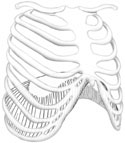
Figure 2-2
Basic structure and position of the diaphragm.
Basic structure and position of the diaphragm.
The bone and muscle combination making up the wall of the thoracic cage is very strong. It is able to withstand the negative pressures of respiration while protecting the vital organs it contains.