Use the two halves of the head (and brain) to identify surface features of the brainstem, the cranial nerves and the remaining arteries associated with the brain (refer to the Ventral Brain interactive photograph).
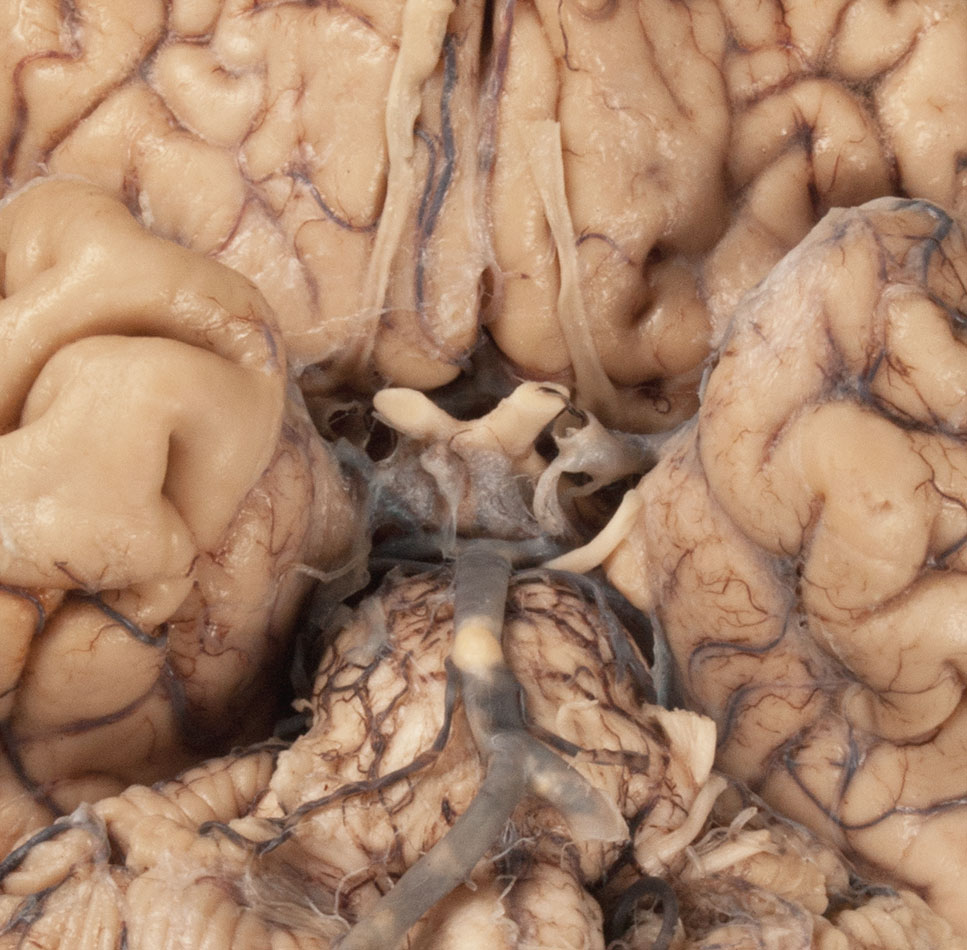
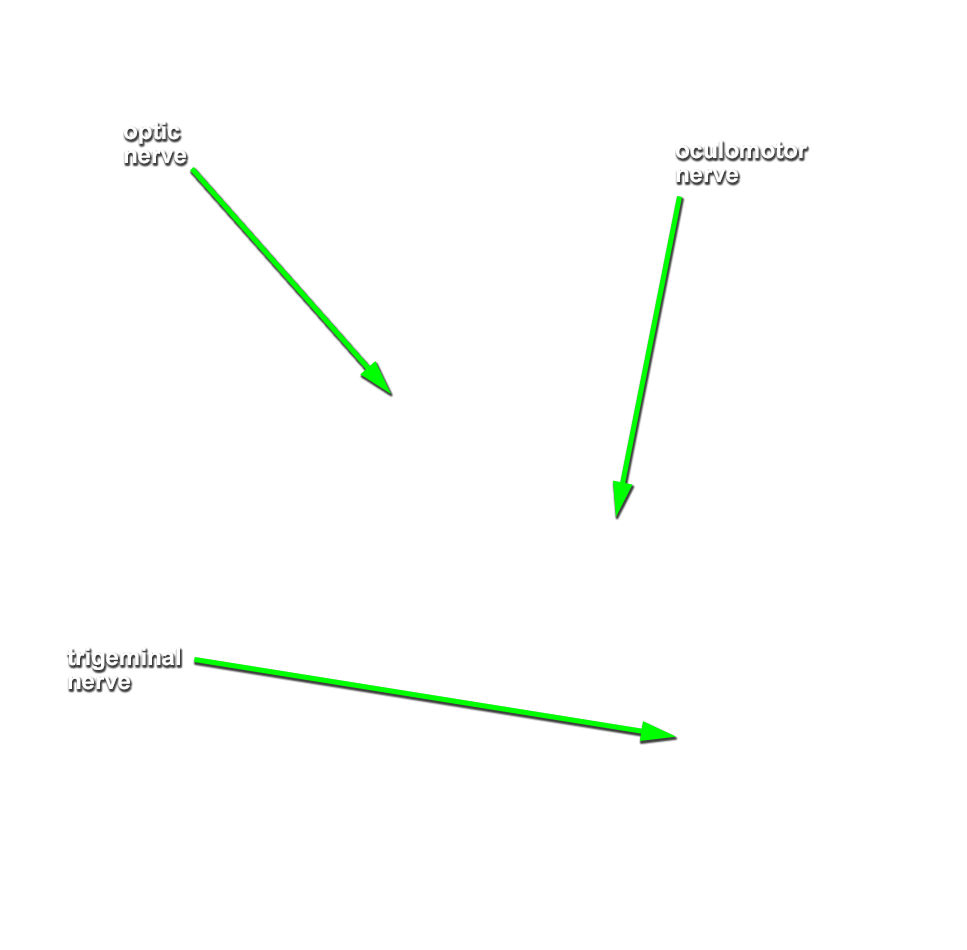
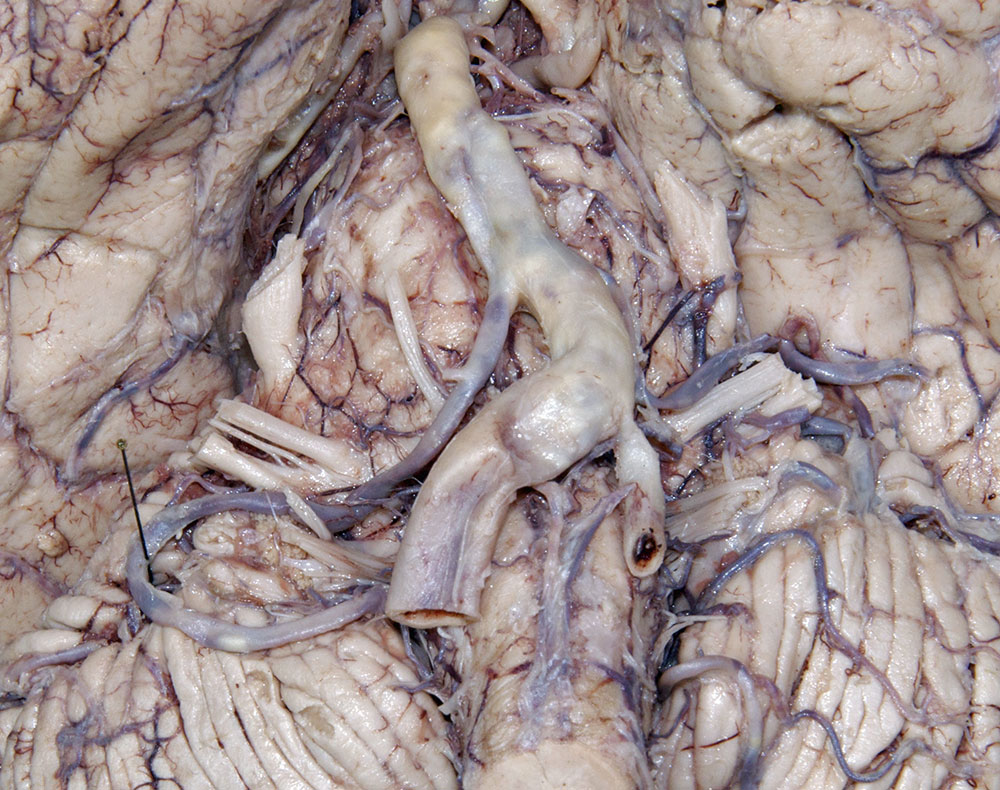
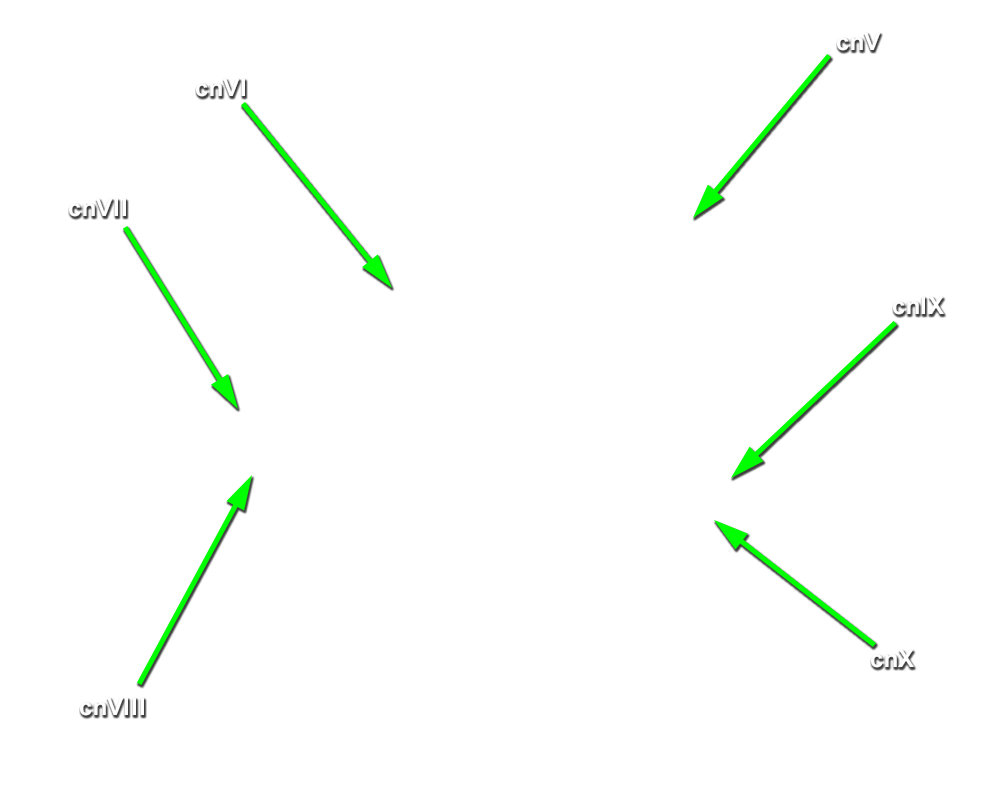
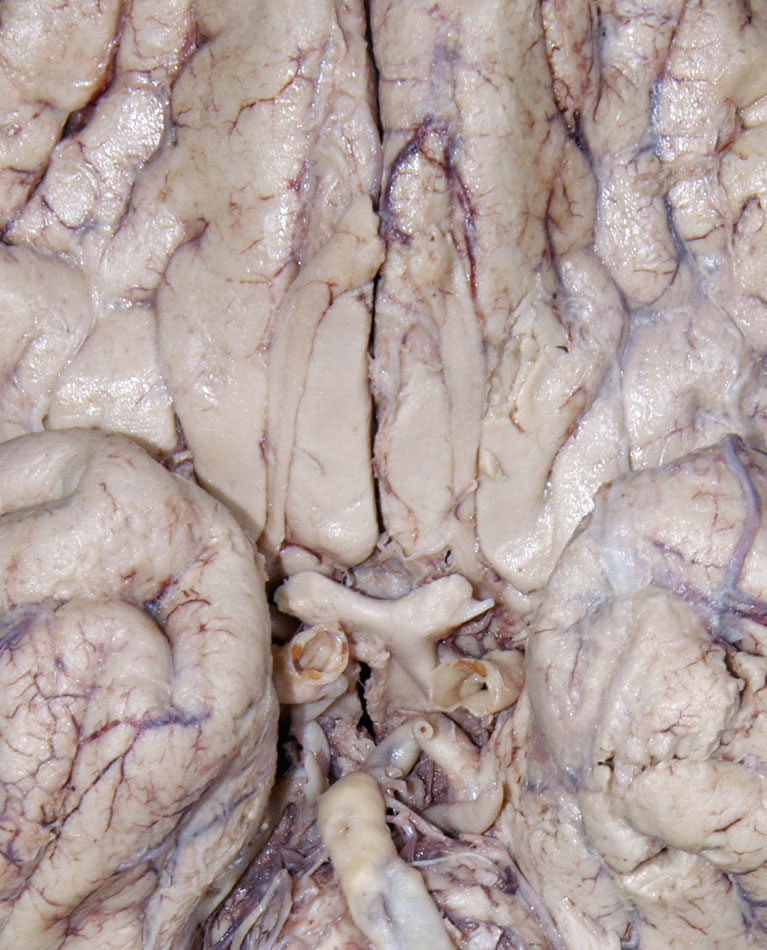
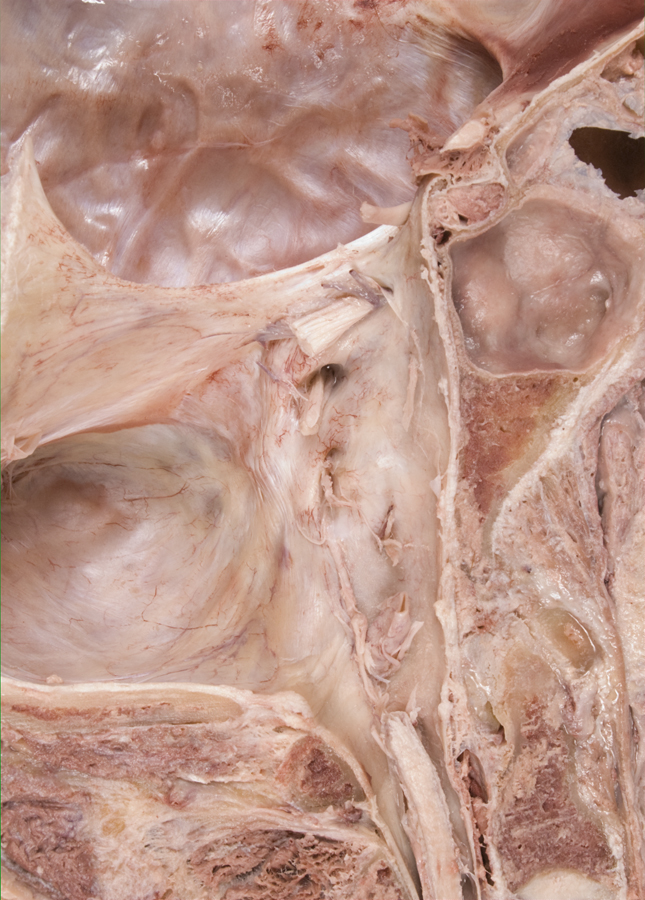
- Identify the cerebral peduncle, medullary olive, pyramid, and optic, oculomotor, trigeminal, abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory and hypoglossal nerves. (G 7.32;N 115;Gl 47.16) Attempt to identfy the olfactory bulb and tract, and the trochlear nerve.
- (ON THE SIDE WITHOUT THE BRAIN) Identify the optic, oculomotor, trigeminal, abducens, facial (the smaller, more anterior of the two nerves entering the internal auditory meatus), vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal (the most superior of the nerve rootlets entering the jugular foramen), vagus, accessory and hypoglossal nerves in the cranial cavity. (G 7.26;N 105;Gl 37.10)
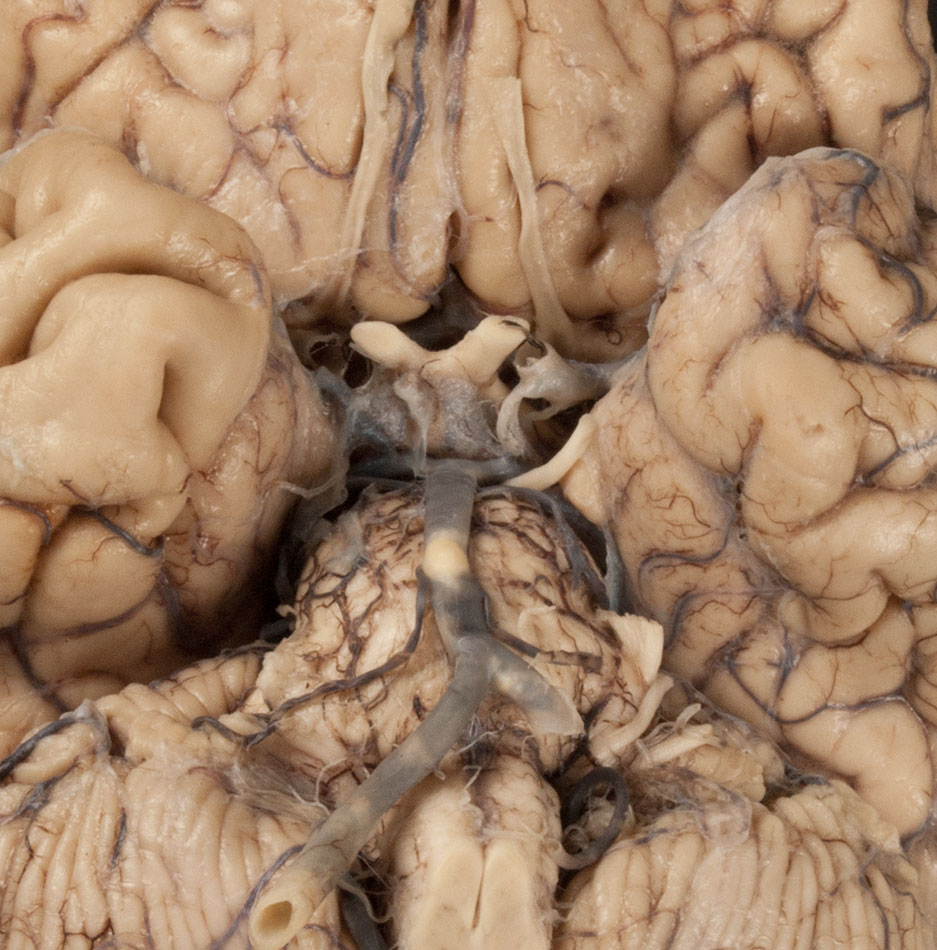
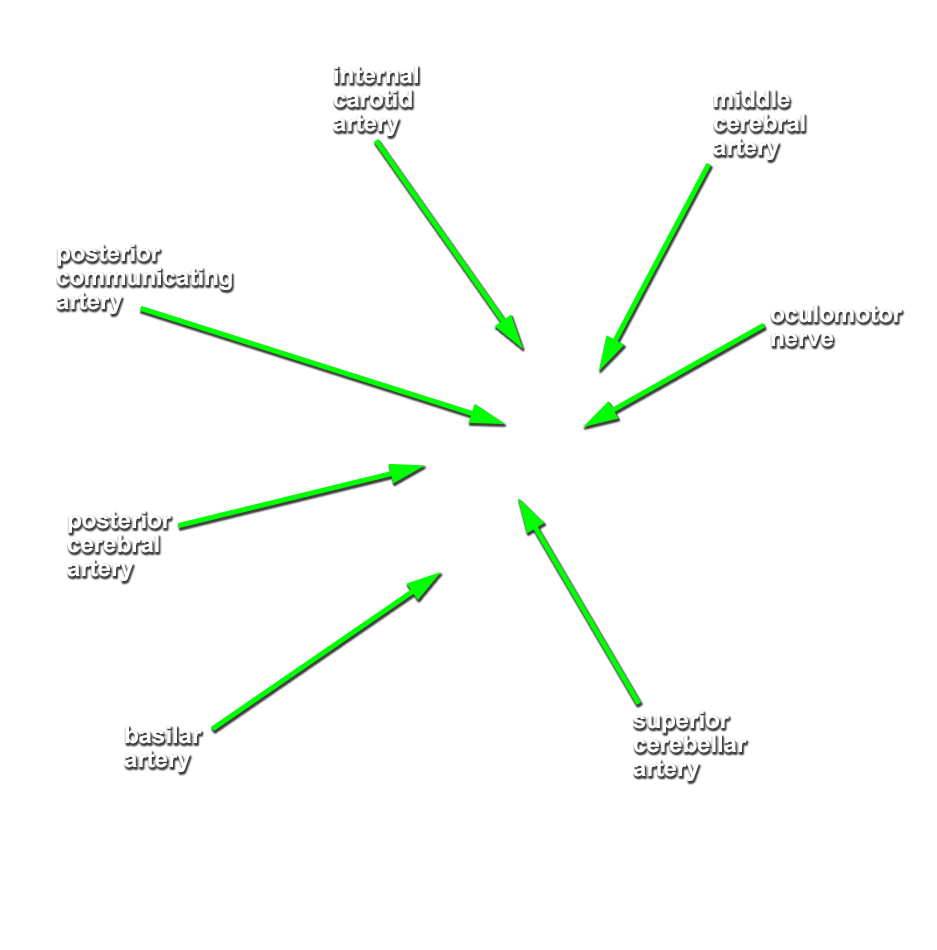
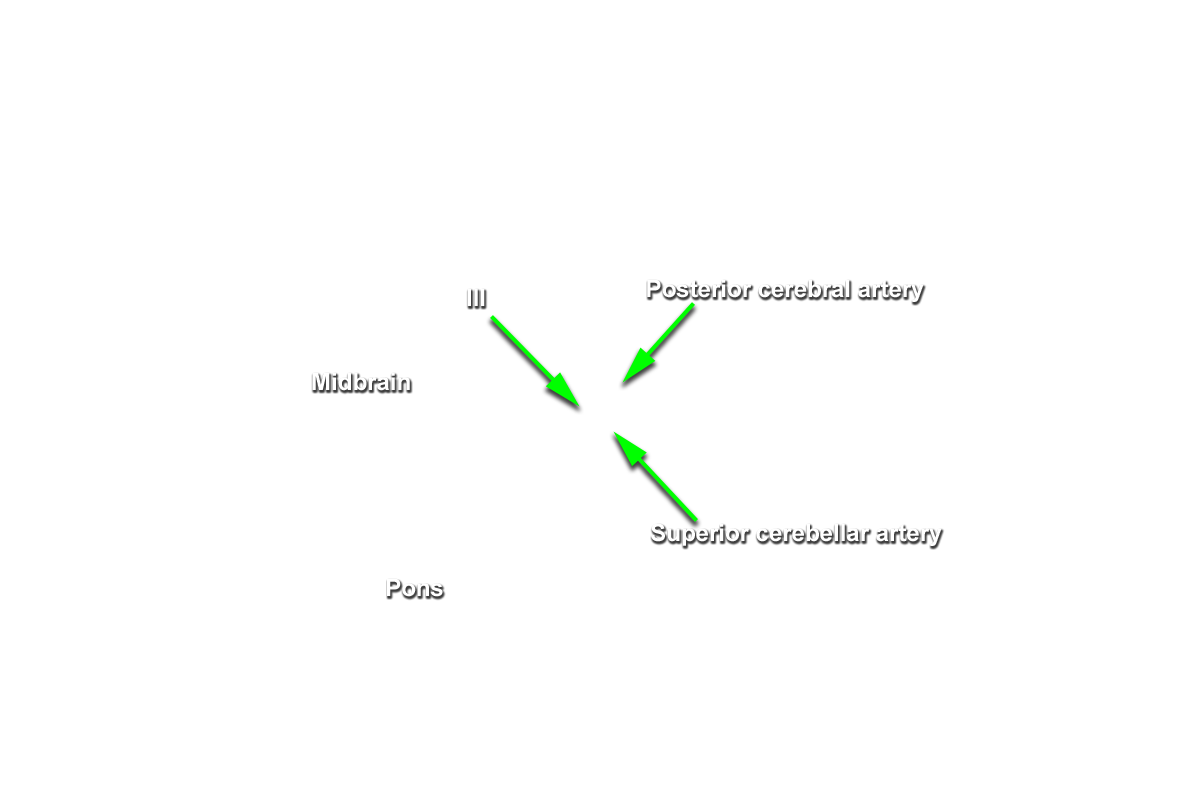
- The oculomotor nerve passes medial to the cerebral peduncle of the midbrain.
- The oculomotor nerve passes directly inferior to the posterior cerebral artery and directly superior to the superior cerebellar artery.
- The glossopharyngeal nerve passes directly lateral to the medullary olive.
- The hypoglossal nerve passes directly lateral to the medullary pyramid.
- The vagus nerve passes directly lateral to the medullary olive.
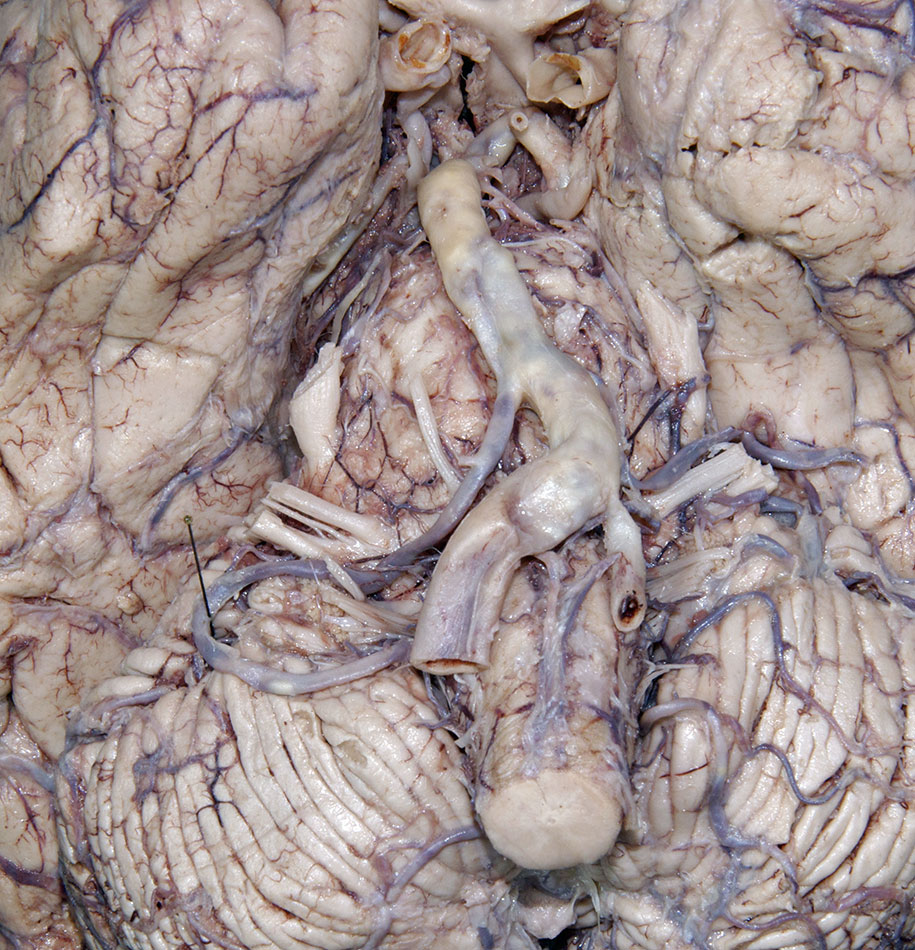
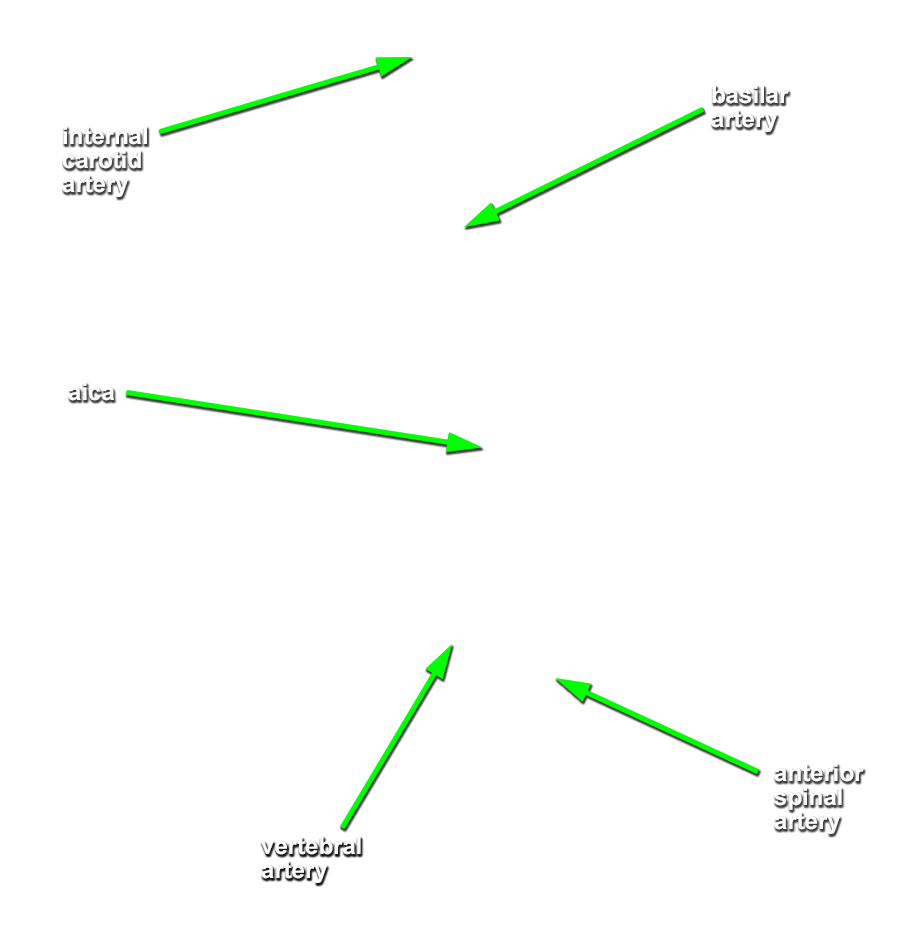
- Identify the
vertebral,
basilar and
posterior cerebral arteries. (G 7.32;N 140;Gl 48.6) Attempt to identify the
posterior communicating,
superior cerebellar, anterior inferior cerebellar (AICA) and
posterior inferior cerebellar (PICA) arteries.
Important Relationship
- The basilar artery is positioned ventral to the pons.
Important Relationship