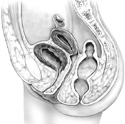
The female pelvis bisected.
On the bisected specimen begin again with the most anterior organ in the pelvic cavity, the urinary bladder, located just posterior to the pubic symphysis.
Follow the ureters superiorly out the lateral urinary bladder wall and note how they cross the external iliac veins.
Follow the urethra out of the bladder to the external urethral opening. (Figure 4-8)
Posterior to the urethra locate the vagina and the vaginal orifice. Follow the vagina superiorly to its attachment to the sides of the uterus. Note how the uterus projects into the vaginal canal thus creating so called vaginal fornices.
Now find the uterus. Identify the body of the uterus and the cervix of the uterus. Note how the cervix protrudes into the vaginal canal, and the body of the uterus is flexed 90 degrees forward in an anteverted position.
Again locate the uterine tube as it runs laterally away from the uterus, ending in the fimbriae.
Find the ovary in a shallow depression bounded by the ureter, external iliac vein and the uterine tube. Posterior to the uterus and vagina, locate the rectum.
Once again find the common iliac artery splitting into an internal and external iliac artery. Realize the internal iliac artery supplies the pelvic viscera and the gluteal region. Also locate the internal and external iliac veins, the common iliac veins and the inferior vena cava.