Identify and clean the nerves and arteries associated with the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.
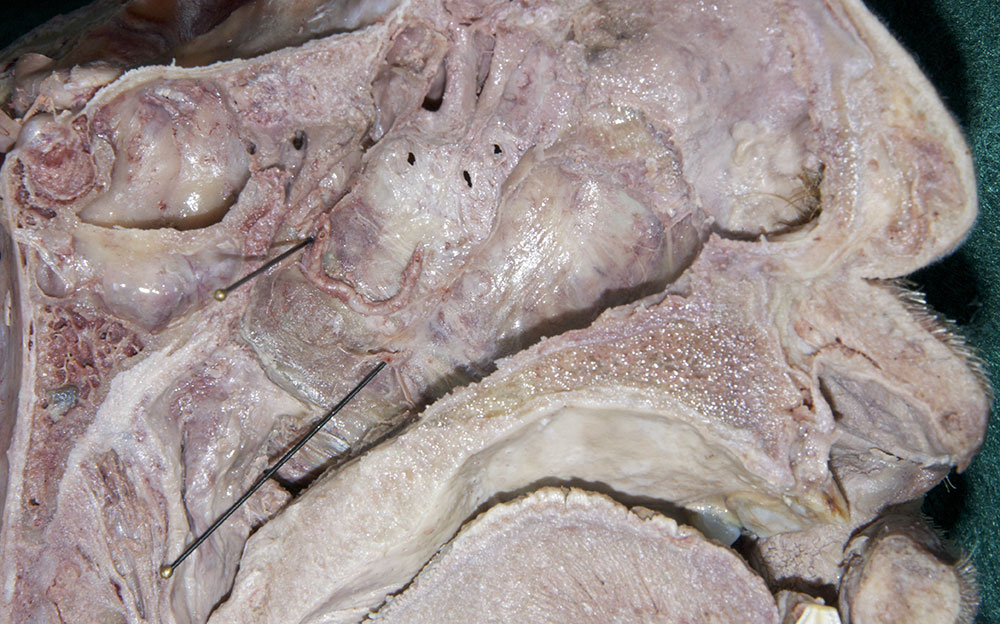
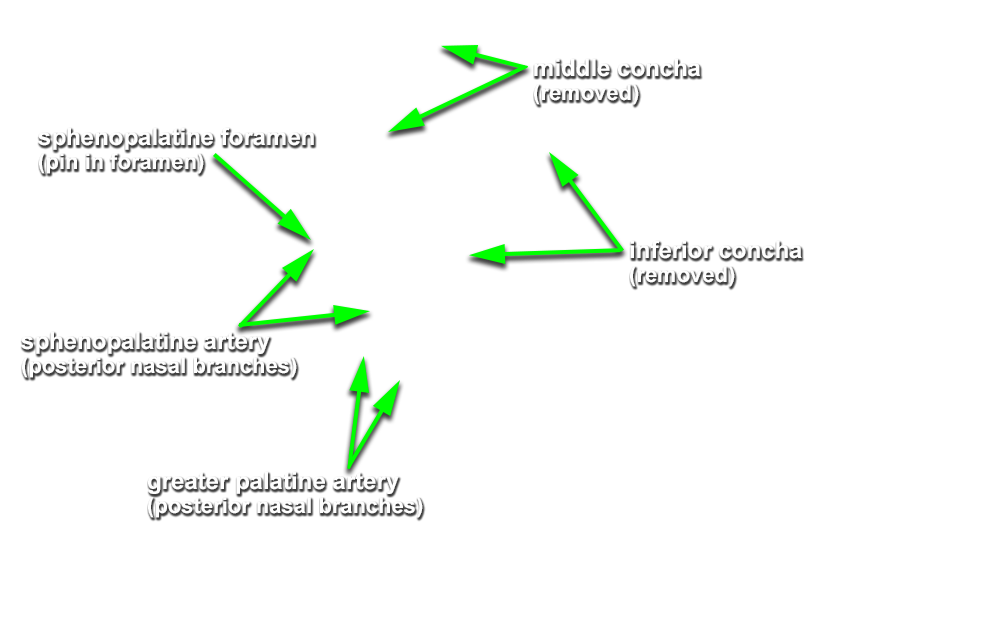
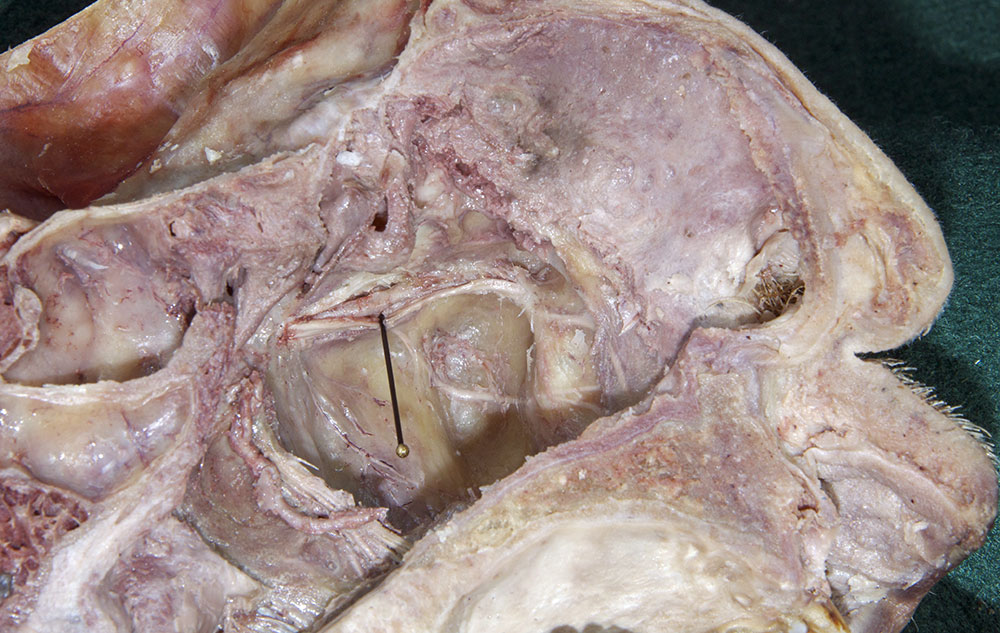
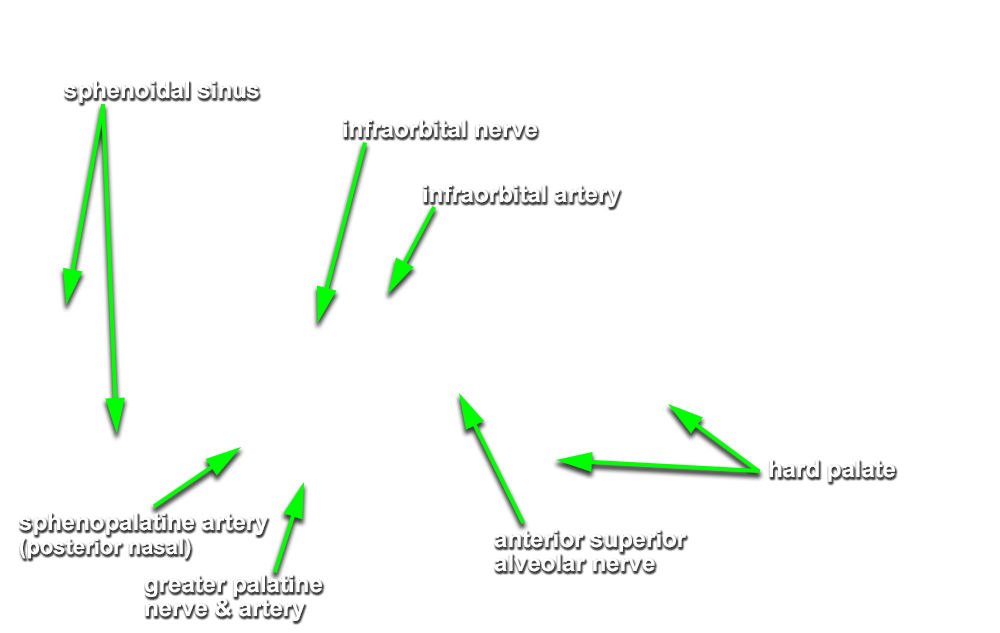
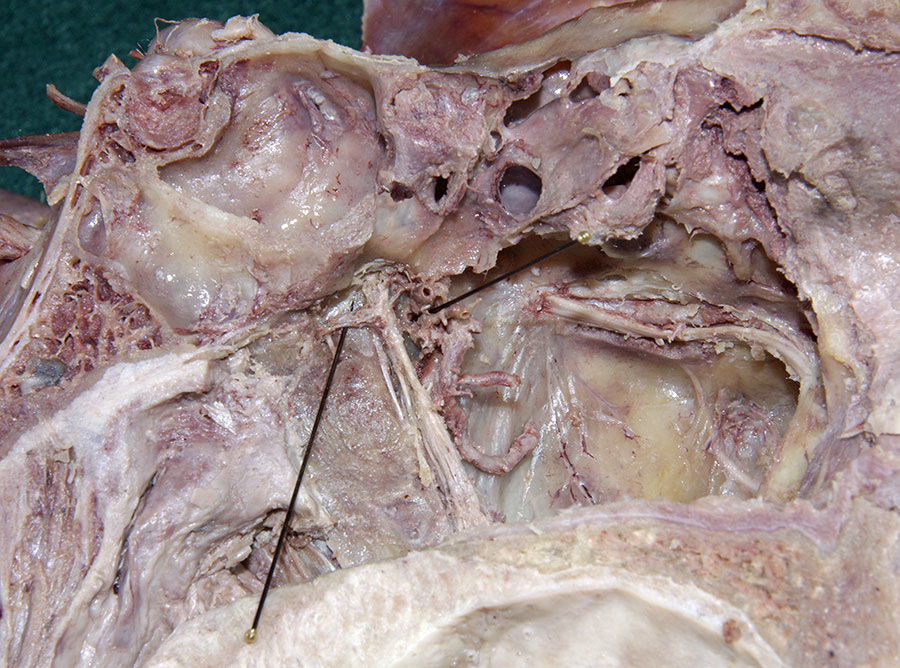
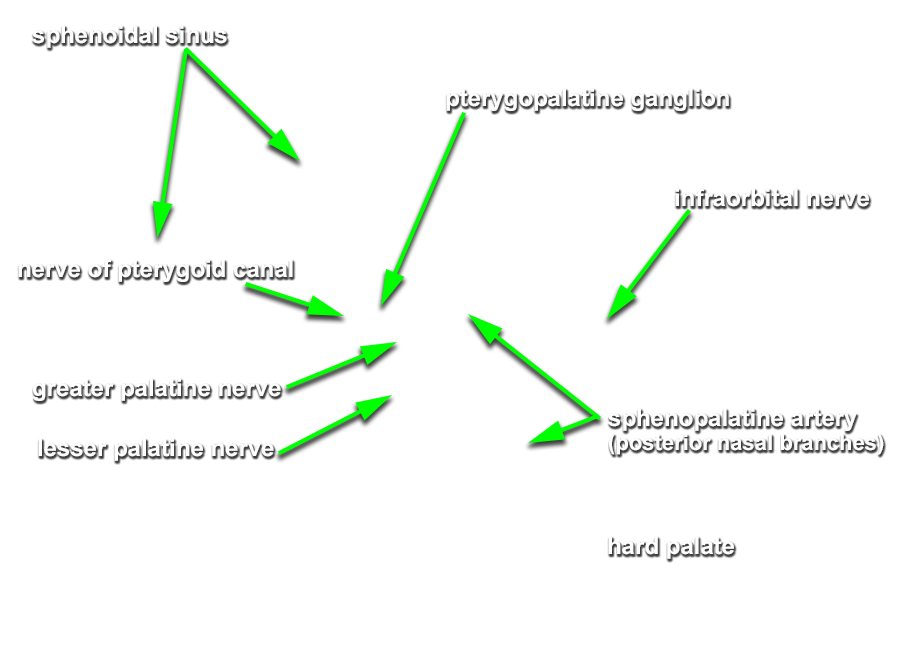
- (ON THE SIDE WITHOUT THE NASAL SEPTUM) Carefully strip the nasal mucosa in the posterior direction, toward the sphenoidal sinus. Identify the nasal branches of the sphenopalatine artery as they traverse the sphenopalatine foramen. (G 7.60A;N 40;Gl 36.7B) Remove the mucosa but leave the sphenopalatine artery and its posterior nasal branches.
- (ON THE SIDE WITHOUT THE NASAL SEPTUM) Carefully open the greater palatine canal by chipping away the bone inferior to the sphenopalatine foramen. Identify the greater palatine artery and nerve. (G 7.52C;N 42;Gl 36.8B)
-
(ON THE SIDE WITHOUT THE NASAL SEPTUM) Strip the mucosa from the roof and lateral wall of the maxillary sinus. Identify the ridge of bone surrounding the infraorbital artery and nerve. (G 7.64A;N 44) Chip away this thin bone to expose and identify the
infraorbital artery and
nerve. (G 7.67;Gl 38.17)) Attempt to identify the
anterior superior alveolar and
middle superior alveolar nerves in the wall of the maxillary sinus.
Important Relationship
- The infraorbital artery and nerve pass directly superior to the maxillary sinus.
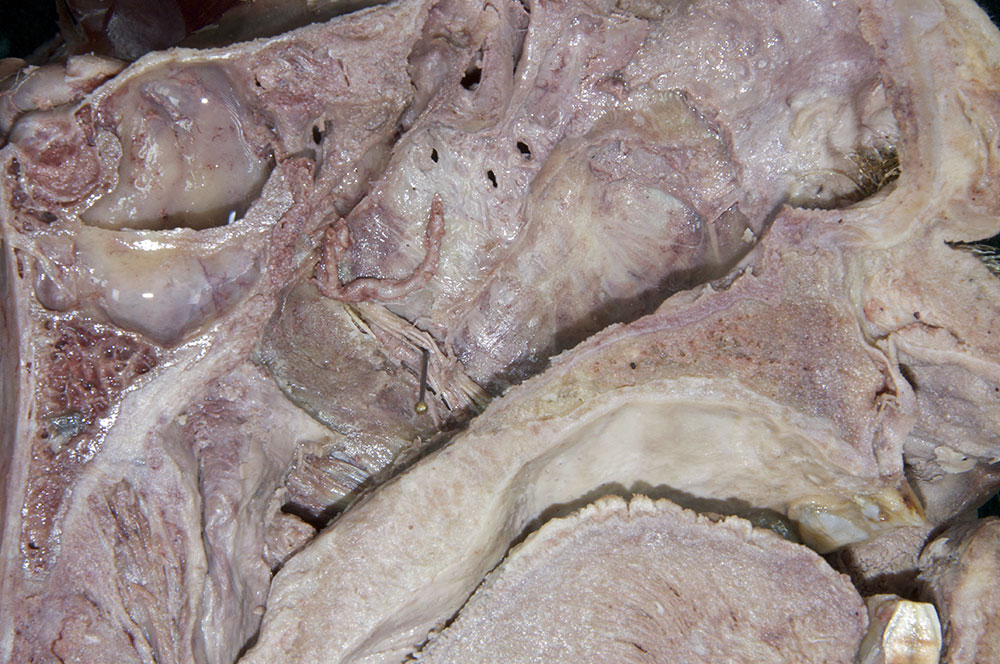
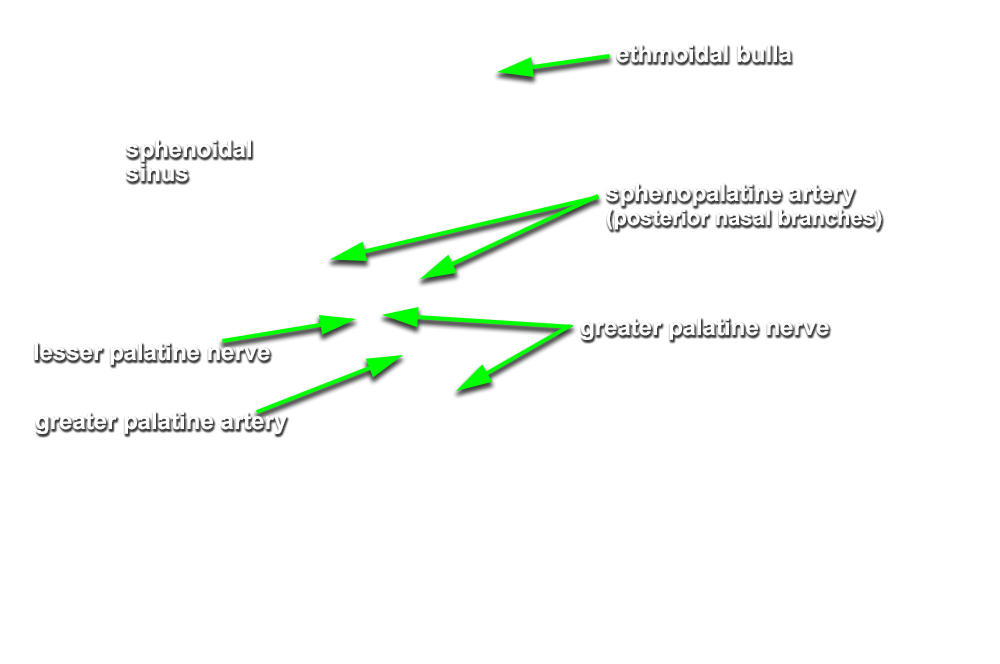
- (ON THE SIDE WITHOUT THE NASAL SEPTUM) Carefully chip away the bone bordering the posterior aspect of the sphenopalatine foramen. Trace the greater palatine nerve in the superior direction until you reach a swelling immediately posterior to where the nasal branches of the sphenopalatine artery emerge through the foramen. The swelling is the pterygopalatine ganglion. (G 7.52C;N 42;Gl 36.8B) Attempt to identify the nerve of the pterygoid canal. The nerve of the pterygoid canal is often surrounded by a ridge of bone in the floor of the sphenoidal sinus.