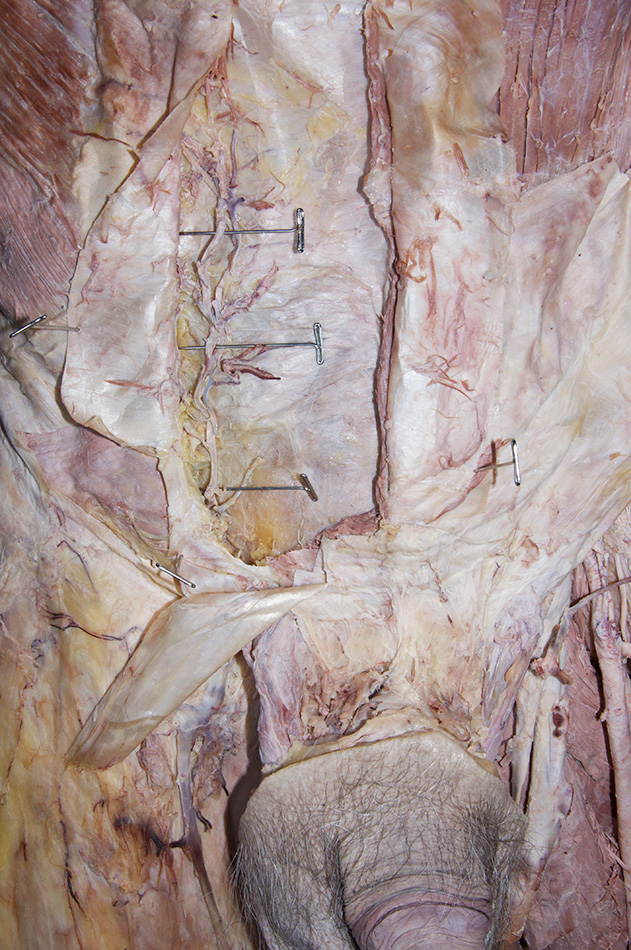
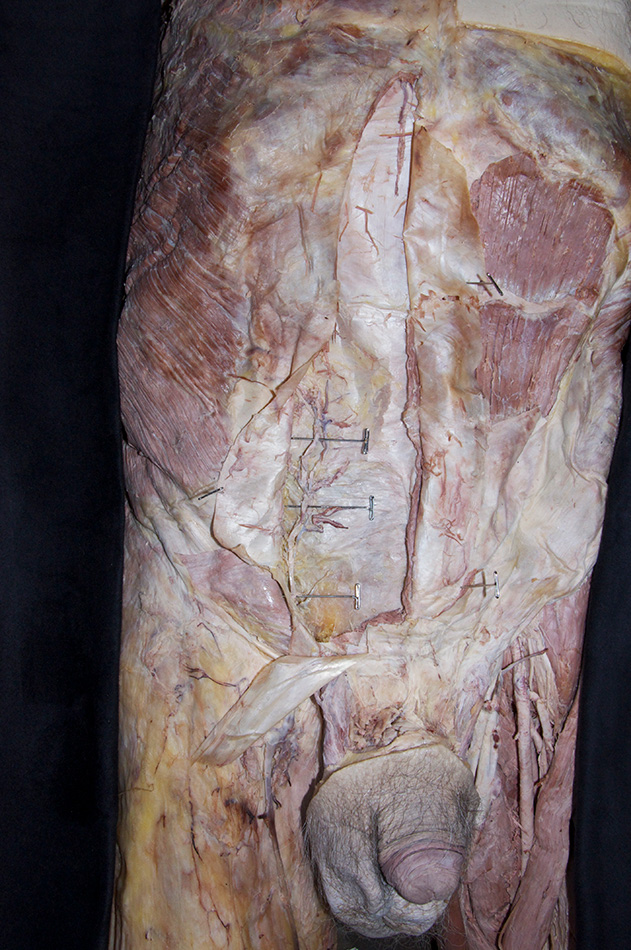
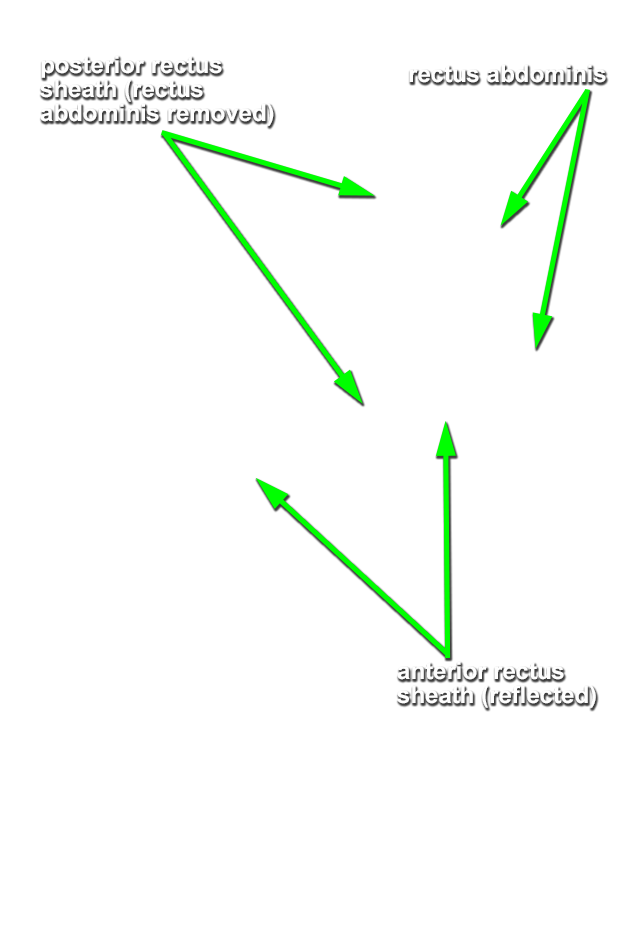
Identify and reflect the rectus sheath and remove the rectus abdominis muscle on the right side of the cadaver.
- Use scissors to make a longitudinal incision in the rectus sheath from the costal margin to a point 5 cm superior to the pubic symphysis. Use a scalpel and blunt dissection to remove the rectus sheath anterior to the rectus abdominis muscle.
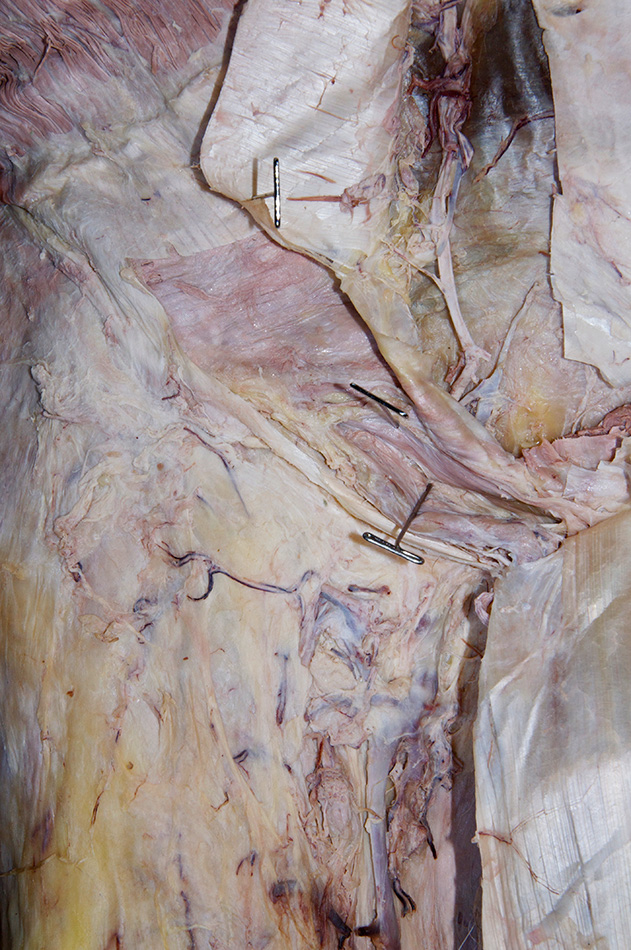
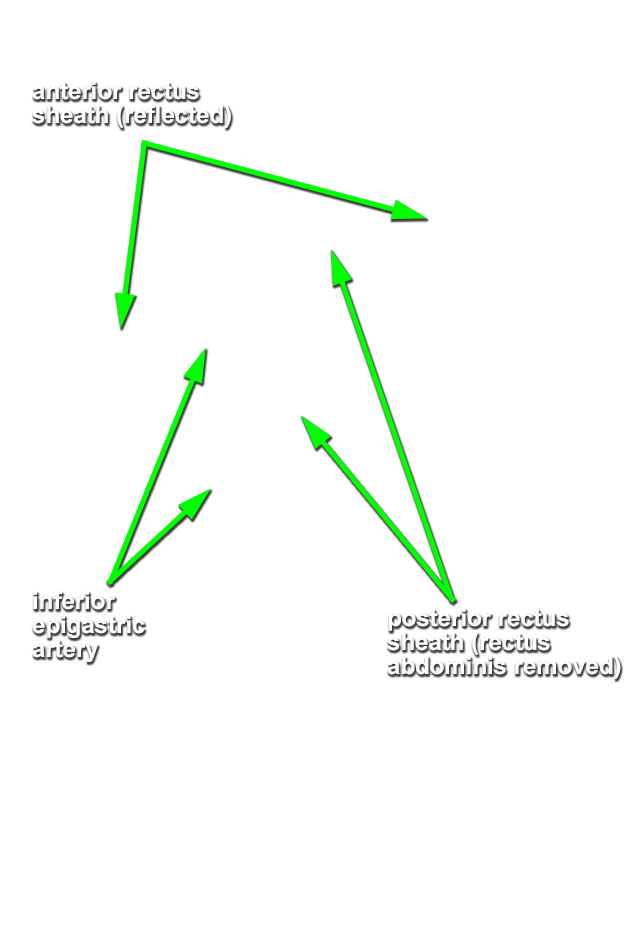
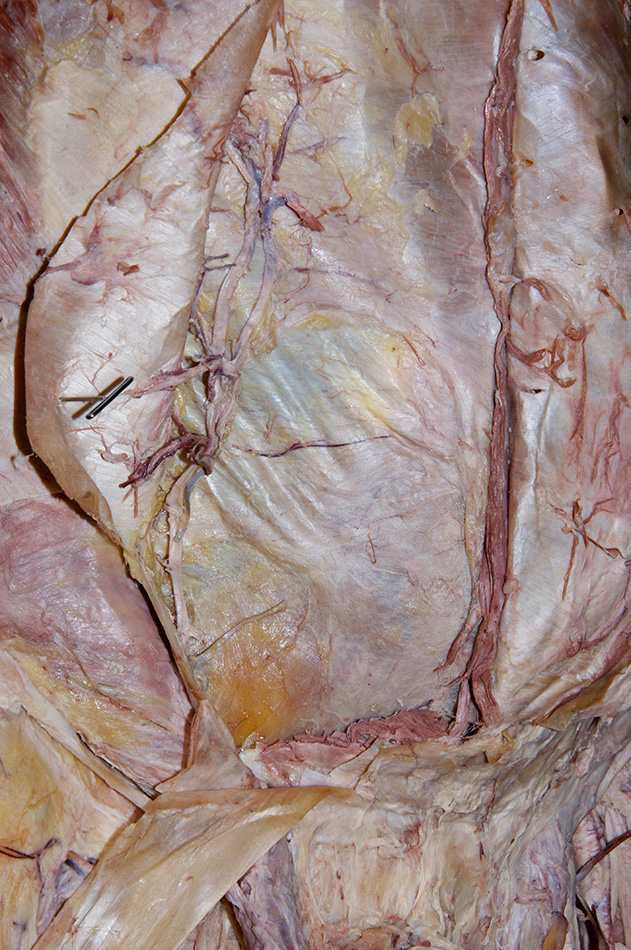
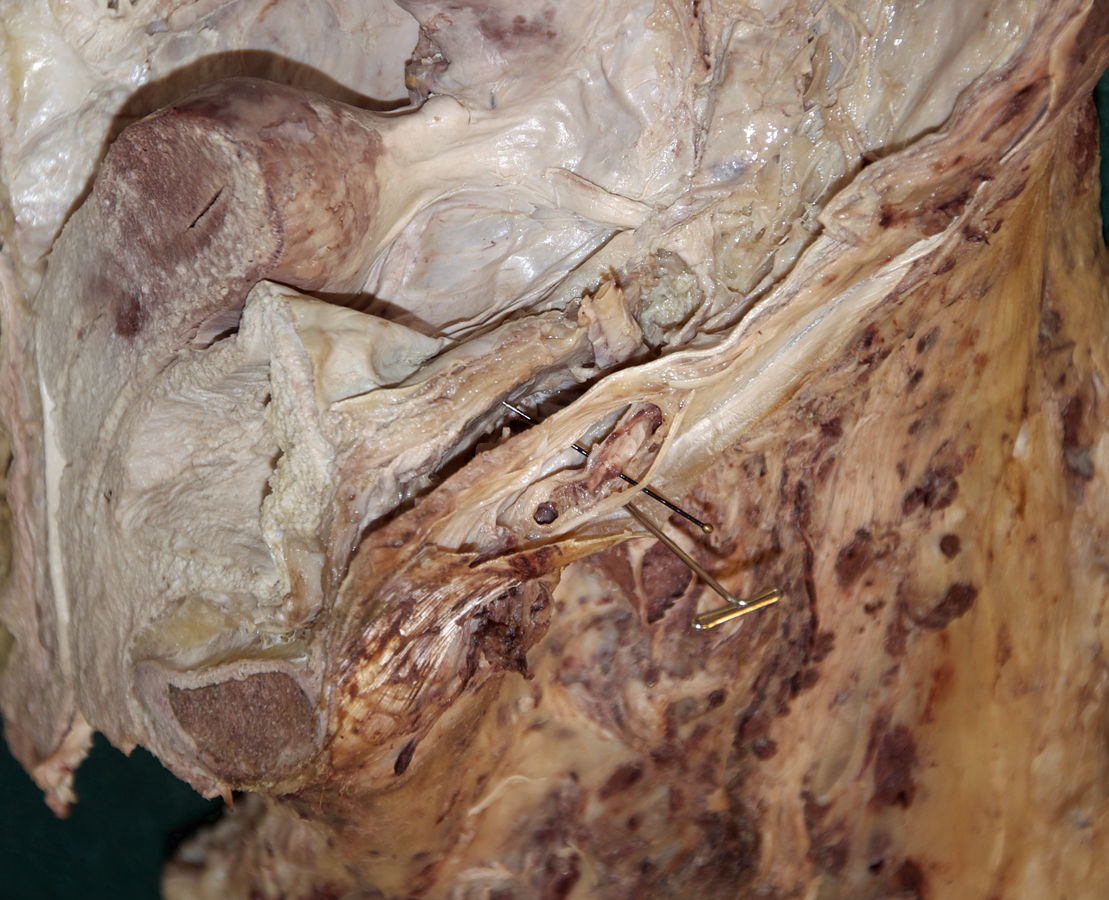
- Remove the rectus abdominis muscle while protecting the inferior epigastric vessels (deep to the rectus abdominis muscle).
- Identify and clean the inferior epigastric artery. Trace the artery as far as possible in the superior direction.
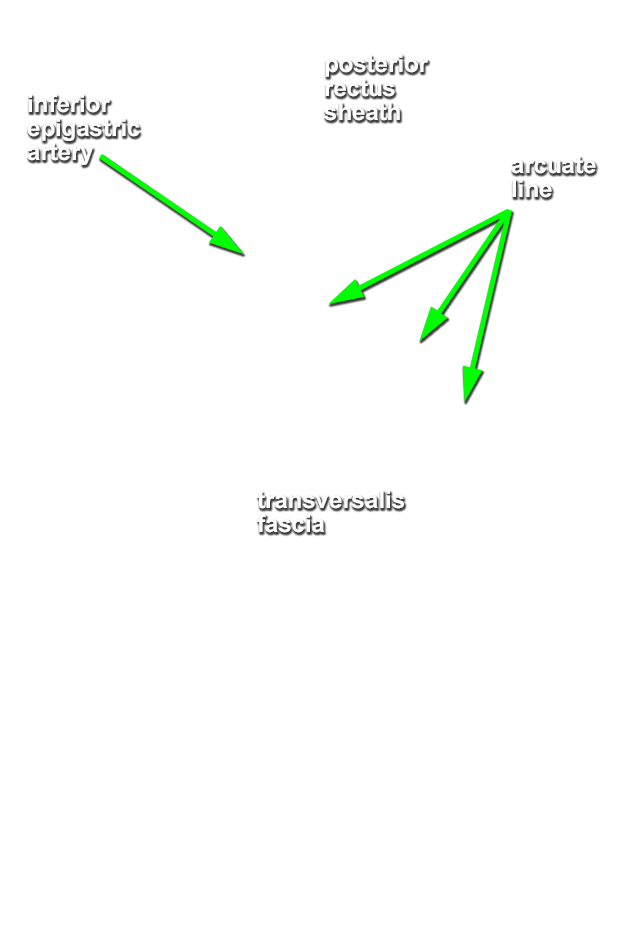
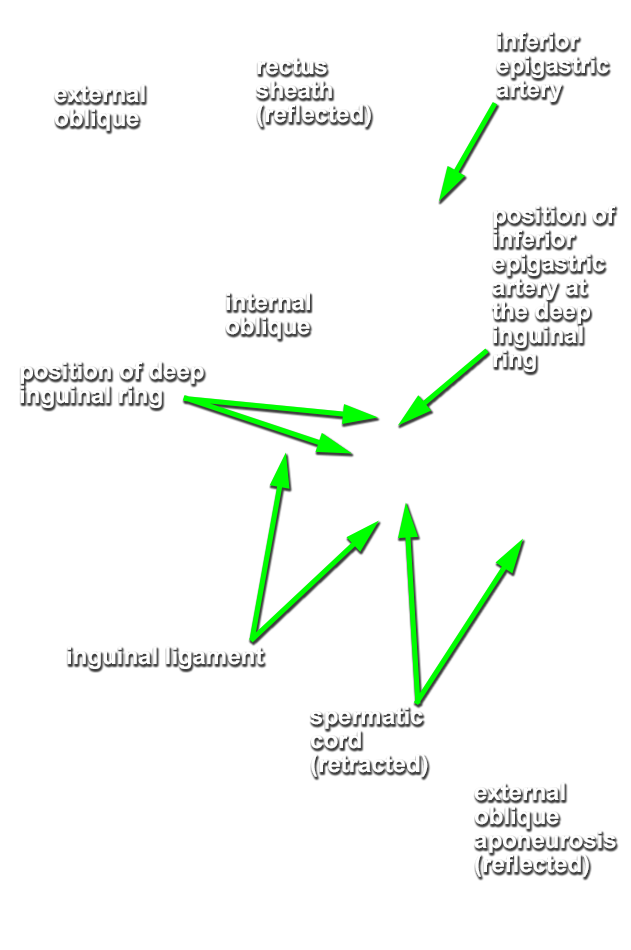
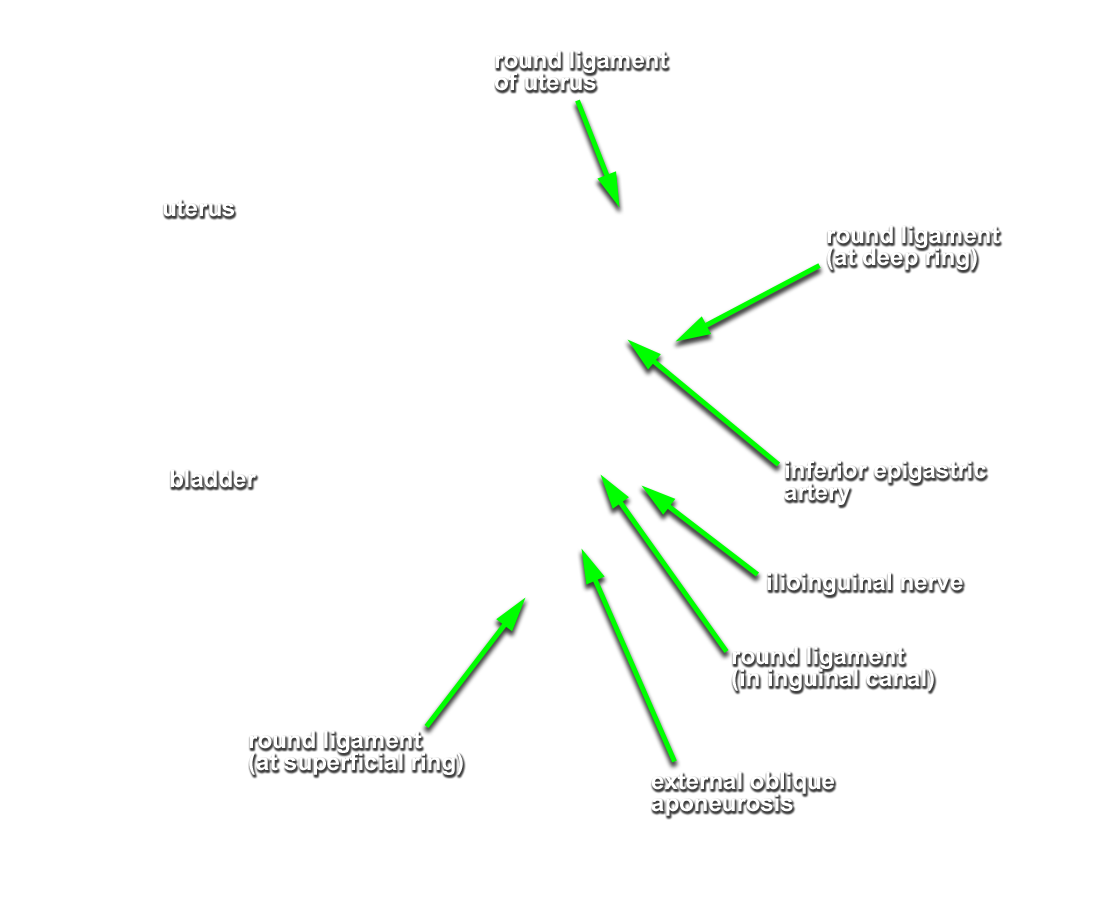
- Identify the posterior aspect of the rectus sheath, arcuate line and transversalis fascia. (G 4.8B;N 251;Gl 13.10D) Carefully retract the spermatic cord (laterally). The deep inguinal ring is directly lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels adjacent to the origin of the spermatic cord from the anterior abdominal wall. (G 4.13;N 256;Gl 13.18) In female cadavers, trace the round ligament of the uterus from the deep ring to the superficial ring.