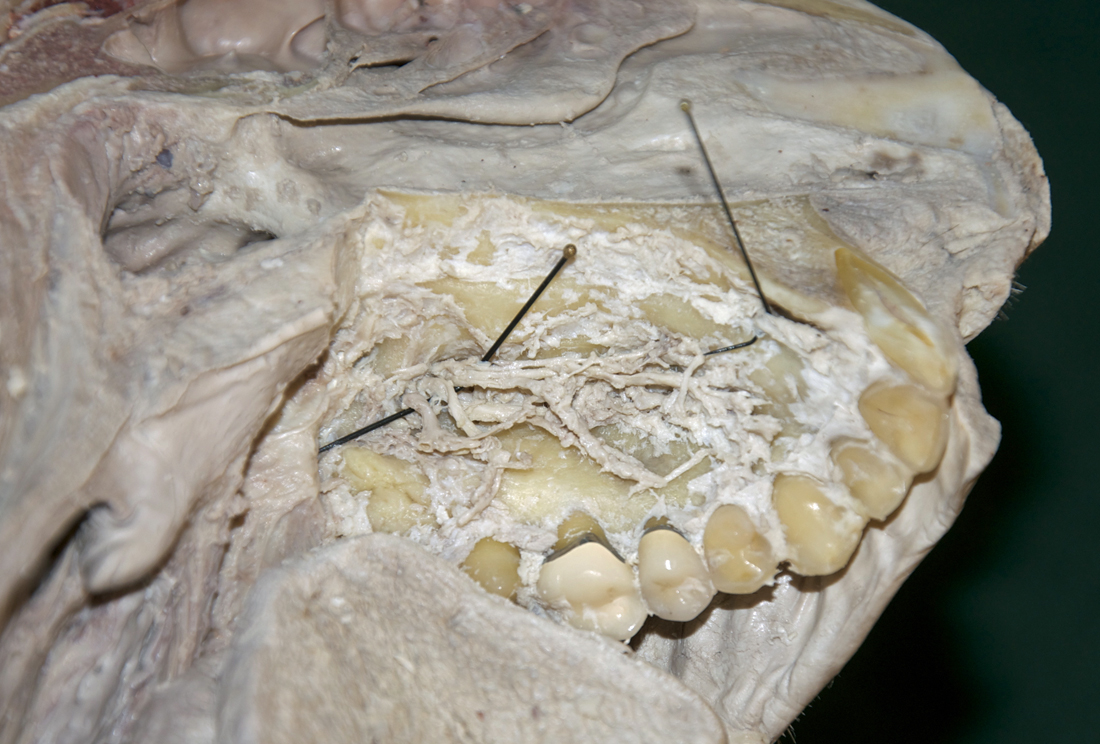
- (ON THE SIDE WITHOUT THE NASAL SEPTUM) Carefully strip the mucosa (from medial to lateral) from the hard palate and identify the greater palatine artery and nerve. (G 7.52D;N 52;Gl 38.18) The nerve and artery typically emerge from the greater palatine foramen adjacent to the third molar or the posterior border of the second molar. If you like challenges, then trace the greater palatine artery to the incisive fossa where it contributes to the blood supply of the anterior aspect of the nasal cavity.